User guide 2 - Finding celestial treasures
... Finding the Bright Planets The planets are not represented on the maps because they always move, some slowly, others more quickly, across the celestial dome. However, they always appear somewhere near the ecliptic, which represents the annual path of the sun across the sky. Planets shine with a stea ...
... Finding the Bright Planets The planets are not represented on the maps because they always move, some slowly, others more quickly, across the celestial dome. However, they always appear somewhere near the ecliptic, which represents the annual path of the sun across the sky. Planets shine with a stea ...
Source: https://www
... habitable zone take into account more subtle effects, such as the effect of the carbonate-silicate cycle in regulating carbon dioxide in a planet's atmosphere. Work on this particular process by Penn State scientists, including Professor James Kasting, has shown that the habitable zone extends farth ...
... habitable zone take into account more subtle effects, such as the effect of the carbonate-silicate cycle in regulating carbon dioxide in a planet's atmosphere. Work on this particular process by Penn State scientists, including Professor James Kasting, has shown that the habitable zone extends farth ...
Section 27.2
... astronomers categorize stars into groups: Main sequence stars, like the Sun, are in a very stable part of their life cycle. White dwarfs are hot and dim and cannot be seen without a telescope. Red giants are cool and bright and some can be seen without a telescope. Can you locate blue giants o ...
... astronomers categorize stars into groups: Main sequence stars, like the Sun, are in a very stable part of their life cycle. White dwarfs are hot and dim and cannot be seen without a telescope. Red giants are cool and bright and some can be seen without a telescope. Can you locate blue giants o ...
Ay 122a Fall 2012 – HOMEWORK #1
... as it transits through the local meridian, midnight local time. (a) What is the local siderial time? (b) What day of the year is it? (c) What is the approximate universal time (assume that you are in California)? (d) Can you do this from Palomar anyway (Palomar’s latitude is +33◦ 210 2100 (e) What i ...
... as it transits through the local meridian, midnight local time. (a) What is the local siderial time? (b) What day of the year is it? (c) What is the approximate universal time (assume that you are in California)? (d) Can you do this from Palomar anyway (Palomar’s latitude is +33◦ 210 2100 (e) What i ...
Regents Review Questions.Unit 2.Astronomy
... 15 Describe the relationship between the distance from the Sun and the period of revolution for these four planets. Astronomers have discovered more than 400 planets outside of our solar system. The first extrasolar planet was detected in 1995 orbiting a star known as 51 Pegasi, which is similar in ...
... 15 Describe the relationship between the distance from the Sun and the period of revolution for these four planets. Astronomers have discovered more than 400 planets outside of our solar system. The first extrasolar planet was detected in 1995 orbiting a star known as 51 Pegasi, which is similar in ...
DTU_9e_ch13
... Sirius, the brightest-appearing star in the night sky, is actually a double star. The smaller star, Sirius B, is a white dwarf, seen here at the five o’clock position in the glare of Sirius. The spikes and rays around the bright star, Sirius A, are created by optical effects within the telescope. ...
... Sirius, the brightest-appearing star in the night sky, is actually a double star. The smaller star, Sirius B, is a white dwarf, seen here at the five o’clock position in the glare of Sirius. The spikes and rays around the bright star, Sirius A, are created by optical effects within the telescope. ...
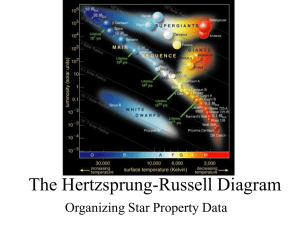
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
... Why is the gas ionized? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are form ...
from gas giants to super
... Launch in 2022 following the launch of the first L mission of the Cosmic Vision program. Launch could be brought forward to 2020 if the L mission slip in time. The M-mission should address the science goals and questions of the Cosmic Vision plan. The total ceiling cost covered by ESA is 470 M€, whi ...
... Launch in 2022 following the launch of the first L mission of the Cosmic Vision program. Launch could be brought forward to 2020 if the L mission slip in time. The M-mission should address the science goals and questions of the Cosmic Vision plan. The total ceiling cost covered by ESA is 470 M€, whi ...
Student 1
... Barnard’s star. An ancient Red Dwarf. Barnard's Star is a very low-mass red dwarf star about six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Barnard's Star is the fourth-closest known individual star to the Sun, after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system. Despite its ...
... Barnard’s star. An ancient Red Dwarf. Barnard's Star is a very low-mass red dwarf star about six light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Barnard's Star is the fourth-closest known individual star to the Sun, after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system. Despite its ...
Stellar temperatures and spectral types
... Hydrogen lines in the visible part of the spectrum (known as the Balmer Series) are created when a photon is absorbed by bouncing an electron from the 1st excited level to a higher excited level. • Photons with just the right energy to move an electron from the 1st excited state to the 2nd excited s ...
