PowerPoint
... In the paper “A Celestial Cubic”, Charles Groetsch shows how the orbital radius and mass of an unseen planet circling a star can be obtained from the star’s spectral shift data, via the solution of a cubic equation! ...
... In the paper “A Celestial Cubic”, Charles Groetsch shows how the orbital radius and mass of an unseen planet circling a star can be obtained from the star’s spectral shift data, via the solution of a cubic equation! ...
Summation Packet KEY
... 21. Some stars that are in the night’s sky have already died. Explain why we can still see them, even if they exploded thousands of years ago. The stars are so far away that it takes millions of years for the light to reach Earth. 22. The picture to the right is of a boat using its foghorn. Describe ...
... 21. Some stars that are in the night’s sky have already died. Explain why we can still see them, even if they exploded thousands of years ago. The stars are so far away that it takes millions of years for the light to reach Earth. 22. The picture to the right is of a boat using its foghorn. Describe ...
(a) Because the core of heavy-mass star never reaches high enough
... 17. Which one of the following is correct? (a) Right after the big bang, the most abundant element in the universe was helium (b) The first generation stars tend to be more massive than today’s stars (c) High mass stars tend to have red color (d) Large and high luminosity stars tend to live longer t ...
... 17. Which one of the following is correct? (a) Right after the big bang, the most abundant element in the universe was helium (b) The first generation stars tend to be more massive than today’s stars (c) High mass stars tend to have red color (d) Large and high luminosity stars tend to live longer t ...
Star Formation
... core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation • Is there another form of pressure that can stop contraction? ...
... core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its surface through radiation • Is there another form of pressure that can stop contraction? ...
Physics Observing The Universe
... The moon • The moon appears to travel east to west across the sky once every 24hrs 49mins. One complete cycle takes 28days. • Why does the Moon take longer to cross the sky than the Sun? • Because it orbits the Earth in the same direction as the Earth rotates. So by the time the Earth rotates enoug ...
... The moon • The moon appears to travel east to west across the sky once every 24hrs 49mins. One complete cycle takes 28days. • Why does the Moon take longer to cross the sky than the Sun? • Because it orbits the Earth in the same direction as the Earth rotates. So by the time the Earth rotates enoug ...
STAR UNIT FLASH BACKS
... fusion will begin b.) stars must reach a critical point c.) stars must lose mass before fusion will begin ...
... fusion will begin b.) stars must reach a critical point c.) stars must lose mass before fusion will begin ...
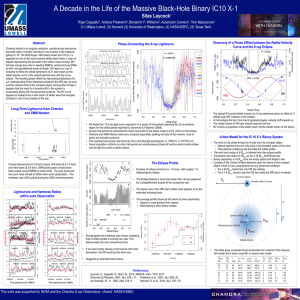
A Decade in the Life of the Massive Black-Hole Binary... Silas Laycock !
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
... galaxy IC 10. The Wolf Rayet + BH binary known as IC10 X-1 is regarded as one of the most massive stellar black holes; a class of objects representing the pinnacle of the stellar mass function. BH binaries occupy key roles in seeding SMBHs, producing long GRBs at birth, and gravitational waves at de ...
1 How luminous are stars?
... middle, rA = rB. The more unequal the masses are, the more it shifts toward the more massive star. ...
... middle, rA = rB. The more unequal the masses are, the more it shifts toward the more massive star. ...
The Hidden Lives of Galaxies NSTA 2001
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
life cycle of stars
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
... • Under collapse, protons and electrons combine to form neutrons. • 10 Km across Black Hole (If mass of core > 5 x Solar) • Not even compacted neutrons can support weight of very massive stars. ...
What tool do astronomers use to understand the evolution of stars?
... Luminosity, temperaure, radius Two stars are found to have the same luminosity. However, one star has twice the surface temperature of the other. From this information, what can you determine about their radii? A) The hotter star has half the radius of the cooler star. B) The cooler star has half t ...
... Luminosity, temperaure, radius Two stars are found to have the same luminosity. However, one star has twice the surface temperature of the other. From this information, what can you determine about their radii? A) The hotter star has half the radius of the cooler star. B) The cooler star has half t ...
Cosmic Distance Ladder
... of the Earth causes nearby stars to appear to move relative to the more distant stars. • The annual parallax is defined as the difference in position of a star as seen from the Earth and Sun, i.e. the angle subtended at a star by the mean radius of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. ...
... of the Earth causes nearby stars to appear to move relative to the more distant stars. • The annual parallax is defined as the difference in position of a star as seen from the Earth and Sun, i.e. the angle subtended at a star by the mean radius of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. ...
Prospecting for Planets – Radial Velocity Searches
... The first planet orbiting a star other than our Sun (or 'exoplanet') was discovered in 1992, orbiting an odd type of star known as a pulsar. It wasn't until three years later that the next exoplanet was discovered, this time around a star similar to our Sun. Since then the number of exoplanets we ha ...
