Chapter 11: Stars
... temperature can only be inferred from models. • Surface T is easier to measure than its luminosity because it does not depend on distance. ...
... temperature can only be inferred from models. • Surface T is easier to measure than its luminosity because it does not depend on distance. ...
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
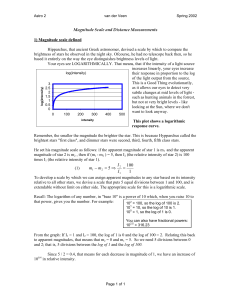
... determine the distance to a star cluster by curve-fitting on the H-R Diagram. 1) The absolute magnitude of the Sun is +4.83, of Sirius A is + 1.45, and of Spica is .119. Using the apparent magnitudes given in part 1 of this review, find the distances to these stars using the distance formula. Other ...
... determine the distance to a star cluster by curve-fitting on the H-R Diagram. 1) The absolute magnitude of the Sun is +4.83, of Sirius A is + 1.45, and of Spica is .119. Using the apparent magnitudes given in part 1 of this review, find the distances to these stars using the distance formula. Other ...
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Identify the characteristics of main sequence stars. • Characterize star formation in stellar nurseries from giant molecular clouds, to protostars, to the development of main sequence stars. • Evaluate the relationship between mass and fusion on the dying process and properties of stars. • Differe ...
... • Identify the characteristics of main sequence stars. • Characterize star formation in stellar nurseries from giant molecular clouds, to protostars, to the development of main sequence stars. • Evaluate the relationship between mass and fusion on the dying process and properties of stars. • Differe ...
(as Main Sequence Stars)?
... (amount of energy put out every second in form of radiation). Luminosity also called “absolute brightness”. How bright a star appears to us is the “apparent brightness”, which depends on its luminosity and distance from us: apparent brightness ...
... (amount of energy put out every second in form of radiation). Luminosity also called “absolute brightness”. How bright a star appears to us is the “apparent brightness”, which depends on its luminosity and distance from us: apparent brightness ...
Morning Announcements
... neatly. You can draw it or create a model out of pipe cleaners and construction paper. Every page must be titled with the stage of the life cycle Sign the back of each card you create. Each team r will create pages individually or together and sign that it is there work for verification. This is ...
... neatly. You can draw it or create a model out of pipe cleaners and construction paper. Every page must be titled with the stage of the life cycle Sign the back of each card you create. Each team r will create pages individually or together and sign that it is there work for verification. This is ...
Stellar Evolution Before…..During……and After…. The Main
... – Instability comes from partial absorption of radiation in the interior of the star • Helium absorbs radiation, and the outer layers of the star get pushed away from core • As the star expands, the density decreases, letting photons escape • Outer layers head back inward toward core ...
... – Instability comes from partial absorption of radiation in the interior of the star • Helium absorbs radiation, and the outer layers of the star get pushed away from core • As the star expands, the density decreases, letting photons escape • Outer layers head back inward toward core ...
HR Diagram Lab Handout
... stars! Please read the directions in each step of the activity closely before answering questions. Each of the star data points has the following information: Star Name: the common or catalog name of the star Temperature: the temperature of the surface of the star Brightness: the number of tim ...
... stars! Please read the directions in each step of the activity closely before answering questions. Each of the star data points has the following information: Star Name: the common or catalog name of the star Temperature: the temperature of the surface of the star Brightness: the number of tim ...
The Stars: Distance, Luminosity, Size
... Stellar Parallax: Takes advantage of the fact that Earth orbits the Sun The measurements are taken six months apart. The baseline is the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. ...
... Stellar Parallax: Takes advantage of the fact that Earth orbits the Sun The measurements are taken six months apart. The baseline is the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. ...
Stars - Mrs. Tosh`s class
... What are stars made of ? How do stars differ from one another? Do stars move? Write your answers in your science journal. Then, after you have completed this section, review your responses and change them if ...
... What are stars made of ? How do stars differ from one another? Do stars move? Write your answers in your science journal. Then, after you have completed this section, review your responses and change them if ...
The universe
... Planets around the sun and the surrounding planets revolve around the center of the galaxy (Milky Way). ...
... Planets around the sun and the surrounding planets revolve around the center of the galaxy (Milky Way). ...
Astronomy1: Midterm 3 Practice Exam
... a. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, red b. red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet c. violet, indigo, green, blue, red, orange, yellow d. red, orange, yellow, blue, green, indigo, violet e. blue, indigo, violet, yellow, green, orange, red ____ 12. What kind of spectrum do stars ...
... a. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, red b. red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet c. violet, indigo, green, blue, red, orange, yellow d. red, orange, yellow, blue, green, indigo, violet e. blue, indigo, violet, yellow, green, orange, red ____ 12. What kind of spectrum do stars ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
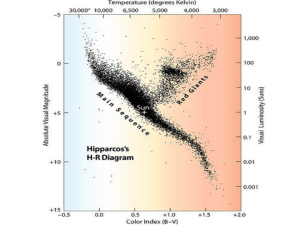
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form. These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but ...
