Lesson 2_GoingSolar
... Earth) traps some of the heat under it like a blanket. Just like a blanket, this keeps the dark part of Earth that is not facing the sun warm. ...
... Earth) traps some of the heat under it like a blanket. Just like a blanket, this keeps the dark part of Earth that is not facing the sun warm. ...
Can you write numbers in scientific notation
... What are the properties of each of the Sun’s different layers? How is energy produced in the Sun’s core? How does the Sun’s magnetic field influence each type of solar activity discussed in class (sunspots, plages, prominences, solar flares, coronal mass ejections)? Why is it important for us to be ...
... What are the properties of each of the Sun’s different layers? How is energy produced in the Sun’s core? How does the Sun’s magnetic field influence each type of solar activity discussed in class (sunspots, plages, prominences, solar flares, coronal mass ejections)? Why is it important for us to be ...
Notes for Unit 5
... -gravity can cause a small section of the nebula to collapse into a small, rotating cloud. More material gets drawn in and its temperature rises. If the temperature rises enough, it will glow; this is called a protostar. The core of the protostar continues to get hotter. Once the core temperature re ...
... -gravity can cause a small section of the nebula to collapse into a small, rotating cloud. More material gets drawn in and its temperature rises. If the temperature rises enough, it will glow; this is called a protostar. The core of the protostar continues to get hotter. Once the core temperature re ...
What is the Zodiac? The Zodiac is defined by 12 constellations
... Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. T ...
... Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. T ...
Sermon Notes
... Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. T ...
... Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constellations that are recognized as the Zodiac. The IAU (International Astronomical Union) established in 1919 has identified 88 constellations. T ...
November 2005 - Otterbein University
... • Notation: 1m.4 (smaller brighter) • Originally six groupings – 1st magnitude the brightest – 6th magnitude the dimmest ...
... • Notation: 1m.4 (smaller brighter) • Originally six groupings – 1st magnitude the brightest – 6th magnitude the dimmest ...
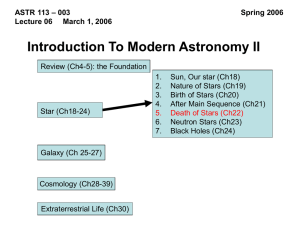
Stellar Evolution: the Death of Stars
... – Type 1a supernova: explosion of white dwarf in a closed binary system; mass accumulation exceeds the critical mass and ignites the carbon fusion at the core – Type 1b supernova: core collapse of massive star with hydrogen shell lost before – Type 1c supernova: core collapse of massive star with bo ...
... – Type 1a supernova: explosion of white dwarf in a closed binary system; mass accumulation exceeds the critical mass and ignites the carbon fusion at the core – Type 1b supernova: core collapse of massive star with hydrogen shell lost before – Type 1c supernova: core collapse of massive star with bo ...
WINNING STORY - Atlantis Short Story Contest
... I was slowly floating, completely at ease, when I realized I had just gone past the two most conspicuous of the stars that make up the Orion constellation. I was taken aback by how large, mighty and bright they were. From people’s viewpoint on Earth, it looks like these celestial bodies are located ...
... I was slowly floating, completely at ease, when I realized I had just gone past the two most conspicuous of the stars that make up the Orion constellation. I was taken aback by how large, mighty and bright they were. From people’s viewpoint on Earth, it looks like these celestial bodies are located ...
Astronomy 20 Homework # 5 1.
... radiation pressure. The former is more e ective on protons and the later on electrons, but the electrostatic force binds them together. The critical luminosity for a given mass at which the two forces balance is called the Eddington luminosity, LE . (a) Derive the formula for LE , by assuming the Th ...
... radiation pressure. The former is more e ective on protons and the later on electrons, but the electrostatic force binds them together. The critical luminosity for a given mass at which the two forces balance is called the Eddington luminosity, LE . (a) Derive the formula for LE , by assuming the Th ...
ecliptic
... • Assumption is that the position of the Sun and planets at the exact moment of your birth determines what will happen in your life. • Horoscopes: very general statements that can apply to anybody. What is the probability that 1/12 of the world’s people are having the same kind of day? • Different s ...
... • Assumption is that the position of the Sun and planets at the exact moment of your birth determines what will happen in your life. • Horoscopes: very general statements that can apply to anybody. What is the probability that 1/12 of the world’s people are having the same kind of day? • Different s ...
Star Facts - Dr. Noha MH Elnagdi
... absorbs a color or more of the continuous spectrum, the elements in the atmosphere of a star emits an absorption spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. A absorption spectrum is produced when light from a hot solid or dense gas passes through a cooler gas (which is the atmospheric gases of the ...
... absorbs a color or more of the continuous spectrum, the elements in the atmosphere of a star emits an absorption spectrum rather than a continuous spectrum. A absorption spectrum is produced when light from a hot solid or dense gas passes through a cooler gas (which is the atmospheric gases of the ...