... The first planet orbiting a star other than our Sun (or 'exoplanet') was discovered in 1992, orbiting an odd type of star known as a pulsar. It wasn't until three years later that the next exoplanet was discovered, this time around a star similar to our Sun. Since then the number of exoplanets we ha ...
P1 - Foundation
... Earth was the centre of the Universe. This was called the geocentric model. The evidence for this model came from observations of the sky using the naked eye. After the telescope was invented, astronomers quickly gathered evidence which showed that the geocentric model is not correct. Describe the e ...
... Earth was the centre of the Universe. This was called the geocentric model. The evidence for this model came from observations of the sky using the naked eye. After the telescope was invented, astronomers quickly gathered evidence which showed that the geocentric model is not correct. Describe the e ...
Level 4
... mapped group of constellations with their information. Students design and create a model that demonstrates the axis and rotation of the earth and the cause of seasons as well as day and night. ...
... mapped group of constellations with their information. Students design and create a model that demonstrates the axis and rotation of the earth and the cause of seasons as well as day and night. ...
Deep Space (PDF: 224k)
... Clouds and are easily visible with the naked eye from the Southern Hemisphere, as they were to Magellan when he circumnavigated the globe. Our galaxy and its satellites, along with the spiral galaxies M31 and M33 and their attendant satellites, are all bound together in a small group with the imagin ...
... Clouds and are easily visible with the naked eye from the Southern Hemisphere, as they were to Magellan when he circumnavigated the globe. Our galaxy and its satellites, along with the spiral galaxies M31 and M33 and their attendant satellites, are all bound together in a small group with the imagin ...
Stars and Constellations
... The Milky Way is the galaxy which contains our solar system. On a summer evening you can see a dusty trail of stars stretching across the sky. This is our Milky Way galaxy consisting of hundreds of billions of stars. Instead of seeing each star individually, the combined light appears as a faded ba ...
... The Milky Way is the galaxy which contains our solar system. On a summer evening you can see a dusty trail of stars stretching across the sky. This is our Milky Way galaxy consisting of hundreds of billions of stars. Instead of seeing each star individually, the combined light appears as a faded ba ...
Lec9_2D
... The Death of a Low Mass Star • After mass loss, stars that had initial masses less than about 8 M have final masses less than 1.4 M. The electrostatic repulsion of carbon (6 protons) and oxygen (8 protons) is so great that these objects cannot fuse carbon and oxygen. • When on the 2nd Giant Branc ...
... The Death of a Low Mass Star • After mass loss, stars that had initial masses less than about 8 M have final masses less than 1.4 M. The electrostatic repulsion of carbon (6 protons) and oxygen (8 protons) is so great that these objects cannot fuse carbon and oxygen. • When on the 2nd Giant Branc ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... Man has always been fascinated by the universe. Astronomy is the science that studies the composition, motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematic ...
... Man has always been fascinated by the universe. Astronomy is the science that studies the composition, motions, positions, dimensions, and destinies of the planets, stars, and other heavenly bodies in our universe. Man has known or conjectured about our solar system for many years through mathematic ...
Where to begin the adventure with variable stars?
... because they belong to constellations that are visible all year round in the northern hemisphere. They are located in relation to one another in the following way: ...
... because they belong to constellations that are visible all year round in the northern hemisphere. They are located in relation to one another in the following way: ...
answers
... 3. How many guide laws are there? [6] 4. Who was the first person to walk on the moon [Neil Armstrong] 5. Name a constellation [there are lots of these, such as Cassiopeia, Ursa Major, Orion] 6. Name a constellation NO REPEATS – THEY HAVE TO GIVE A NEW ONE 7. Name a constellation 8. Name a constella ...
... 3. How many guide laws are there? [6] 4. Who was the first person to walk on the moon [Neil Armstrong] 5. Name a constellation [there are lots of these, such as Cassiopeia, Ursa Major, Orion] 6. Name a constellation NO REPEATS – THEY HAVE TO GIVE A NEW ONE 7. Name a constellation 8. Name a constella ...
2009_ASU_Exam
... 2) RS Ophiuchi is a recurrent nova variable star. a) Which image contains a light curve produced by RS Ophiuchi? b) What type of system produces this type of variability? c) This system is comprised of what specific types of objects? d) Which image illustrates this type of system? e) Which image con ...
... 2) RS Ophiuchi is a recurrent nova variable star. a) Which image contains a light curve produced by RS Ophiuchi? b) What type of system produces this type of variability? c) This system is comprised of what specific types of objects? d) Which image illustrates this type of system? e) Which image con ...
Instrumentation for Cosmology
... Suppose the age of the galaxy is 10 billion years. Its inner regions rotate once in 200 million years… Therefore, we’d expect about 50 turns. The galaxy would look like a clock spring. ...
... Suppose the age of the galaxy is 10 billion years. Its inner regions rotate once in 200 million years… Therefore, we’d expect about 50 turns. The galaxy would look like a clock spring. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.