The Celestial E-Sphere
... trhese on Roger O’Brian’s presentation at the Mallorca Observatory’s planetarium in September 2007). These include: • constellations and their boundaries; • ecliptic; • labelling of solstices; • north and south celestial poles; • labelling of coordinates; • projection of equator onto celestial spher ...
... trhese on Roger O’Brian’s presentation at the Mallorca Observatory’s planetarium in September 2007). These include: • constellations and their boundaries; • ecliptic; • labelling of solstices; • north and south celestial poles; • labelling of coordinates; • projection of equator onto celestial spher ...
Gravitation and Orbital Motion
... 12. In June 2002, scientists at Caltech discovered a new orbiting body in the solar system, half the diameter of Pluto. Quaoar (KWAH-o-ar) takes 288 years to complete one orbit around the sun, and its orbit is remarkably circular. Find the distance from Quaoar to the sun (the sun's mass is 1.99×1030 ...
... 12. In June 2002, scientists at Caltech discovered a new orbiting body in the solar system, half the diameter of Pluto. Quaoar (KWAH-o-ar) takes 288 years to complete one orbit around the sun, and its orbit is remarkably circular. Find the distance from Quaoar to the sun (the sun's mass is 1.99×1030 ...
The Universe Section 1
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
Some Physics of the Kepler Laws and Orbits Kepler`s First Law
... orbits. We have different cases: 1) If E = 0, then the eccentricity is 1, which means the aphelion becomes extended and we have a parabolic orbit. 2) If E<0, then the eccentricity is nonzero and we have the general equation for elliptical orbit. 3) If E = 2L2/m(GmM)2 < 0, then the eccentricity is ze ...
... orbits. We have different cases: 1) If E = 0, then the eccentricity is 1, which means the aphelion becomes extended and we have a parabolic orbit. 2) If E<0, then the eccentricity is nonzero and we have the general equation for elliptical orbit. 3) If E = 2L2/m(GmM)2 < 0, then the eccentricity is ze ...
Take Something Like a Star
... Use language we can comprehend. Tell us what elements you blend. It gives us strangely little aid, But does tell something in the end. And steadfast as Keats’ Eremite*, Not even stooping from its sphere, It asks a little of us here. It asks of us a certain height, So when at times the mob is swayed ...
... Use language we can comprehend. Tell us what elements you blend. It gives us strangely little aid, But does tell something in the end. And steadfast as Keats’ Eremite*, Not even stooping from its sphere, It asks a little of us here. It asks of us a certain height, So when at times the mob is swayed ...
Biblical Astrophysics - The Call of the Bride
... A Solar System Parable? As I was looking at the diagram of the asteroid belt (shown on page three) and considering the origin of all that debris, I suddenly became aware of a possible parable beginning to emerging. It occurred to me that some of the asteroids have been saved by the king (Jupiter). S ...
... A Solar System Parable? As I was looking at the diagram of the asteroid belt (shown on page three) and considering the origin of all that debris, I suddenly became aware of a possible parable beginning to emerging. It occurred to me that some of the asteroids have been saved by the king (Jupiter). S ...
Stars in the night Sky - ScienceEducationatNewPaltz
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the nadir, direct ...
... Find north by using the Big Dipper to locate Polaris, the north star. Polaris is closer to true north than a magnetic compass. o Note: In Japan, azimuth is measured clockwise starting from the south. The point directly overhead is called an observer's zenith. Opposite the zenith is the nadir, direct ...
Observing Planetary Motion 15.3 Directions: Following the
... There are many stars like our Sun. Some of these other stars also may have planets that orbit them. Even though Earth-based astronomers may not have yet seen a planet orbiting another star, they know such orbiting planets exist. How do they know? Because when a planet orbits a star, it makes the sta ...
... There are many stars like our Sun. Some of these other stars also may have planets that orbit them. Even though Earth-based astronomers may not have yet seen a planet orbiting another star, they know such orbiting planets exist. How do they know? Because when a planet orbits a star, it makes the sta ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. State any one of Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 6. What is Equation of time? 7. Define Synodic month. 8. What is meant by ‘phase of moon’? 9. What are inner planets? 10. Define ‘Stationary points’. ...
... 5. State any one of Kepler’s laws of planetary motion. 6. What is Equation of time? 7. Define Synodic month. 8. What is meant by ‘phase of moon’? 9. What are inner planets? 10. Define ‘Stationary points’. ...
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1
... 1. What is the Julian date at midnight CST on 2-3 September 2013? 2. What is the CST of local midnight? 3. At midnight CST: Compute the hour angles of the 5 brightest stars. Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be ...
... 1. What is the Julian date at midnight CST on 2-3 September 2013? 2. What is the CST of local midnight? 3. At midnight CST: Compute the hour angles of the 5 brightest stars. Which, if any, are observable (zenith distance <60o )? Which, if any, are above the horizon? 4. Which of these 5 stars can be ...
Passport to the Universe Educator`s Guide Text
... the Earth and the other planets in the larger scheme of things. From out here, the sizes of and distances between the Earth, Sun, and other planets appear relatively small. On our trip, we pass three of the eight planets—Mars, Jupiter (and its moons, Io and Europa), and Saturn. We now head out for ...
