SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 6
... conditions, M1 can be a tough quarry. Ursa Major (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 32) The Big Dipper asterism within the constellation Ursa Major is one of the most wellknown patterns in the sky. But the Big Bear boasts more delights than those within the dipper. Lets go Owl hunting. Messier 97 is a faint ...
... conditions, M1 can be a tough quarry. Ursa Major (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 32) The Big Dipper asterism within the constellation Ursa Major is one of the most wellknown patterns in the sky. But the Big Bear boasts more delights than those within the dipper. Lets go Owl hunting. Messier 97 is a faint ...
Earth Science: Chapter 7: Stellar Evolution: Spring 2017: Student
... Greater than 20 Less than 10 million years Same as above except the mass is great enough to solar masses form a BLACK HOLE (see below) Planetary nebula: after a red giant forms material from the star is ejected and forms what looks like a nebula. The name planetary is actually misnamed by an early a ...
... Greater than 20 Less than 10 million years Same as above except the mass is great enough to solar masses form a BLACK HOLE (see below) Planetary nebula: after a red giant forms material from the star is ejected and forms what looks like a nebula. The name planetary is actually misnamed by an early a ...
Make one copy for each student on plain paper. Life Cycle of Star
... its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. They live for billions of years before becoming a red giant. ...
... its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. They live for billions of years before becoming a red giant. ...
Life Cycle of Star Pictures
... its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. They live for billions of years before becoming a red giant. ...
... its own heat and light by nuclear reactions. They live for billions of years before becoming a red giant. ...
Supernova: Five Stages in the Death of a Star
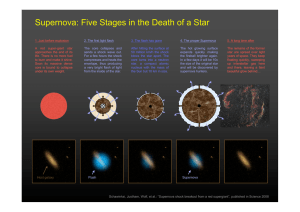
... For a few hours the shock compresses and heats the envelope, thus producing a very bright flash of light from the inside of the star. ...
... For a few hours the shock compresses and heats the envelope, thus producing a very bright flash of light from the inside of the star. ...
File
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
... called the plane of the ecliptic (or just the ecliptic). The zodiac is the group (or “belt”) of constellations that fall along the plane of the ecliptic. It is through these constellations that our Sun appears to “pass” during the year. While there are 12 astrological constellations of the zodiac, t ...
Stellar Evolution 1 Star Formation 2 Nebulae
... What are the basic properties of giant molecular clouds? How do clumps form in giant molecular clouds? How do clumps in giant molecular clouds evolve? What are the conditions for which this kind of evolution takes place? Where are protostars found on an H-R diagram? How do their locations on ...
... What are the basic properties of giant molecular clouds? How do clumps form in giant molecular clouds? How do clumps in giant molecular clouds evolve? What are the conditions for which this kind of evolution takes place? Where are protostars found on an H-R diagram? How do their locations on ...
29.2 - Stars - s3.amazonaws.com
... Star • A star is a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat • Appear to be tiny specks of white light • Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth ...
... Star • A star is a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat • Appear to be tiny specks of white light • Most vary in color and are much larger than Earth ...
Star Questions 2008 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... A core collapse of a supermassive star or a star that has a core mass that exceeds 1.4 solar masses that produces an extreme explosion and fuses all heavy elements observed in the universe. 10. Describe the difference between a Type I and Type II supernova? Type I supernovae develop as the star accu ...
... A core collapse of a supermassive star or a star that has a core mass that exceeds 1.4 solar masses that produces an extreme explosion and fuses all heavy elements observed in the universe. 10. Describe the difference between a Type I and Type II supernova? Type I supernovae develop as the star accu ...
Assessment 1 - Stars - Teacher Key
... A red giant forms when the star’s hydrogen level drops. 4 ...
... A red giant forms when the star’s hydrogen level drops. 4 ...
STAR SYTEMS AND GALAXIES
... • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enough gravity to effect the star. ...
... • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enough gravity to effect the star. ...
Astronomy Study Guide #2
... 23. What is the ``Doppler Effect" and how does it apply to light? And to stars? 24. Why are the Balmer lines of hydrogen important? What are they and how are they formed? (Hint: We saw these in the spectral tube demonstrations.) 25. How will stars less massive than 1.5 M_0 end their Post-Main Seque ...
... 23. What is the ``Doppler Effect" and how does it apply to light? And to stars? 24. Why are the Balmer lines of hydrogen important? What are they and how are they formed? (Hint: We saw these in the spectral tube demonstrations.) 25. How will stars less massive than 1.5 M_0 end their Post-Main Seque ...
PPT - UBC
... Kepler's Laws, Mass-radius relationship. Pre-reading pages 23 - 33, 48 - 49, 180 - 198. (f) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, dwarf, giant and supergiant stars, white dwarfs, first clues to stellar evolution. Pre-reading Chapter 8. ...
... Kepler's Laws, Mass-radius relationship. Pre-reading pages 23 - 33, 48 - 49, 180 - 198. (f) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, dwarf, giant and supergiant stars, white dwarfs, first clues to stellar evolution. Pre-reading Chapter 8. ...
Wednesday, April 2 - Otterbein University
... • Then do the following Gedankenexperiment: – In your mind, put the star from its actual position to a position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its a ...
... • Then do the following Gedankenexperiment: – In your mind, put the star from its actual position to a position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its a ...
Phys 100 – Astronomy (Dr. Ilias Fernini) Review Questions for
... Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, galaxy clusters Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Earth, Milky Way, Solar System, galaxy clusters Galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way, Earth ...
... Earth, Solar System, Milky Way, galaxy clusters Solar System, Earth, galaxy clusters, Milky Way Earth, Milky Way, Solar System, galaxy clusters Galaxy clusters, Solar System, Milky Way, Earth ...
Star Life Cycle
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
... A Red Giant Star is a main sequence star that is not longer in equilibrium. There is a ...
8.3 Stars
... Over a very long time, a white dwarf will cool to temperatures at which it is no longer visible and become a cold black dwarf; become a lump of coal in the sky when all its nuclear energy is gone ...
... Over a very long time, a white dwarf will cool to temperatures at which it is no longer visible and become a cold black dwarf; become a lump of coal in the sky when all its nuclear energy is gone ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.