a light year is
... a) the characteristic size of light , b) the distance the Earth travels around the sun in one year c) the distance light travels in one year, d) the time it takes light to travel around the Earth's orbit 2. Constellations are a) apparent patterns or designs of stars in the sky , b) physical, related ...
... a) the characteristic size of light , b) the distance the Earth travels around the sun in one year c) the distance light travels in one year, d) the time it takes light to travel around the Earth's orbit 2. Constellations are a) apparent patterns or designs of stars in the sky , b) physical, related ...
ASTRONOMY 130
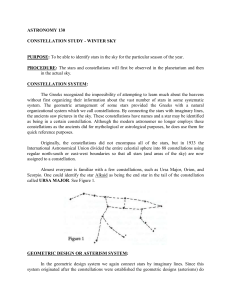
... Turn to face the south or southeastern part of the sky. You should find three bright stars that form the apexes of a large equilateral triangle. The star to the right is Betelgeuse (in Orion), the one to the left is Procyon (in Canis Minor), and the one farthest south is Sirius (in Canis Major). The ...
... Turn to face the south or southeastern part of the sky. You should find three bright stars that form the apexes of a large equilateral triangle. The star to the right is Betelgeuse (in Orion), the one to the left is Procyon (in Canis Minor), and the one farthest south is Sirius (in Canis Major). The ...
using a cepheid variable to determine distance
... In this exercise you will use data taken from observations of a Cepheid variable star over a period of 80 days. On each day, the apparent visual magnitude was recorded. Using this data you will be able to plot a light-curve for this Cepheid, and from this light curve, determine the period of the lig ...
... In this exercise you will use data taken from observations of a Cepheid variable star over a period of 80 days. On each day, the apparent visual magnitude was recorded. Using this data you will be able to plot a light-curve for this Cepheid, and from this light curve, determine the period of the lig ...
The Night Sky
... The magnitude system that astronomers use is based on the way our eyes scale the intensity of light, which is not linear but logarithmic. What do you think would be the advantage of having eyes which scale intensity in such a fashion? ...
... The magnitude system that astronomers use is based on the way our eyes scale the intensity of light, which is not linear but logarithmic. What do you think would be the advantage of having eyes which scale intensity in such a fashion? ...
Questions for this book (Word format)
... It took astronomers many years to realise that some of the “fuzzy patches” or “nebulae” in the night sky are actually galaxies like the Milky Way. One reason for this was that only some of the objects catalogued as “nebulae” are actually galaxies. List at least three types of nebula which are not ex ...
... It took astronomers many years to realise that some of the “fuzzy patches” or “nebulae” in the night sky are actually galaxies like the Milky Way. One reason for this was that only some of the objects catalogued as “nebulae” are actually galaxies. List at least three types of nebula which are not ex ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... More nega;ve = brighter (NB: this is counter-‐intui;ve, beware!) Typical range of Abs. mag: stars -‐1 to +10, galaxies -‐24 to -‐6 Typical range of app. mag: stars/galaxies, -‐27 (Sun) to +30 ( ...
... More nega;ve = brighter (NB: this is counter-‐intui;ve, beware!) Typical range of Abs. mag: stars -‐1 to +10, galaxies -‐24 to -‐6 Typical range of app. mag: stars/galaxies, -‐27 (Sun) to +30 ( ...
sunmoon - University of Glasgow
... Finding the Pole Star To find the Pole Star, first find the Plough, part of the Great Bear. ...
... Finding the Pole Star To find the Pole Star, first find the Plough, part of the Great Bear. ...
Star Evolution
... Red dwarfs: the small, faint, end of the main sequence stars White dwarfs: remnants of star with less than 8 solar masses Black dwarfs: White dwarfs that have cooled to invisibility Brown dwarfs: less than 0.08Msun=80 Jupiters; never burn Hydrogen Planets are less massive than 13 Jupiters & cannot b ...
... Red dwarfs: the small, faint, end of the main sequence stars White dwarfs: remnants of star with less than 8 solar masses Black dwarfs: White dwarfs that have cooled to invisibility Brown dwarfs: less than 0.08Msun=80 Jupiters; never burn Hydrogen Planets are less massive than 13 Jupiters & cannot b ...
Problem Set No. 5
... A one solar mass star will spend 10 billion years on the main sequence. The universe is only 13-14 billion years old. From the formula T = 1/M 2.5 and the sun’s lifetime, we see that a star of 0.9 solar masses should spend 13 billion years on the main sequence. So no stars of lower mass would have h ...
... A one solar mass star will spend 10 billion years on the main sequence. The universe is only 13-14 billion years old. From the formula T = 1/M 2.5 and the sun’s lifetime, we see that a star of 0.9 solar masses should spend 13 billion years on the main sequence. So no stars of lower mass would have h ...
Homework #7 (Ch. 19)
... Be careful about units! Please CIRCLE or put a box around your final answer if it is numerical. If you wish, you may discuss the questions with friends, but please turn in your own hand-written solutions, with questions answered in your own way. 1. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.1 Briefly describ ...
... Be careful about units! Please CIRCLE or put a box around your final answer if it is numerical. If you wish, you may discuss the questions with friends, but please turn in your own hand-written solutions, with questions answered in your own way. 1. Chaisson Review and Discussion 19.1 Briefly describ ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbits ...
