Astronomy 100—Exam 1
... A. The baby was just born. D. The baby is about 1 day old. B. The baby is about 4 years old. E. The baby is about 100 years old. C. The baby is about 100 light-years old. 10. The principal use of dividing the sky up into constellations today is to A. identify regions and/or designate positions for o ...
... A. The baby was just born. D. The baby is about 1 day old. B. The baby is about 4 years old. E. The baby is about 100 years old. C. The baby is about 100 light-years old. 10. The principal use of dividing the sky up into constellations today is to A. identify regions and/or designate positions for o ...
Supernova and Supernova Remnants lec 1-2
... Type I SN and Cosmology • how old is the universe, how fast is it expanding, how much material and of what type is in it, what is its fate? • Need to determine the relationship between distance and redshift – Redshift (‘z’) is the measure of Doppler shift by the expansion of the universe- (1+z)~v/c ...
... Type I SN and Cosmology • how old is the universe, how fast is it expanding, how much material and of what type is in it, what is its fate? • Need to determine the relationship between distance and redshift – Redshift (‘z’) is the measure of Doppler shift by the expansion of the universe- (1+z)~v/c ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
Papervision3D star (sun) tutorial and source - 02
... The star’s gradient Actually, it took quite some tweaking to get a nice gradient of white in the middle and yellow to red on the edge. It’s a basic Sprite gradient fill, using three colors, alpha layering and a specific color ratio array to get the last two colors (yellow and red) on the edge. Then ...
... The star’s gradient Actually, it took quite some tweaking to get a nice gradient of white in the middle and yellow to red on the edge. It’s a basic Sprite gradient fill, using three colors, alpha layering and a specific color ratio array to get the last two colors (yellow and red) on the edge. Then ...
Bringing E.T. into Your Classroom The Search for
... to find planets using the transit method. If it doesn't matter, write EQUAL CHANCE 1. Less massive stars or more massive stars. 2. Planets with orbits that are closer to circular or highly elliptical orbits. 3. Face-on orbits or edge-on orbits. 4. Small diameter planets or large diameter planets. 5. ...
... to find planets using the transit method. If it doesn't matter, write EQUAL CHANCE 1. Less massive stars or more massive stars. 2. Planets with orbits that are closer to circular or highly elliptical orbits. 3. Face-on orbits or edge-on orbits. 4. Small diameter planets or large diameter planets. 5. ...
Galaxy clusters - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... • From this, the amount of X-ray emitting gas can be calculated to be 2×1014 M • The mass of X-ray emitting gas is greater than the mass in all the stars in all the galaxies in the cluster and about 10% of the total mass. ...
... • From this, the amount of X-ray emitting gas can be calculated to be 2×1014 M • The mass of X-ray emitting gas is greater than the mass in all the stars in all the galaxies in the cluster and about 10% of the total mass. ...
Galaxies - Stockton University
... In the Solar neighborhood, an average main-sequence star (excluding binary stars) is separated by of order 107 times its size from its nearest neighbors (1 Solar Radius vs. 1 pc). Galaxies on the other hand have sizes ranging from 1 to 100 Kpc, but are separated by of order 1 to 10 Mpc from their ne ...
... In the Solar neighborhood, an average main-sequence star (excluding binary stars) is separated by of order 107 times its size from its nearest neighbors (1 Solar Radius vs. 1 pc). Galaxies on the other hand have sizes ranging from 1 to 100 Kpc, but are separated by of order 1 to 10 Mpc from their ne ...
Where do elements come from?
... What happens to the high mass stars when they exhaust their He fuel? • They have enough gravitational energy to heat up to 6 x 108 K. – C fuses into O ...
... What happens to the high mass stars when they exhaust their He fuel? • They have enough gravitational energy to heat up to 6 x 108 K. – C fuses into O ...
Size and Scale of the Universe
... • Need telescopes with high resolution, and must observe over several years • The Hipparchos satellite measured distances using this method for tens of thousands of stars within 1,500 light-years of the Sun ...
... • Need telescopes with high resolution, and must observe over several years • The Hipparchos satellite measured distances using this method for tens of thousands of stars within 1,500 light-years of the Sun ...
Studying Science
... Objects that are very far away do not appear to move at all Same for stars and planets ...
... Objects that are very far away do not appear to move at all Same for stars and planets ...
Using photometric analysis to determine characteristics of the V
... In this paper, we will therefore focus our attention at looking at the visual light curves of V‐2491 (photometric analysis) to further categorize this newly seen classical nova based on its behavior according to the duration of rise to maximum and the fall to minimum light. ...
... In this paper, we will therefore focus our attention at looking at the visual light curves of V‐2491 (photometric analysis) to further categorize this newly seen classical nova based on its behavior according to the duration of rise to maximum and the fall to minimum light. ...
The Evolution of Stars - a More Detailed Picture (Chapter 8
... is born, and the star appears on the Main Sequence. The timescale of evolution onto the Main Sequence is relatively short, given by the Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale : t KH = ...
... is born, and the star appears on the Main Sequence. The timescale of evolution onto the Main Sequence is relatively short, given by the Kelvin-Helmholtz timescale : t KH = ...
