Gr9_unit1_ch10_notes-2015
... Looking down from the north pole, the earth spins in a counterclockwise direction on an imaginary line called its axis once every day. This accounts for the fact that the sun rises in the east and sets in the west. Movement of Comets and Asteroids Comets are small bodies made up of rock and ice, th ...
... Looking down from the north pole, the earth spins in a counterclockwise direction on an imaginary line called its axis once every day. This accounts for the fact that the sun rises in the east and sets in the west. Movement of Comets and Asteroids Comets are small bodies made up of rock and ice, th ...
this article as a PDF
... spot where Scorpio, the Scorpion stung Orion after a brief and fierce battle. Its Arabic name means the Foot. Rigel is a multiple star system. The brighter component, Rigel A, is a blue super giant that shines a remarkable 40,000 times stronger than the Sun! Although 775 light-years distant, its lig ...
... spot where Scorpio, the Scorpion stung Orion after a brief and fierce battle. Its Arabic name means the Foot. Rigel is a multiple star system. The brighter component, Rigel A, is a blue super giant that shines a remarkable 40,000 times stronger than the Sun! Although 775 light-years distant, its lig ...
Stellar Evolution
... layers of the star are now pushed outward. The star expands to larger than it ever was during its lifetime a few to about a hundred times bigger. ...
... layers of the star are now pushed outward. The star expands to larger than it ever was during its lifetime a few to about a hundred times bigger. ...
Thursday October 1 - Montana State University
... Compare absolute and apparent magnitudes • If we know the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of a star, we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
... Compare absolute and apparent magnitudes • If we know the luminosity (or absolute magnitude) of a star, we can find its distance. • A star of known luminosity is called a standard candle. • More on this later... ...
Types of Planetary System
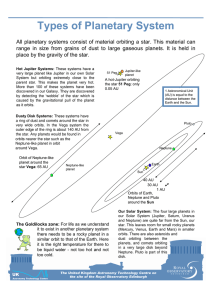
... very large planet like Jupiter in our own Solar System but orbiting extremely close to the parent star. This makes the planet very hot. More than 100 of these systems have been discovered in our Galaxy. They are discovered by detecting the ‘wobble’ of the star which is caused by the gravitational pu ...
... very large planet like Jupiter in our own Solar System but orbiting extremely close to the parent star. This makes the planet very hot. More than 100 of these systems have been discovered in our Galaxy. They are discovered by detecting the ‘wobble’ of the star which is caused by the gravitational pu ...
Lifecycle of the stars.
... hydrogen nuclei smash each other together at high speeds. Then the hydrogen nuclei stick together to make a large nucleus. last, big amounts of energy (fusion is only caused in the sun and in fission bombs aka H-bombs) ...
... hydrogen nuclei smash each other together at high speeds. Then the hydrogen nuclei stick together to make a large nucleus. last, big amounts of energy (fusion is only caused in the sun and in fission bombs aka H-bombs) ...
Binary Star Systems Discussion Points 1. What characteristic of a
... a) The two stars are too close together to be resolved by a telescope. b) The two stars are too far away to be able to separate their images. c) One of the stars is too small or too dim to be able to see it against the glare of the larger, brighter star. 7. The spectroscopic lines periodically split ...
... a) The two stars are too close together to be resolved by a telescope. b) The two stars are too far away to be able to separate their images. c) One of the stars is too small or too dim to be able to see it against the glare of the larger, brighter star. 7. The spectroscopic lines periodically split ...
- Stevenson High School
... stars are circumpolar (perpetually in the sky, even over a 24 hours’ period). Which one of the constellations below besides Little Dipper contains stars that are circumpolar for our mid-northern hemisphere Star Wheel observer? a) Betelgeuse b) Sagittarius c) Cepheus d) Taurus 22. The daily motion of ...
... stars are circumpolar (perpetually in the sky, even over a 24 hours’ period). Which one of the constellations below besides Little Dipper contains stars that are circumpolar for our mid-northern hemisphere Star Wheel observer? a) Betelgeuse b) Sagittarius c) Cepheus d) Taurus 22. The daily motion of ...
Redshift - Old Age and Red Giants
... Giants and Supergiants: Rigel, Deneb, Canopus Q6. Betelgeuse and Antares are both large red stars with short remaining lifetimes. Q7. Large red stars are cooling and near the end of their lifetimes. Q8. Antares is an M1 I star and will likely turn into an M2 I star like Betelgeuse. Q9. Deneb (A2 I) ...
