γ The potential for intensity interferometry with -ray telescope arrays
... used in the past to do optical measurements. For example the telescopes of H.E.S.S. have been used to measure the optical light-curve of the Crab pulsar [5] and to search for ultra-fast optical transients from binary systems (Deil et al. these proceedings). Two initiatives currently exist aiming for ...
... used in the past to do optical measurements. For example the telescopes of H.E.S.S. have been used to measure the optical light-curve of the Crab pulsar [5] and to search for ultra-fast optical transients from binary systems (Deil et al. these proceedings). Two initiatives currently exist aiming for ...
November - LVAstronomy.com
... The Constellation Cassiopeia resides along the bright swath of starry glow known as the Milky Way. We know this glow is the plane of our home galaxy and holds a multitude of open star clusters. Dozens of these galactic clusters are found in Cassiopeia. One of the finest, but often overlooked, is NGC ...
... The Constellation Cassiopeia resides along the bright swath of starry glow known as the Milky Way. We know this glow is the plane of our home galaxy and holds a multitude of open star clusters. Dozens of these galactic clusters are found in Cassiopeia. One of the finest, but often overlooked, is NGC ...
Lecture7
... from surface to center – looking like an onion (see Fig. II-68). This core, looking like an onion, is only the size of the earth. However, by this time the envelope expanded to such a huge degree that the radius of the entire star is as large as Jupiter’s orbit! The core gets denser, core temperatur ...
... from surface to center – looking like an onion (see Fig. II-68). This core, looking like an onion, is only the size of the earth. However, by this time the envelope expanded to such a huge degree that the radius of the entire star is as large as Jupiter’s orbit! The core gets denser, core temperatur ...
classifying stars
... The brightness of a star depends on its size, temperature and distance from the earth. Some stars appear brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them ...
... The brightness of a star depends on its size, temperature and distance from the earth. Some stars appear brighter to us on earth because they are much closer than others, astronomers call this apparent magnitude (HOW BRIGHT A STAR APPEARS.) However, if astronomers could take two stars and place them ...
chapter16StarBirth
... – Stars greater than about 150MSun would be so luminous that radiation pressure would blow ...
... – Stars greater than about 150MSun would be so luminous that radiation pressure would blow ...
A Triple Conjunction
... millennium BC, however, no less than 7 triple conjunctions also took place – one every 140 years, on average – although the interval varied from 40 years (as between 861 and 821 BC and again between 563 and 523 BC) to 377 years (as between 523 BC and 146 BC). Over the millennium there were 43 “norma ...
... millennium BC, however, no less than 7 triple conjunctions also took place – one every 140 years, on average – although the interval varied from 40 years (as between 861 and 821 BC and again between 563 and 523 BC) to 377 years (as between 523 BC and 146 BC). Over the millennium there were 43 “norma ...
Chapter 12
... • Type I supernova is a carbon explosion, occurring when too much mass falls onto a white dwarf. • All heavy elements are formed in stellar cores or in supernovae. • Stellar evolution can be understood by observing star clusters. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Type I supernova is a carbon explosion, occurring when too much mass falls onto a white dwarf. • All heavy elements are formed in stellar cores or in supernovae. • Stellar evolution can be understood by observing star clusters. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
chapter16StarBirth
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure • Emission lines from molecules in a cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio ...
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure • Emission lines from molecules in a cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio ...
HERE - Montana State University Extended University
... Up to this point we have identified that the “just right” condition for life is the presence of liquid water on a planet’s surface. This suggests we should first search for a planet that rests in orbit around a Sun-like star (classes F, G or K) within the star’s zone of habitability. In addition to ...
... Up to this point we have identified that the “just right” condition for life is the presence of liquid water on a planet’s surface. This suggests we should first search for a planet that rests in orbit around a Sun-like star (classes F, G or K) within the star’s zone of habitability. In addition to ...
220913 - SunPM - Pmike
... People have seen patterns in the stars since ancient times. This 1690 depiction of the constellation of Leo, the lion, is by Johannes Hevelius. ...
... People have seen patterns in the stars since ancient times. This 1690 depiction of the constellation of Leo, the lion, is by Johannes Hevelius. ...
ppt document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... much, much more distant stars along the path of the Milky Way than off the Milky Way. The circular path of the Milky Way across the sky indicates that we (the sun and solar system) are inside a fairly thin disk of stars with the plane of the ecliptic tilted about 60o with respect to the plane of the ...
... much, much more distant stars along the path of the Milky Way than off the Milky Way. The circular path of the Milky Way across the sky indicates that we (the sun and solar system) are inside a fairly thin disk of stars with the plane of the ecliptic tilted about 60o with respect to the plane of the ...
Ayres-Kepler-ASC
... Coronal histories: B=red Sun=black (yellow: Cyc 21-23 shifted in time); bottom panel: Chandra (dots) & XMM (shaded, scaled). B has ~8 yr cycle, rising to new max. No clear period for A, modest cycle depth (‘flat activity’ star?) ...
... Coronal histories: B=red Sun=black (yellow: Cyc 21-23 shifted in time); bottom panel: Chandra (dots) & XMM (shaded, scaled). B has ~8 yr cycle, rising to new max. No clear period for A, modest cycle depth (‘flat activity’ star?) ...
Cepheid Variable Star RS Puppis
... measure whether a star was nearby or far away. Distances could be determined within our solar system and out to some of the nearest stars, but astronomers did not have a reliable way to measure the distances to remote stars or nebulae. As far as they could tell, our Milky Way Galaxy was the entire u ...
