Stars
... Our star, the Sun, is considered to be average in comparison to the size of other stars. ...
... Our star, the Sun, is considered to be average in comparison to the size of other stars. ...
The Ursa Major Moving Cluster, Collinder 285
... at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluster is centered at a distance of about 75 light years from us (i.e., our solar system). As it is spread over a volume of 30 light years length and 18 light years width, it covers an enourmous portion of the sky, an ...
... at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluster is centered at a distance of about 75 light years from us (i.e., our solar system). As it is spread over a volume of 30 light years length and 18 light years width, it covers an enourmous portion of the sky, an ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • Matter started to “clump” back together • This was due to gravity • The galaxies, stars and planets formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of billions of stars ...
... • Matter started to “clump” back together • This was due to gravity • The galaxies, stars and planets formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of billions of stars ...
File
... The explosion called a supernova occurs after a large star has become a red supergiant. When the star stops expanding because it can no longer create enough energy to support its own mass, it collapses completely and makes a giant explosion. A supernova is brighter than all the stars in the galaxy c ...
... The explosion called a supernova occurs after a large star has become a red supergiant. When the star stops expanding because it can no longer create enough energy to support its own mass, it collapses completely and makes a giant explosion. A supernova is brighter than all the stars in the galaxy c ...
Chapter 24 Vocabulary
... 1. constellation- grouping of stars that has a shape resembling an animal, mythological character, or other object and is thus named for it 2. magnitude- in earthquake studies, a measure of the energy released by an earthquake; the Richter scale is used to describe earthquake magnitude 3. parallax- ...
... 1. constellation- grouping of stars that has a shape resembling an animal, mythological character, or other object and is thus named for it 2. magnitude- in earthquake studies, a measure of the energy released by an earthquake; the Richter scale is used to describe earthquake magnitude 3. parallax- ...
The Sun's Crowded Delivery Room
... formation, have no evidence for 60Fe (low ε60Ni) www.psrd.hawaii.edu/July07/iron-60.html ...
... formation, have no evidence for 60Fe (low ε60Ni) www.psrd.hawaii.edu/July07/iron-60.html ...
Supernova’s
... leading to its collapse • Becomes Red Giant Star • Turns into a White Dwarf Star ...
... leading to its collapse • Becomes Red Giant Star • Turns into a White Dwarf Star ...
The Sun . . .
... where it expands and grows cooler and more luminous. Its final stage is white dwarf, after it collapses upon itself and only the hot, dense core will remain. ...
... where it expands and grows cooler and more luminous. Its final stage is white dwarf, after it collapses upon itself and only the hot, dense core will remain. ...
Lesson 10 Red Shift
... "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, violet and red each have a characteristic range of wavelengths. In the visible spectrum, violet has the shortest wavelengths and red as the longest. Normally when we look at white light, such as from the Sun ...
... "visual spectrum." In the visual spectrum, wavelength corresponds to colour. In other words, violet and red each have a characteristic range of wavelengths. In the visible spectrum, violet has the shortest wavelengths and red as the longest. Normally when we look at white light, such as from the Sun ...
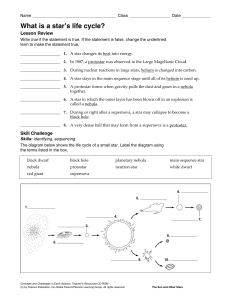
What is a star`s life cycle?
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Star Characteristics
... Color + Temperature = Length of life Blue and white are the brightest Yellow stars last 10 billion years Red stars last longer It then turns into a super giant or red giant. ...
... Color + Temperature = Length of life Blue and white are the brightest Yellow stars last 10 billion years Red stars last longer It then turns into a super giant or red giant. ...
Roy - WordPress.com
... stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its brightest stars form a V shape along with the brighter red giant Aldebaran, which is not part of the cluster, but merely lying along our line of sight. The age of the Hyades is e ...
... stars sharing the same age, place of origin, chemical content, and motion through space. In the constellation Taurus, its brightest stars form a V shape along with the brighter red giant Aldebaran, which is not part of the cluster, but merely lying along our line of sight. The age of the Hyades is e ...
PowerPoint - Earth Science with Mrs. Wilson
... system. It is about 4 light years away. Going the speed of light it would take us 4 years to get there. Traveling as fast as the average spaceship, it would take between 70,000 and 100,000 years to get there! ...
... system. It is about 4 light years away. Going the speed of light it would take us 4 years to get there. Traveling as fast as the average spaceship, it would take between 70,000 and 100,000 years to get there! ...
Astronomy Part 2 - Malvern Troop 7
... To the top left, above the winter triangle lies Castor and Pollux, the celestial twins in the constellation Gemini. ...
... To the top left, above the winter triangle lies Castor and Pollux, the celestial twins in the constellation Gemini. ...
Virtual Sky II (Rev 10/11)
... Cygnus, Lyra, Ursa Major and Ursa Minor. Label Deneb and Polaris. ...
... Cygnus, Lyra, Ursa Major and Ursa Minor. Label Deneb and Polaris. ...
Scientists Observe Star Triplets Being Born : Space
... multiple-star system. Scientists suspected that the process was casused by a gravitational instability, but new observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) showed the process in action. John Tobin, from the University of Okl ...
... multiple-star system. Scientists suspected that the process was casused by a gravitational instability, but new observations from the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) showed the process in action. John Tobin, from the University of Okl ...
Distance and Luminosity (new 2012)
... Because of the Earth's revolution around the Sun, nearby stars appear to move with respect to very distant stars which seem to be standing still. Measure the angle to the star and observe how it changes as the position of the earth changes. In the diagram if the observation point is at the top of th ...
... Because of the Earth's revolution around the Sun, nearby stars appear to move with respect to very distant stars which seem to be standing still. Measure the angle to the star and observe how it changes as the position of the earth changes. In the diagram if the observation point is at the top of th ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.