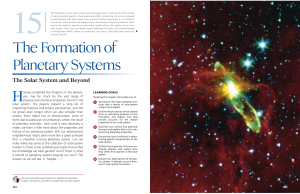
The Formation of Planetary Systems
... While our theory of the solar system must explain the facts just listed, it is equally important to recognize what it does not have to explain. There is plenty of scope for planets to evolve after their formation, so things that may have happened after the initial state of the solar system was estab ...
... While our theory of the solar system must explain the facts just listed, it is equally important to recognize what it does not have to explain. There is plenty of scope for planets to evolve after their formation, so things that may have happened after the initial state of the solar system was estab ...
Astronomers discovered what they thought was the first black hole
... and his colleagues say the system was born between 8.7 and 11.4 million years ago with two massive stars orbiting each other. The more massive star – the one that is now the black hole – was born at least 110 times heavier than the Sun, making it one of the most luminous stars in the galaxy. Its par ...
... and his colleagues say the system was born between 8.7 and 11.4 million years ago with two massive stars orbiting each other. The more massive star – the one that is now the black hole – was born at least 110 times heavier than the Sun, making it one of the most luminous stars in the galaxy. Its par ...
Lecture18
... Some stars hot but faint, or cool but very bright: Stars not on the main sequence: giants and super-giants, white dwarfs (all late phases in a star’s lifetime). “Luminosity class” used to distinguish a red main sequence (e.g. M5V) from a red supergiant (M5I). Sizes of stars vary tremendously: White ...
... Some stars hot but faint, or cool but very bright: Stars not on the main sequence: giants and super-giants, white dwarfs (all late phases in a star’s lifetime). “Luminosity class” used to distinguish a red main sequence (e.g. M5V) from a red supergiant (M5I). Sizes of stars vary tremendously: White ...
Hands On Astronomy
... The Moon is about 2000 miles in diameter. Let’s say that the moon looked like it was about 1/2 pinkie nail width in apparent size. Anything you can just barely cover with the tip of your entire pinkie is 60 times farther away than its diameter. Since the moon appeared to be only 1/2 pinkie in size, ...
... The Moon is about 2000 miles in diameter. Let’s say that the moon looked like it was about 1/2 pinkie nail width in apparent size. Anything you can just barely cover with the tip of your entire pinkie is 60 times farther away than its diameter. Since the moon appeared to be only 1/2 pinkie in size, ...
The First Stars in the Universe
... that was clumpy and filamentary and possibly shaped like a disk. But because the dark-matter particles would not emit radiation or lose energy, they would remain scattered in the primordial cloud. Thus, the star-forming system would come to resemble a miniature galaxy, with a disk of ordinary matter ...
... that was clumpy and filamentary and possibly shaped like a disk. But because the dark-matter particles would not emit radiation or lose energy, they would remain scattered in the primordial cloud. Thus, the star-forming system would come to resemble a miniature galaxy, with a disk of ordinary matter ...
Doppler Shift - El Camino College
... When we study an astronomical object like a star or galaxy, we usually examine the spectrum of light it gives off. Recall that the spectrum of an object contains lines that work like fingerprints to help identify different elements. Since the lines of a spectrum occur at specific wavelengths we can ...
... When we study an astronomical object like a star or galaxy, we usually examine the spectrum of light it gives off. Recall that the spectrum of an object contains lines that work like fingerprints to help identify different elements. Since the lines of a spectrum occur at specific wavelengths we can ...
Seasons What causes the seasons?
... a band of the sky divided into 12 parts of width 30 degrees. – The signs of the zodiac are no longer of special importance in astronomy. ...
... a band of the sky divided into 12 parts of width 30 degrees. – The signs of the zodiac are no longer of special importance in astronomy. ...
Chemical Evolution
... each GC was formed in situ or in a satellite galaxy and subsequently accreted onto the Milky Way (Roediger et al arxiv 1310.3275) • High abundances (1.7-2.5x solar) indicates that GCs formed rapidly before type Ia's contributed much to the gas (~1 Gyr) • However their remains puzzling patterns in ho ...
... each GC was formed in situ or in a satellite galaxy and subsequently accreted onto the Milky Way (Roediger et al arxiv 1310.3275) • High abundances (1.7-2.5x solar) indicates that GCs formed rapidly before type Ia's contributed much to the gas (~1 Gyr) • However their remains puzzling patterns in ho ...
Exploration géochimique du Système Solaire
... have Yini and αMLT) • CHEOPS & TESS: Accurate planet radius in visible • Asteroseismic observations to improve the stellar mass and age we need ...