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbits ...
J S U N I L T U... 2011 “Chase Excellence- Success Will Follow” ll Follow”
... (b) Orion appears like a hunter. Three bright stars appear in the belt, while five bright stars are arranged in the form of a quadrilateral (as shown in the above figure). ...
... (b) Orion appears like a hunter. Three bright stars appear in the belt, while five bright stars are arranged in the form of a quadrilateral (as shown in the above figure). ...
HW #8 Answers (Due 10/21)
... 2) List four star formation mechanisms with a short description of how each cause star formation and also which ones initiate star formation in a cloud and which are part of self-sustained star formation. Cloud collision with spiral arms – As molecular clouds orbit in a spiral galaxy they pass they ...
... 2) List four star formation mechanisms with a short description of how each cause star formation and also which ones initiate star formation in a cloud and which are part of self-sustained star formation. Cloud collision with spiral arms – As molecular clouds orbit in a spiral galaxy they pass they ...
large PDF file
... • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, moving at supersonic speeds through interstellar gases and dust, glows as a nebula called a supernova remnant ...
... • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, moving at supersonic speeds through interstellar gases and dust, glows as a nebula called a supernova remnant ...
Chapter 10 Measuring the Stars: Giants, Dwarfs, and the Main
... Stellar Motion * Stars have transverse and radial motion • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3 ...
... Stellar Motion * Stars have transverse and radial motion • Transverse - perpendicular to line of sight • Radial - along our line of sight * ___________________ - annual movement of a star across the sky as seen from Earth • _____________________ has the largest known proper motion of any star – 10.3 ...
Chapter 20 Notes (smaller PDF file)
... which its core collapses and most of its matter is ejected into space at high speeds • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, moving at supersonic speeds through interstellar gases ...
... which its core collapses and most of its matter is ejected into space at high speeds • The luminosity of the star increases suddenly by a factor of around 108 during this explosion, producing a supernova • The matter ejected from the supernova, moving at supersonic speeds through interstellar gases ...
Ch16: The Milky Way
... motion (radius and velocity) tells us mass within Sun’s orbit: 1.0 x 1011 MSun The total amount of light suggests ~ few x 109 Msun Dark matter! ...
... motion (radius and velocity) tells us mass within Sun’s orbit: 1.0 x 1011 MSun The total amount of light suggests ~ few x 109 Msun Dark matter! ...
Test 3, February 7, 2007 - Brock physics
... 42. In order to detect a black hole one looks for (a) a spot into which stars and their planets fall. (b) a binary system where a companion star is not visible but has a mass greater than 3 solar masses and is an intense X-ray source. (c) intense source of visible light. (d) the accompanying white h ...
... 42. In order to detect a black hole one looks for (a) a spot into which stars and their planets fall. (b) a binary system where a companion star is not visible but has a mass greater than 3 solar masses and is an intense X-ray source. (c) intense source of visible light. (d) the accompanying white h ...
Stars…Giants, Supergiants, Dwarfs….
... Starlight…application of spectroscopy to stars • Continuous spectrum gives surface temperature (Wien’s Law) • Spectral lines give chemical composition, temperature (also), speed of rotation (How?) and other properties • Examples of stellar spectra…what can we say? ...
... Starlight…application of spectroscopy to stars • Continuous spectrum gives surface temperature (Wien’s Law) • Spectral lines give chemical composition, temperature (also), speed of rotation (How?) and other properties • Examples of stellar spectra…what can we say? ...
A Star is
... • Apparent Motion of Stars: – motion visible to the unaided eye. Apparent motion is caused by the movement of Earth. • The rotation of Earth causes the apparent motion of stars seem as though the stars are moving counter-clockwise around the North Star. ...
... • Apparent Motion of Stars: – motion visible to the unaided eye. Apparent motion is caused by the movement of Earth. • The rotation of Earth causes the apparent motion of stars seem as though the stars are moving counter-clockwise around the North Star. ...
Star Classification
... Kelvin and is higher on the left side of the x-axis. How does our Sun fare in terms of brightness and color compared with other stars? ...
... Kelvin and is higher on the left side of the x-axis. How does our Sun fare in terms of brightness and color compared with other stars? ...
CO 2 Cycle
... carried sediment in the past several years…The atmosphere on Mars is so thin that liquid water cannot persist at the surface. However, researchers propose that water could remain liquid long enough, after breaking out from an underground source, to carry debris before totally evaporating and freezin ...
... carried sediment in the past several years…The atmosphere on Mars is so thin that liquid water cannot persist at the surface. However, researchers propose that water could remain liquid long enough, after breaking out from an underground source, to carry debris before totally evaporating and freezin ...
Chapter 21 notes - Clinton Public Schools
... spiral galaxies: bulge in middle and arms that spiral outward, like pinwheel. Most new stars form in these spiral arms elliptical galaxy: like round flattened balls, contains billions of stars, but have little gas and dust between the stars: stars are no longer forming in elliptical galaxies. Irregu ...
... spiral galaxies: bulge in middle and arms that spiral outward, like pinwheel. Most new stars form in these spiral arms elliptical galaxy: like round flattened balls, contains billions of stars, but have little gas and dust between the stars: stars are no longer forming in elliptical galaxies. Irregu ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.