... Hydrogen lines in the visible part of the spectrum (known as the Balmer Series) are created when a photon is absorbed by bouncing an electron from the 1st excited level to a higher excited level. • Photons with just the right energy to move an electron from the 1st excited state to the 2nd excited s ...
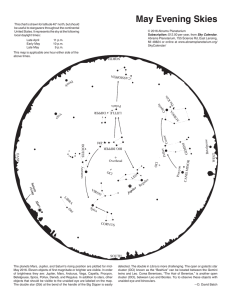
Mountain-Skies-2016-0718
... to the west and shines brightly about a third of the way up in the southwest as the sky darkens. It is quickly sinking into the west and will be lost to us by early September. The red planet Mars is well up in the south these evenings. It is qu ...
... to the west and shines brightly about a third of the way up in the southwest as the sky darkens. It is quickly sinking into the west and will be lost to us by early September. The red planet Mars is well up in the south these evenings. It is qu ...
Mountain Skies - Pisgah Astronomical Research Institute
... to the west and shines brightly about a third of the way up in the southwest as the sky darkens. It is quickly sinking into the west and will be lost to us by early September. The red planet Mars is well up in the south these evenings. It is quickly dimming as the earth moves away from it but still ...
... to the west and shines brightly about a third of the way up in the southwest as the sky darkens. It is quickly sinking into the west and will be lost to us by early September. The red planet Mars is well up in the south these evenings. It is quickly dimming as the earth moves away from it but still ...
Packet 3
... 6b. If the sun were 32.6 light-years away, what would it’s absolute magnitude be? _____________ 7. Stars that are closer than 32.6 light-years away appear __________________________. Therefore those stars that are further than 32.6 light-years away appear ________________________. 8. How far away a ...
... 6b. If the sun were 32.6 light-years away, what would it’s absolute magnitude be? _____________ 7. Stars that are closer than 32.6 light-years away appear __________________________. Therefore those stars that are further than 32.6 light-years away appear ________________________. 8. How far away a ...
Test 1, Feb. 2, 2016 - Brock physics
... (a) all of a star’s hydrogen is returned to the interstellar medium. (b) the elements heavier than iron are synthesized. (c) the resulting burst of neutrinos keeps the galaxy from collapsing. (d) they produce helium from hydrogen. 37. Most of supernova 1987A energy output (luminosity) was in the for ...
... (a) all of a star’s hydrogen is returned to the interstellar medium. (b) the elements heavier than iron are synthesized. (c) the resulting burst of neutrinos keeps the galaxy from collapsing. (d) they produce helium from hydrogen. 37. Most of supernova 1987A energy output (luminosity) was in the for ...
Introduction to Space
... with beautiful sunrises and sunsets ~The moon is the brightest and most recognizable object in the sky at night, and it the closest celestial body (any object beyond the Earth and visible in the sky) to the Earth ~From a dark site away from city lights, we can see nearly 3000 stars (compared to the ...
... with beautiful sunrises and sunsets ~The moon is the brightest and most recognizable object in the sky at night, and it the closest celestial body (any object beyond the Earth and visible in the sky) to the Earth ~From a dark site away from city lights, we can see nearly 3000 stars (compared to the ...
2.1 Introduction
... at the same time each year (or in practice if we correct for the effects of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun), we find that its position in a reference frame based on very distant objects such as quasars is not the same from year to year (see Figure 2.2). This is proper motion, reflecting the fact t ...
... at the same time each year (or in practice if we correct for the effects of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun), we find that its position in a reference frame based on very distant objects such as quasars is not the same from year to year (see Figure 2.2). This is proper motion, reflecting the fact t ...
Astronomy 111 – Lecture 2
... – There is a time when it is light. = Day – There is a time when it is dark. = Night ...
... – There is a time when it is light. = Day – There is a time when it is dark. = Night ...
Constellation Argo Navis
... Homunculus Nebula is a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye that is being ejected by the erratic luminous blue variable star Eta Carinae, the most massive visible star known. Eta Carinae is so massive that it has reached the theoretical upper limit for the mass of a star and is therefore unstab ...
... Homunculus Nebula is a planetary nebula visible to the naked eye that is being ejected by the erratic luminous blue variable star Eta Carinae, the most massive visible star known. Eta Carinae is so massive that it has reached the theoretical upper limit for the mass of a star and is therefore unstab ...
Stars I
... – something twice as far away will be four times fainter – something 10 times further away will be 100 times fainter – something 1000 times further away will be a million times fainter ...
... – something twice as far away will be four times fainter – something 10 times further away will be 100 times fainter – something 1000 times further away will be a million times fainter ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.