... measure whether a star was nearby or far away. Distances could be determined within our solar system and out to some of the nearest stars, but astronomers did not have a reliable way to measure the distances to remote stars or nebulae. As far as they could tell, our Milky Way Galaxy was the entire u ...
1 Exoplanets 2 Types of Exoplanets
... Exoplanets are a hot topic in astronomy right now. As of January, 2015, there are over 1500 confirmed exoplanet discoveries with more than 3000 candidates still waiting to be confirmed. These exoplanets and exoplanet systems are of extreme interest to astronomers as they provide insights into planet ...
... Exoplanets are a hot topic in astronomy right now. As of January, 2015, there are over 1500 confirmed exoplanet discoveries with more than 3000 candidates still waiting to be confirmed. These exoplanets and exoplanet systems are of extreme interest to astronomers as they provide insights into planet ...
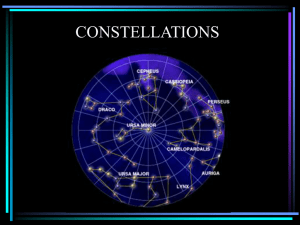
Constellations Overview
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
Post main sequence evolution
... -All stars in the cluster have the same age (were born at the same time) -Massive stars run out of fuel (leave the main sequence) sooner than less massive stars. The position of the “turn off point” is what tells us the age of a cluster. This is due to the fact that mass is related to the lifetime o ...
... -All stars in the cluster have the same age (were born at the same time) -Massive stars run out of fuel (leave the main sequence) sooner than less massive stars. The position of the “turn off point” is what tells us the age of a cluster. This is due to the fact that mass is related to the lifetime o ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... in proportions found in Bright Star Catalog (i.e. real sky). Top right -numbers calculated via equation 3. Bottom left, equal numbers of each magnitude. Bottom right -- numbers of each magnitude selected at random. If stars are not suns scattered through space then there is no reason for the real sk ...
... in proportions found in Bright Star Catalog (i.e. real sky). Top right -numbers calculated via equation 3. Bottom left, equal numbers of each magnitude. Bottom right -- numbers of each magnitude selected at random. If stars are not suns scattered through space then there is no reason for the real sk ...
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Stars and Gas in Galaxies
... • Multiple images of some quasars. • Background sources are magnified and distorted by gravitational lensing as the light passes through an intervening galaxy or cluster of galaxies. ...
... • Multiple images of some quasars. • Background sources are magnified and distorted by gravitational lensing as the light passes through an intervening galaxy or cluster of galaxies. ...
overview - FOSSweb
... The Sun, Moon, and Stars Module consists of three sequential investigations, each designed to introduce students to objects we see in the sky. Through outdoor observations made during the day and at night, active simulations, readings, videos, and discussions, students study the Sun, Moon, and stars ...
... The Sun, Moon, and Stars Module consists of three sequential investigations, each designed to introduce students to objects we see in the sky. Through outdoor observations made during the day and at night, active simulations, readings, videos, and discussions, students study the Sun, Moon, and stars ...
Observers` Forum - British Astronomical Association
... been monitoring the object on a semi-regular basis since early 2009. Gyulbudaghian’s nebula, also known as GM29, is illuminated by light emitted from the young energetic protostar PV Cephei. This has a mass of probably less than 7 solar masses, is of apparent type A5 and has been recorded as varying ...
... been monitoring the object on a semi-regular basis since early 2009. Gyulbudaghian’s nebula, also known as GM29, is illuminated by light emitted from the young energetic protostar PV Cephei. This has a mass of probably less than 7 solar masses, is of apparent type A5 and has been recorded as varying ...
Studies of young stellar objects (25+5)
... The structure of disks can tell us a lot about how is planet formation taking place… • According to Durisen (2009) there are two main models for the formation of giant planets: • 1. Core accretion: Will produce gaps in disks, as possibly observed in HL Tau. • 2. Disk instability: Will produce spira ...
... The structure of disks can tell us a lot about how is planet formation taking place… • According to Durisen (2009) there are two main models for the formation of giant planets: • 1. Core accretion: Will produce gaps in disks, as possibly observed in HL Tau. • 2. Disk instability: Will produce spira ...
Stellar Evolution 1
... Life tracks for protostars Star birth similar for all stars, but massive stars pass through the stages faster ...
... Life tracks for protostars Star birth similar for all stars, but massive stars pass through the stages faster ...
Formation of Solar System
... Rotating solar nebula was gaseous and hot. The molecules move quickly and are ionised in collisions – thus a plasma of ions and free electrons forms. The motion of charged particles creates a magnetic field. The nucleus of the solar nebula thus had a magnetic field associated with it. Matter close ...
... Rotating solar nebula was gaseous and hot. The molecules move quickly and are ionised in collisions – thus a plasma of ions and free electrons forms. The motion of charged particles creates a magnetic field. The nucleus of the solar nebula thus had a magnetic field associated with it. Matter close ...
More About Individual Term Projects
... In this case, you may use the known period of 2.8673 days if your observations do not let you determine the period independently. You will need to observe more than one minimum if you want to independently determine the period of Algol. ...
... In this case, you may use the known period of 2.8673 days if your observations do not let you determine the period independently. You will need to observe more than one minimum if you want to independently determine the period of Algol. ...
Document
... changes. From an observed line profile, one can construct an image of the surface of the star. This technique has been applied to many different types of stars. ...
... changes. From an observed line profile, one can construct an image of the surface of the star. This technique has been applied to many different types of stars. ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.