UCCS PES 1050 Astronomy 1 WK Spring 2012 Assignment 1 name
... How many individual stars might a person with good vision but without optical aids be able to see as separate points of light between sunrise and sunset on a clear night from a site away from cities that is not light-polluted? At best a few dozen A few thousand About 1,000,000 Billions Hundreds of t ...
... How many individual stars might a person with good vision but without optical aids be able to see as separate points of light between sunrise and sunset on a clear night from a site away from cities that is not light-polluted? At best a few dozen A few thousand About 1,000,000 Billions Hundreds of t ...
Properties of Stars - Indiana State University
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
... Analyzing the HR Diagram • The Stefan-Boltzmann law is a key to understanding the H-R diagram – For stars of a given temperature, the larger the radius, the larger the luminosity – Therefore, as one moves up the H-R diagram, a star’s radius must become bigger – On the other hand, for a given lumino ...
The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog
... planned their schemes. The presses of the newspapers roared through the night, and many a priest of this church and that would not open his holy building to further what he considered a foolish panic. The newspapers insisted on the lesson of the year 1000--for then, too, people had anticipated the e ...
... planned their schemes. The presses of the newspapers roared through the night, and many a priest of this church and that would not open his holy building to further what he considered a foolish panic. The newspapers insisted on the lesson of the year 1000--for then, too, people had anticipated the e ...
ISP 205: Visions of the Universe
... • Light travels at a finite speed (300,000 km/s). • The farther away we look in distance, the further back we look in time. • Allows us to study the history of the Universe. ...
... • Light travels at a finite speed (300,000 km/s). • The farther away we look in distance, the further back we look in time. • Allows us to study the history of the Universe. ...
February 2013 - astronomy for beginners
... Lyrae and is the 5th star in Lyra. In the chart above it can be found just north (above) the brightest star α (Vega). The two pairs of the double double are labelled as ε1 and ε2 and are separated by 208″. In turn each pair is separated by just 2″, about 160 AU (1 AU = Earth / Sun distance). The fou ...
... Lyrae and is the 5th star in Lyra. In the chart above it can be found just north (above) the brightest star α (Vega). The two pairs of the double double are labelled as ε1 and ε2 and are separated by 208″. In turn each pair is separated by just 2″, about 160 AU (1 AU = Earth / Sun distance). The fou ...
Class II Supernova
... •It will produce as much energy in it’s time span, then the sun will in its lifetime. •It is not uncommon for a supernova to outshine an entire galaxy. •Quite rare, but sometimes 1 supernova will trigger another one to start. •A type II must have from 3-9 solar masses. ...
... •It will produce as much energy in it’s time span, then the sun will in its lifetime. •It is not uncommon for a supernova to outshine an entire galaxy. •Quite rare, but sometimes 1 supernova will trigger another one to start. •A type II must have from 3-9 solar masses. ...
hwk06ans
... This is the desired formula, with C2 = C12 ( f(s) f(s) / s2 ) d s . Recall that part (a) gave a formula for C1 . So far we have accumulated a bunch of definite and indefinite integrals. Since each of them is specified in terms of the original function f(s) , a computer would not have any ser ...
... This is the desired formula, with C2 = C12 ( f(s) f(s) / s2 ) d s . Recall that part (a) gave a formula for C1 . So far we have accumulated a bunch of definite and indefinite integrals. Since each of them is specified in terms of the original function f(s) , a computer would not have any ser ...
Study Guide Beginning Astronomy
... Where did various kinds of atoms come from? During the first 5 minutes after the Big Bang protons, helium nuclei, a teeny bit of deuterium and lithium, plus lots of electrons were created. 400,000 years later the universe was cool enough for the electrons to combine with those protons to make neutr ...
... Where did various kinds of atoms come from? During the first 5 minutes after the Big Bang protons, helium nuclei, a teeny bit of deuterium and lithium, plus lots of electrons were created. 400,000 years later the universe was cool enough for the electrons to combine with those protons to make neutr ...