... Giants and Supergiants: Rigel, Deneb, Canopus Q6. Betelgeuse and Antares are both large red stars with short remaining lifetimes. Q7. Large red stars are cooling and near the end of their lifetimes. Q8. Antares is an M1 I star and will likely turn into an M2 I star like Betelgeuse. Q9. Deneb (A2 I) ...
Sample Midterm - IUPUI Physics
... • B) The period of variability allows you to determine its absolute brightness • C) The time it takes to vary its brightness is determined by how long the light took to get to us • D) all of the above 8) If attempting to determine the distance to a nearby galaxy which is the better type of variable ...
... • B) The period of variability allows you to determine its absolute brightness • C) The time it takes to vary its brightness is determined by how long the light took to get to us • D) all of the above 8) If attempting to determine the distance to a nearby galaxy which is the better type of variable ...
Page # 320 15
... 12. Pluto has strongly elliptical orbit so sometimes it passes inside Neptune’s orbit 13. Pluto, Uranus, Venus rotate backward (retrograde) ...
... 12. Pluto has strongly elliptical orbit so sometimes it passes inside Neptune’s orbit 13. Pluto, Uranus, Venus rotate backward (retrograde) ...
Page 1 Astronomy 110 Homework #08 Assigned: 03/13/2007 Due
... A) to dim and redden distant stars by preferentially scattering their blue light. B) to scatter the red light from stars preferentially, making them appear more blue than expected. C) almost nonexistent, because light does not interact with dust. D) to make stars appear less bright than expected by ...
... A) to dim and redden distant stars by preferentially scattering their blue light. B) to scatter the red light from stars preferentially, making them appear more blue than expected. C) almost nonexistent, because light does not interact with dust. D) to make stars appear less bright than expected by ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... • Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula • Once stars are formed they enter the main sequence stage. In this stage they continuously generate energy in the core through nuclear fusion. • Size, structure and composition change very little during this stage. ...
... • Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called a nebula • Once stars are formed they enter the main sequence stage. In this stage they continuously generate energy in the core through nuclear fusion. • Size, structure and composition change very little during this stage. ...
HNRS 227 Lecture #2 Chapters 2 and 3
... The Tully-Fisher relation, which correlates the width of the 21cm line of hydrogen in a spiral galaxy with its luminosity, can also be used for determining distance A method that can be used for elliptical galaxies is the fundamental plane, which relates the galaxy’s size to its surface brightne ...
... The Tully-Fisher relation, which correlates the width of the 21cm line of hydrogen in a spiral galaxy with its luminosity, can also be used for determining distance A method that can be used for elliptical galaxies is the fundamental plane, which relates the galaxy’s size to its surface brightne ...
Red Giants
... I'll give you a short answer and a longer one. The short answer is that towards the end of a star's life, the temperature near the core rises and this causes the size of the star to expand. This is the fate of the Sun in about 5 billion years. You might want to mark your calendar!The long answer is ...
... I'll give you a short answer and a longer one. The short answer is that towards the end of a star's life, the temperature near the core rises and this causes the size of the star to expand. This is the fate of the Sun in about 5 billion years. You might want to mark your calendar!The long answer is ...
Stars - Red, Blue, Old, New pt.3
... • The Sun (and other stars less than about 10 solar masses) will never be a supergiant. • Stars more massive than about 10 solar masses do get to be supergiants. • The massive stars fuse elements up to iron and they do it fast…timescales 1000s of ...
... • The Sun (and other stars less than about 10 solar masses) will never be a supergiant. • Stars more massive than about 10 solar masses do get to be supergiants. • The massive stars fuse elements up to iron and they do it fast…timescales 1000s of ...
File
... following causes the phases of the moon? A. Over the course of a month, different parts of the moon’s reflected sunlight are visible from Earth. B. The moon reflects differing amounts of sunlight as it revolves around the Earth. C. The moon rotates more slowly than the Earth, with one rotation every ...
... following causes the phases of the moon? A. Over the course of a month, different parts of the moon’s reflected sunlight are visible from Earth. B. The moon reflects differing amounts of sunlight as it revolves around the Earth. C. The moon rotates more slowly than the Earth, with one rotation every ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.