... have Yini and αMLT) • CHEOPS & TESS: Accurate planet radius in visible • Asteroseismic observations to improve the stellar mass and age we need ...
Dipper, Sword, Snake and Turtle
... such observations did not arise from academic or scientific interest in a modern sense, but were tightly linked to cosmological and religious concepts extant not only in prehistoric and early historic Mesopotamia and China (Kelley/Malone, 2005; Selin (Ed.), 2001; Hunger/Pingree 1999; Rogers, 1998; K ...
... such observations did not arise from academic or scientific interest in a modern sense, but were tightly linked to cosmological and religious concepts extant not only in prehistoric and early historic Mesopotamia and China (Kelley/Malone, 2005; Selin (Ed.), 2001; Hunger/Pingree 1999; Rogers, 1998; K ...
Document
... 1999: using ASCA, X-1 in M82 was found to vary by up to a factor of four, confirming that this bright source was indeed a single object. *Over half of ULXs are known to be variable, ruling out the multiple source or SNR hypothesis. ...
... 1999: using ASCA, X-1 in M82 was found to vary by up to a factor of four, confirming that this bright source was indeed a single object. *Over half of ULXs are known to be variable, ruling out the multiple source or SNR hypothesis. ...
Distance Measures: Parallax
... this background? This is because the center of your eyes are a few centimeters apart from each other, so each eye as a different point of view. Because stars are SO far away, their parallaxes are most conveniently measured in seconds of arc (arc seconds). The angular size of your thumb held at arm’s ...
... this background? This is because the center of your eyes are a few centimeters apart from each other, so each eye as a different point of view. Because stars are SO far away, their parallaxes are most conveniently measured in seconds of arc (arc seconds). The angular size of your thumb held at arm’s ...
Distance Measures: Parallax
... this background? This is because the center of your eyes are a few centimeters apart from each other, so each eye as a different point of view. Because stars are SO far away, their parallaxes are most conveniently measured in seconds of arc (arc seconds). The angular size of your thumb held at arm’s ...
... this background? This is because the center of your eyes are a few centimeters apart from each other, so each eye as a different point of view. Because stars are SO far away, their parallaxes are most conveniently measured in seconds of arc (arc seconds). The angular size of your thumb held at arm’s ...
The Physics of Massive Star Formation
... Cores follow the stellar IMF and are mass segregated, just like stars. It is appealing to explain properties of massive stars in terms of massive cores …but if massive cores fragment to many stars, there is no direct core-star mapping, MF agreement is just a coincidence. Do massive cores fragment? ...
... Cores follow the stellar IMF and are mass segregated, just like stars. It is appealing to explain properties of massive stars in terms of massive cores …but if massive cores fragment to many stars, there is no direct core-star mapping, MF agreement is just a coincidence. Do massive cores fragment? ...
Chapter 13 Power Point Lecture
... extrasolar planets? – Direct starlight is billions of times brighter than the starlight reflected from planets. • How can a star's motion reveal the presence of planets? – A star's periodic motion (detected through Doppler shifts or by measuring its motion across the sky) tells us about its planets. ...
... extrasolar planets? – Direct starlight is billions of times brighter than the starlight reflected from planets. • How can a star's motion reveal the presence of planets? – A star's periodic motion (detected through Doppler shifts or by measuring its motion across the sky) tells us about its planets. ...
the moons of jovian planets.
... a) a planet that once orbited the Sun but later was destroyed. b) ancient material from the formation of the solar system. c) a collision between Jupiter and one of its larger moons. d) comets that were trapped by Jupiter’s gravitational field. Explanation: Asteroids, meteoroids, and comets may have ...
... a) a planet that once orbited the Sun but later was destroyed. b) ancient material from the formation of the solar system. c) a collision between Jupiter and one of its larger moons. d) comets that were trapped by Jupiter’s gravitational field. Explanation: Asteroids, meteoroids, and comets may have ...
The Galilean Moons of Jupiter
... Galilean Moons of Jupiter. The application also provides static and dynamic data about the Jupiter system which is of special interest to amateur astronomers because of its fast changes and suitability to both large and small telescopes. During summer 2007, Jupiter is favorably positioned in the eve ...
... Galilean Moons of Jupiter. The application also provides static and dynamic data about the Jupiter system which is of special interest to amateur astronomers because of its fast changes and suitability to both large and small telescopes. During summer 2007, Jupiter is favorably positioned in the eve ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.