Planetary Motion
... Rotation – the spinning of an object around it’s axis. Axis runs North to South. ...
... Rotation – the spinning of an object around it’s axis. Axis runs North to South. ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing surface temperature on ...
... Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing surface temperature on ...
157a_midterm_2016
... details. Plot the relative intensity that we would observe as a function of time (i.e. as a function of the planet position in its orbit) at a wavelength of 16 microns. Can we detect the presence of the planet? Ignore the star light reflected from the planet. Hint: The total intensity is the sum of ...
... details. Plot the relative intensity that we would observe as a function of time (i.e. as a function of the planet position in its orbit) at a wavelength of 16 microns. Can we detect the presence of the planet? Ignore the star light reflected from the planet. Hint: The total intensity is the sum of ...
Stars - Red, Blue, Old, New pt.4
... patterns of stars have depended strongly on mass, and the same goes for the final stages of evolution. • Stars do lose mass as they go from the main sequence through other stages. • Recall that the low mass stars are by far the most common. ...
... patterns of stars have depended strongly on mass, and the same goes for the final stages of evolution. • Stars do lose mass as they go from the main sequence through other stages. • Recall that the low mass stars are by far the most common. ...
A Summary of Stages
... experience similar evolutionary tracks on the H-R Diagram, but end up at different points on the ZAMS; recall that mass => gravity => squeezing => core T => fusion E => luminosity.] Although lowmass stars seem to vastly outnumber their high-mass relatives, a star with too small a mass (<.08 suns) wi ...
... experience similar evolutionary tracks on the H-R Diagram, but end up at different points on the ZAMS; recall that mass => gravity => squeezing => core T => fusion E => luminosity.] Although lowmass stars seem to vastly outnumber their high-mass relatives, a star with too small a mass (<.08 suns) wi ...
Sun, Moon and Stars - Mona Shores Public Schools
... The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. Each time the Earth rotates we have one day and one night. When we are on the sun side of the earth, we have daylight. When we rotate away from the sun, we have night. ...
... The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. Each time the Earth rotates we have one day and one night. When we are on the sun side of the earth, we have daylight. When we rotate away from the sun, we have night. ...
docx - STAO
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
Teacher Demo: Bright Star or Close Star?
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
... galaxies), using appropriate scientific terminology and units (e.g., astronomical units, scientific notation, light years) ...
Answer Key
... 5. From observations of supernova explosions in distant galaxies, it is predicted that there should be about five supernovae per century in our galaxy, whereas we have seen only about one every 300 years from Earth. Why is this? A) Most supernovae occur in the Milky Way, which can be seen only from ...
... 5. From observations of supernova explosions in distant galaxies, it is predicted that there should be about five supernovae per century in our galaxy, whereas we have seen only about one every 300 years from Earth. Why is this? A) Most supernovae occur in the Milky Way, which can be seen only from ...
Recomendación de una estrategia
... goat (shown above). Even without the aurora, the sky would be notable for the arching band of our Milky Way Galaxy and the interesting field of stars, nebulas, and galaxies. ...
... goat (shown above). Even without the aurora, the sky would be notable for the arching band of our Milky Way Galaxy and the interesting field of stars, nebulas, and galaxies. ...
review_one - MSU Solar Physics
... How the method of trigonometric parallax works and its limitations How is the apparent motion of a star related to its distance from us? Explain the idea of a standard candle, and how it helps us measure stellar distances Unit 4 Understand the concept of the EM spectrum, similarities and dif ...
... How the method of trigonometric parallax works and its limitations How is the apparent motion of a star related to its distance from us? Explain the idea of a standard candle, and how it helps us measure stellar distances Unit 4 Understand the concept of the EM spectrum, similarities and dif ...
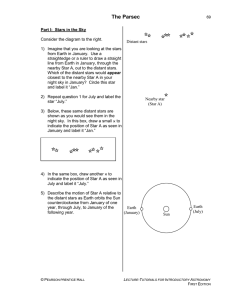
The Parsec
... 11) Consider the following discussion between two students working on this tutorial regarding the relationship between parallax angle and the distance we measure to a star: Student 1: If the distance to the star is more than 1 parsec, then the parallax angle must be more than 1 arcsecond. Larger dis ...
... 11) Consider the following discussion between two students working on this tutorial regarding the relationship between parallax angle and the distance we measure to a star: Student 1: If the distance to the star is more than 1 parsec, then the parallax angle must be more than 1 arcsecond. Larger dis ...