... the Earth and the other planets in the larger scheme of things. From out here, the sizes of and distances between the Earth, Sun, and other planets appear relatively small. On our trip, we pass three of the eight planets—Mars, Jupiter (and its moons, Io and Europa), and Saturn. We now head out for ...
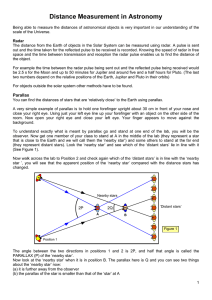
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
... The direction of Centauri is measured against the background of the distant stars at the two points P1 and P2. The angle 2A is measured and so the parallax (angle A) can be found. If you know the angle A and the radius of the Earth’s orbit (R) you can find the distance of the star (D). Stars that ...
Radio-quiet Isolated Neutron Stars
... Detected in the RASS between 1990/09/14~1990/10/02. Identified with the 1992/10/16 PSPC data. No variability at levels greater than ~1% in 1hr, or <30% on ...
... Detected in the RASS between 1990/09/14~1990/10/02. Identified with the 1992/10/16 PSPC data. No variability at levels greater than ~1% in 1hr, or <30% on ...
Document
... • Four fundamental observables used to parameterise stars and compare with models M, R, L, Te • M and R can be measured directly in small numbers of stars (will cover more of this later) • Age and chemical composition also dictate the position of stars in the HR diagram • Stellar clusters very usefu ...
... • Four fundamental observables used to parameterise stars and compare with models M, R, L, Te • M and R can be measured directly in small numbers of stars (will cover more of this later) • Age and chemical composition also dictate the position of stars in the HR diagram • Stellar clusters very usefu ...
lecture 1 - University of Florida Astronomy
... horizon also change with season – It rises and sets due east on the equinox (Sep 21, and March 21) – It rises north of east in the summer south of east in the winter ...
... horizon also change with season – It rises and sets due east on the equinox (Sep 21, and March 21) – It rises north of east in the summer south of east in the winter ...
ppp
... • If the velocity of a star is too low then it will be sucked into the center of the galaxy • The direction of the velocity should also be tangential to the desired orbit ...
... • If the velocity of a star is too low then it will be sucked into the center of the galaxy • The direction of the velocity should also be tangential to the desired orbit ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412
... • Four fundamental observables used to parameterise stars and compare with models M, R, L, Te • M and R can be measured directly in small numbers of stars (will cover more of this later) • Age and chemical composition also dictate the position of stars in the HR diagram • Stellar clusters very usefu ...
... • Four fundamental observables used to parameterise stars and compare with models M, R, L, Te • M and R can be measured directly in small numbers of stars (will cover more of this later) • Age and chemical composition also dictate the position of stars in the HR diagram • Stellar clusters very usefu ...
THE INCREDIBLE ORIGIN OF THE CHEMICAL ELEMENTS
... magnesium-24. It is no accident that amongst the lighter elements the most common isotopes have mass numbers which are multiples of 4. Other processes build up small quantities of heavier elements. These processes involve the decay of unstable nuclei. In this process, neutrons are emitted and then c ...
... magnesium-24. It is no accident that amongst the lighter elements the most common isotopes have mass numbers which are multiples of 4. Other processes build up small quantities of heavier elements. These processes involve the decay of unstable nuclei. In this process, neutrons are emitted and then c ...
ASTR3007/4007/6007, Class 1: Observing the Stars 23 February
... experiments on Earth, and as a result tens of thousands of spectral lines that appear in stars have been definitively assigned to the species that produces them. Stellar spectra show certain characteristic patterns, which lead astronomers to do what they always do: when confronted with something you ...
... experiments on Earth, and as a result tens of thousands of spectral lines that appear in stars have been definitively assigned to the species that produces them. Stellar spectra show certain characteristic patterns, which lead astronomers to do what they always do: when confronted with something you ...
Stars are classified by their TEMPERATURE (color) SPECTRAL
... a DISTANCE unit. LUMINOSITY is INTRINSIC to the star, just as is its mass. ...
... a DISTANCE unit. LUMINOSITY is INTRINSIC to the star, just as is its mass. ...
November 2007
... of the Sun, and a mass around three-fourths solar. Such sun-like stars abound in space, but they are normally so faint that few can be seen without a telescope. Although not one of the 50 closest stars to our solar system it is the 8th closest of the naked eye stars. This is a close neighbor and it ...
... of the Sun, and a mass around three-fourths solar. Such sun-like stars abound in space, but they are normally so faint that few can be seen without a telescope. Although not one of the 50 closest stars to our solar system it is the 8th closest of the naked eye stars. This is a close neighbor and it ...
Drawing Constellations
... Betelgeuse, the right arm of Orion (or "armpit" as the name suggests), glows with a dull red. Rigel, in the opposite corner of the constellation, is blue and much brighter. ...
... Betelgeuse, the right arm of Orion (or "armpit" as the name suggests), glows with a dull red. Rigel, in the opposite corner of the constellation, is blue and much brighter. ...
Globular Clusters - Lick Observatory
... Picking and Choosing We have a big pile of stars, now what? ...
... Picking and Choosing We have a big pile of stars, now what? ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.