INSIDE LAB 7: Measuring the Velocities of Stars
... a star is a plot of the intensity of the light coming from that star as a function of wavelength. Although we like to pretend that stellar spectra are simply block body distributions, the reality is far more complex. Consider, for example, the spectrum in Fig. 1, showing the actual spectrum of a sta ...
... a star is a plot of the intensity of the light coming from that star as a function of wavelength. Although we like to pretend that stellar spectra are simply block body distributions, the reality is far more complex. Consider, for example, the spectrum in Fig. 1, showing the actual spectrum of a sta ...
Size and Scale of the Universe
... • Need telescopes with high resolution, and must observe over several years • The Hipparchos satellite measured distances using this method for tens of thousands of stars within 1,500 light-years of the Sun ...
... • Need telescopes with high resolution, and must observe over several years • The Hipparchos satellite measured distances using this method for tens of thousands of stars within 1,500 light-years of the Sun ...
No Slide Title
... Solar Eclipse. A solar eclipse can occur when there is a new moon. This does not occur every month because the moon's orbital plane doesn't "lie flat" along the ecliptic, but forms an angle of about 5º as you can see in this diagram (note: the distances in this diagram are not to scale). http://www. ...
... Solar Eclipse. A solar eclipse can occur when there is a new moon. This does not occur every month because the moon's orbital plane doesn't "lie flat" along the ecliptic, but forms an angle of about 5º as you can see in this diagram (note: the distances in this diagram are not to scale). http://www. ...
Chapter 20
... 12.1b The Birth Cries of Stars The jets of gas were formed as the pre-main-sequence star contracted under the force of its own gravity. Because a thick disk of cool gas and dust surrounds the premainsequence star, the gas squirts outward along the pre-main-sequence star’s axis of rotation at speeds ...
... 12.1b The Birth Cries of Stars The jets of gas were formed as the pre-main-sequence star contracted under the force of its own gravity. Because a thick disk of cool gas and dust surrounds the premainsequence star, the gas squirts outward along the pre-main-sequence star’s axis of rotation at speeds ...
MySci Unit 23
... A. The Earth, Sun, and Moon are part of a larger system that includes other planets and smaller celestial bodies a. Observe and identify the Earth is one of several planets within a solar system that orbits the Sun b. Observe and identify the Moon orbits the Earth in about a month Identify that plan ...
... A. The Earth, Sun, and Moon are part of a larger system that includes other planets and smaller celestial bodies a. Observe and identify the Earth is one of several planets within a solar system that orbits the Sun b. Observe and identify the Moon orbits the Earth in about a month Identify that plan ...
Chapter 2 Test Review Vocabulary • axis – an imaginary line
... Why does the moon’s shape look different on different nights? As the moon revolves around Earth, different amounts of its bright side can be seen. Stars Why does the sun look larger than the other stars you can see? The sun looks larger than other stars you can see because it is so much clos ...
... Why does the moon’s shape look different on different nights? As the moon revolves around Earth, different amounts of its bright side can be seen. Stars Why does the sun look larger than the other stars you can see? The sun looks larger than other stars you can see because it is so much clos ...
Celestial Motions - Georgia State University
... – We can see over 2,000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along the horizon • Why do stars rise and set? – Becau ...
... – We can see over 2,000 stars and the Milky Way with our naked eyes, and each position on the sky belongs to one of 88 constellations – We can specify the position of an object in the local sky by its altitude above the horizon and its direction along the horizon • Why do stars rise and set? – Becau ...
Measuring Radii and Temperatures of Stars
... (work in cgs or MKS units or work in AU and use the definition of a parsec) What would the angular diameter of the Sun be at 10 pc? ...
... (work in cgs or MKS units or work in AU and use the definition of a parsec) What would the angular diameter of the Sun be at 10 pc? ...
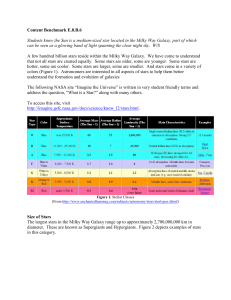
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... Students know the Sun is a medium-sized star located in the Milky Way Galaxy, part of which can be seen as a glowing band of light spanning the clear night sky. W/S Common misconceptions associated with this benchmark 1. Students have a misconception that all stars are the same size. When viewing th ...
... Students know the Sun is a medium-sized star located in the Milky Way Galaxy, part of which can be seen as a glowing band of light spanning the clear night sky. W/S Common misconceptions associated with this benchmark 1. Students have a misconception that all stars are the same size. When viewing th ...
Astronomy
... Unlike the others (which are in sight and thereby reached by the light), your back not belong (because it is not facing the light). Which Doesn’t Belong & Why? ...
... Unlike the others (which are in sight and thereby reached by the light), your back not belong (because it is not facing the light). Which Doesn’t Belong & Why? ...
Corvus (constellation)

Corvus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its name comes from the Latin word ""raven"" or ""crow"". It includes only 11 stars with brighter than 4.02 magnitudes. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The four brightest stars, Gamma, Delta, Epsilon, and Beta Corvi from a distinctive quadrilateral in the night sky. The young star Eta Corvi has been found to have two debris disks.