Groups of Stars
... • The largest galaxies consist of more than a trillion stars. Galaxies vary widely in size and ...
... • The largest galaxies consist of more than a trillion stars. Galaxies vary widely in size and ...
mslien~1
... From above the Jeans criterion can be derived as M c M J where the Jeans mass MJ is given by the RHS of ...
... From above the Jeans criterion can be derived as M c M J where the Jeans mass MJ is given by the RHS of ...
MS Word
... An H-R diagram is a plot of stellar spectral type versus absolute magnitude (and sometimes luminosity). Familiarize yourself with Figure 1 which is an empty H-R diagram. Along the bottom of the diagram are the common spectral types (we have left off O type stars since there are no O stars anywhere n ...
... An H-R diagram is a plot of stellar spectral type versus absolute magnitude (and sometimes luminosity). Familiarize yourself with Figure 1 which is an empty H-R diagram. Along the bottom of the diagram are the common spectral types (we have left off O type stars since there are no O stars anywhere n ...
Astronomy Part 2 - Malvern Troop 7
... Start with the familiar Big Dipper which is high in the sky in early spring. The two stars the farthest away from the handle are called the pointers. Connect a line between the pointers upward (about 5 times the distance of the pointers) brings you to Polaris (the north star). Opposite of Polaris li ...
... Start with the familiar Big Dipper which is high in the sky in early spring. The two stars the farthest away from the handle are called the pointers. Connect a line between the pointers upward (about 5 times the distance of the pointers) brings you to Polaris (the north star). Opposite of Polaris li ...
Back to basics: naked-eye astronomical observation
... 3. For older pupils. Star brightnesses are given a scale (logarithmic to match the nonlinear response of the eye) for their ‘magnitude’ as apparent to us on the Earth’s surface. The smaller the number the brighter the object. Most well known constellations will have 0 or 1st magnitude stars. A few o ...
... 3. For older pupils. Star brightnesses are given a scale (logarithmic to match the nonlinear response of the eye) for their ‘magnitude’ as apparent to us on the Earth’s surface. The smaller the number the brighter the object. Most well known constellations will have 0 or 1st magnitude stars. A few o ...
Here
... • Imagine the sky as a hollow sphere with the stars attached to it. This sphere rotates once every 24 hours. This imaginary sphere is called the celestial sphere. • Even though we know it is not the case, it is useful to imagine the Earth as being stationary while the celestial sphere rotates ...
... • Imagine the sky as a hollow sphere with the stars attached to it. This sphere rotates once every 24 hours. This imaginary sphere is called the celestial sphere. • Even though we know it is not the case, it is useful to imagine the Earth as being stationary while the celestial sphere rotates ...
As a nebula
... 6. How does a star begin its life cycle? • As a nebula 7. What type of star is the sun known as? • Main sequence ...
... 6. How does a star begin its life cycle? • As a nebula 7. What type of star is the sun known as? • Main sequence ...
Is the Sun a Star? - Classroom Websites
... each planetary system has a central starjust as our own solar system has one star, sometimes called by its Roman name, Sol. In some systems there are two (or even more stars) at the center. • Another approach, appropriate for middle and high school levels, is to have students research the history of ...
... each planetary system has a central starjust as our own solar system has one star, sometimes called by its Roman name, Sol. In some systems there are two (or even more stars) at the center. • Another approach, appropriate for middle and high school levels, is to have students research the history of ...
Document
... asteroids, and comets 2. The known planets in the solar system are: Mercury, Venus, Earth , Mars, Jupiter, Saturn , Uranus, Neptune and what was once known as Pluto is now a dwarf planet. 3. A full movement is called a revolution. 4. Gravity keeps the moon orbiting around Earth 5. The earth spins ar ...
... asteroids, and comets 2. The known planets in the solar system are: Mercury, Venus, Earth , Mars, Jupiter, Saturn , Uranus, Neptune and what was once known as Pluto is now a dwarf planet. 3. A full movement is called a revolution. 4. Gravity keeps the moon orbiting around Earth 5. The earth spins ar ...
ABSOLUTE AND APPARENT MAGNITUDES
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
... As a general (not vastly accurate, but close enough) rule of thumb, the highest apparent magnitude that the naked eye can see under ideal viewing conditions is about +6. Objects can cast visible shadows around an apparent magnitude -4 (you’d need a very dark night to see them though - they’d get pr ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.