Lecture 15: The Main Sequence
... If any of these conditions is not met, the star is not on the main-sequence. These conditions define a region on the H-R diagram where stars hang out for long periods of time. That’s why so many stars in the sky (85%) are on the main sequence. ...
... If any of these conditions is not met, the star is not on the main-sequence. These conditions define a region on the H-R diagram where stars hang out for long periods of time. That’s why so many stars in the sky (85%) are on the main sequence. ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... Up in the sky for 8 months. Brightest- SN 1006 recorded by Chinese and Islamic astronomers SN 1054 produced the Crab Nebula. Latest observed in the milky way with the naked eye was SN 1572 and SN 1604 Telescope has allowed us to look farther than the milky way. 1885 observation of supern ...
... Up in the sky for 8 months. Brightest- SN 1006 recorded by Chinese and Islamic astronomers SN 1054 produced the Crab Nebula. Latest observed in the milky way with the naked eye was SN 1572 and SN 1604 Telescope has allowed us to look farther than the milky way. 1885 observation of supern ...
Sections F and G
... The Sun has a dipole field with average strength ~10−4T. It is probably generated by the dynamo process, by electric currents in the solar interior. It is distorted by the differential rotation of the Sun and by convective cells. The field varies in strength with a 22 year period, reversing directio ...
... The Sun has a dipole field with average strength ~10−4T. It is probably generated by the dynamo process, by electric currents in the solar interior. It is distorted by the differential rotation of the Sun and by convective cells. The field varies in strength with a 22 year period, reversing directio ...
1 Sep: 6.13am BST 15 Sep: 6.43am BST 30 Sep: 7.14am BST
... and Aquila (the Eagle) whose brightest stars of Deneb, Vega and Altair respectively make up the Summer Triangle. The Swan’s beak is marked by Albireo and halfway between Albireo and Altair is Sagitta (the Arrow) a small but lovely constellation representing an arrow sailing harmlessly between the tw ...
... and Aquila (the Eagle) whose brightest stars of Deneb, Vega and Altair respectively make up the Summer Triangle. The Swan’s beak is marked by Albireo and halfway between Albireo and Altair is Sagitta (the Arrow) a small but lovely constellation representing an arrow sailing harmlessly between the tw ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... Explanation: Yes it does look like Saturn, but Saturn is only one of four giant ringed planets in our Solar System. And while Saturn has the brightest rings, this system of rings and moons actually belongs to planet Uranus, imaged here in near-infrared light by the Antu telescope at the ESO Paranal ...
... Explanation: Yes it does look like Saturn, but Saturn is only one of four giant ringed planets in our Solar System. And while Saturn has the brightest rings, this system of rings and moons actually belongs to planet Uranus, imaged here in near-infrared light by the Antu telescope at the ESO Paranal ...
Lecture 19: Low
... • Continue with life of a lowlow-mass star (like the Sun) after exhausting H in core -- post MS • Red giant (RG I) phase, with H shell burning • Helium flash goes off in shrinking degenerate core: horizontal branch star with He core burning • Double shell burning (H and He) yields red supergiant (RG ...
... • Continue with life of a lowlow-mass star (like the Sun) after exhausting H in core -- post MS • Red giant (RG I) phase, with H shell burning • Helium flash goes off in shrinking degenerate core: horizontal branch star with He core burning • Double shell burning (H and He) yields red supergiant (RG ...
doc
... radiation pressure and shock waves from pulsations driving matter away—see Discovery 20-2, p. 564.) The star is also pulsating (period ~years); see Fig. 20.9. These bloated envelopes are not very stable! Eventually so much of the envelope is lost that the last bit of envelope gets ejected as a more ...
... radiation pressure and shock waves from pulsations driving matter away—see Discovery 20-2, p. 564.) The star is also pulsating (period ~years); see Fig. 20.9. These bloated envelopes are not very stable! Eventually so much of the envelope is lost that the last bit of envelope gets ejected as a more ...
EVOLUION OF SUN LIKE STAR
... .And higher the mass in main sequence higher the radius and greater the radius the greater the luminosity. Most of a stars life is spent in the main sequence . For example sun took 20 million years to form but it will spend 10 billions its life time in the main sequence. Stars have different mass. T ...
... .And higher the mass in main sequence higher the radius and greater the radius the greater the luminosity. Most of a stars life is spent in the main sequence . For example sun took 20 million years to form but it will spend 10 billions its life time in the main sequence. Stars have different mass. T ...
The eleventh annual AST poster session - Home
... temperature, the older the star. The cluster’s existence can best be compared to a burning candle, as the flame dies out over time. ...
... temperature, the older the star. The cluster’s existence can best be compared to a burning candle, as the flame dies out over time. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.