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form. These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but ...
PHY2083
... If a star appears faint, is it because it is really (i.e. intrinsically) faint, or because it is very far away [or both] ? N.B. For stars at the same distance, the ratio of their fluxes = ratio of their luminosities ...
... If a star appears faint, is it because it is really (i.e. intrinsically) faint, or because it is very far away [or both] ? N.B. For stars at the same distance, the ratio of their fluxes = ratio of their luminosities ...
ExoplanetWorksheet
... mass’ do you get better detail when you plot with linear or logarithmic data points? __________________________________ *All of the rocky planets in our Solar System are at least 3 times more dense than Jupiter. Does it look like we’ve found very many or very few rocky exoplanets? __________________ ...
... mass’ do you get better detail when you plot with linear or logarithmic data points? __________________________________ *All of the rocky planets in our Solar System are at least 3 times more dense than Jupiter. Does it look like we’ve found very many or very few rocky exoplanets? __________________ ...
Astronomy 10 - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... Only once the red giant phase occurs, and the core contracts and heats up to a temperature of around 108 K is the core hot enough to start burning helium. (11) page 321, question 6 When a star sheds its surface in a planetary nebula, it keeps about the same luminosity, but the radius has decreased d ...
... Only once the red giant phase occurs, and the core contracts and heats up to a temperature of around 108 K is the core hot enough to start burning helium. (11) page 321, question 6 When a star sheds its surface in a planetary nebula, it keeps about the same luminosity, but the radius has decreased d ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes visible with bare eye, sometimes faint • Long period variable star: 332 days period • Cool red giants • Sometimes periodic, sometimes irregular • some eject gas into space ...
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes visible with bare eye, sometimes faint • Long period variable star: 332 days period • Cool red giants • Sometimes periodic, sometimes irregular • some eject gas into space ...
Zairamink_Lifecycle of a Star
... A black hole is an object which has such high gravitational pull that not even light can escape. Hence it is black. But in the black hole case the initial star was so massive that nothing could stop its gravitational collapse. All the matter of the star's core is crushed to an infinitely small point ...
... A black hole is an object which has such high gravitational pull that not even light can escape. Hence it is black. But in the black hole case the initial star was so massive that nothing could stop its gravitational collapse. All the matter of the star's core is crushed to an infinitely small point ...
hwk01ans
... The figure shows observations of a visual binary star with period = 60 years. If we take random observational errors into account, the data indicate a circle shown on the right. But the true orbit in space cannot be a circle, because the primary star is far off-center. The orbit must be a highly ecc ...
... The figure shows observations of a visual binary star with period = 60 years. If we take random observational errors into account, the data indicate a circle shown on the right. But the true orbit in space cannot be a circle, because the primary star is far off-center. The orbit must be a highly ecc ...
Study Guide for Stars and Galaxies Quiz ANSWER KEY
... In the middle. 8. Which stars are hotter: blue stars or red stars? Blue. 9. What is the difference between apparent brightness and absolute brightness? ...
... In the middle. 8. Which stars are hotter: blue stars or red stars? Blue. 9. What is the difference between apparent brightness and absolute brightness? ...
Astrophysics E1. This question is about stars.
... E2. This question is about cosmology. (a) The diagram below represents a spherical region of space based on Newton’s model of the universe. Earth is at the centre of the region. The dark line represents a very thin spherical shell of space distance R from Earth. With reference to the diagram and New ...
... E2. This question is about cosmology. (a) The diagram below represents a spherical region of space based on Newton’s model of the universe. Earth is at the centre of the region. The dark line represents a very thin spherical shell of space distance R from Earth. With reference to the diagram and New ...
Slide 1
... gas cloud about 10,000,000 LY from Earth. The hot stars in the Nebula emit high energy photons that are absorbed by the gas. The heated gases produce an emission spectrum and the particular wavelength of the red light of the nebula is 656nm. The exact wavelength of Hydrogen. ...
... gas cloud about 10,000,000 LY from Earth. The hot stars in the Nebula emit high energy photons that are absorbed by the gas. The heated gases produce an emission spectrum and the particular wavelength of the red light of the nebula is 656nm. The exact wavelength of Hydrogen. ...
Knight_ch12
... Two planets orbit a star. Planet 1 has orbital radius r1 and planet 2 has r2 = 4r1. Planet 1 orbits with period T1. Planet 2 orbits with period ...
... Two planets orbit a star. Planet 1 has orbital radius r1 and planet 2 has r2 = 4r1. Planet 1 orbits with period T1. Planet 2 orbits with period ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.