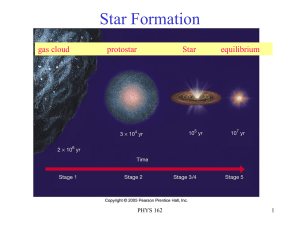
Star Birth: The Formation of Stars Jonathan Rowles
... A star is a luminous ball of gas. They produce energy by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to form helium. They range in size from 0.08 times the mass of the Sun to up to 120 Solar masses. They can have lifetimes ranging from a few million years to the age of the universe. ...
... A star is a luminous ball of gas. They produce energy by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen to form helium. They range in size from 0.08 times the mass of the Sun to up to 120 Solar masses. They can have lifetimes ranging from a few million years to the age of the universe. ...
Laboratory Procedure (Word Format)
... If the star is not in the plane of the ecliptic, but is at a celestial latitude (L), the value of VO just obtained should be corrected for by dividing it by the cosine L. The observational material for this exercise consists of two spectrograms of Arcturus taken about one half year apart on July 1, ...
... If the star is not in the plane of the ecliptic, but is at a celestial latitude (L), the value of VO just obtained should be corrected for by dividing it by the cosine L. The observational material for this exercise consists of two spectrograms of Arcturus taken about one half year apart on July 1, ...
Space Study Guide
... As technology increased, scientists made more and more observations that supported the Big Bang Model. 1. In 1929, Edwin Hubble observed that the spectral lines from other galaxies tended to always shift toward the red end of the spectrum. According to the Doppler Effect, causes this change of obser ...
... As technology increased, scientists made more and more observations that supported the Big Bang Model. 1. In 1929, Edwin Hubble observed that the spectral lines from other galaxies tended to always shift toward the red end of the spectrum. According to the Doppler Effect, causes this change of obser ...
solutions
... C). Conceptually, what effects would it have on the binary? If the velocity kick adds (vectorally) with the orbital motion, it will aid in unbinding the system. If the kick subtracts from the orbital motion, the binary could tighten (one rare possibility is a Thorne-Zytkow object). Note, though, tha ...
... C). Conceptually, what effects would it have on the binary? If the velocity kick adds (vectorally) with the orbital motion, it will aid in unbinding the system. If the kick subtracts from the orbital motion, the binary could tighten (one rare possibility is a Thorne-Zytkow object). Note, though, tha ...
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
... stars with the same age but different masses • Birth Main Sequence Red Giant “live+die” faster if higher mass • tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
T = 5800 K
... The collisions broaden the absorption lines in the star’s spectrum. Giant stars are larger and less dense than main sequence stars, so their absorption lines are narrower than those of main sequence stars. The spectra shown above illustrate this effect. Notice that the absorption lines in the spectr ...
... The collisions broaden the absorption lines in the star’s spectrum. Giant stars are larger and less dense than main sequence stars, so their absorption lines are narrower than those of main sequence stars. The spectra shown above illustrate this effect. Notice that the absorption lines in the spectr ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... Cepheid variable stars expand and contract in a repeating cycle of size changes. The change in size can be observed as a change in apparent brightness (apparent magnitude.) Cepheids have a repeating cycle of change that is periodic - as regular as the AAVSO Cepheid Light Curve (Delta Cephei) beatin ...
... Cepheid variable stars expand and contract in a repeating cycle of size changes. The change in size can be observed as a change in apparent brightness (apparent magnitude.) Cepheids have a repeating cycle of change that is periodic - as regular as the AAVSO Cepheid Light Curve (Delta Cephei) beatin ...
8.4 White Dwarfs
... As the outer layers are blasted into space, the luminosity of the dying star increases by a factor of 108 or 20 magnitudes. In 1987, a supernova exploded in our nearest neighbor galaxy. That supernova, designated SN1987A (the first one discovered in 1987) was visible to the naked eye, rising to a ma ...
... As the outer layers are blasted into space, the luminosity of the dying star increases by a factor of 108 or 20 magnitudes. In 1987, a supernova exploded in our nearest neighbor galaxy. That supernova, designated SN1987A (the first one discovered in 1987) was visible to the naked eye, rising to a ma ...
Binary Orbits
... • In some cases possible to map the motion in the sky and determine important parameters like the mass e.g. α Centauri ...
... • In some cases possible to map the motion in the sky and determine important parameters like the mass e.g. α Centauri ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.