General Astrophysics And Comparative Planetology
... The size of a planet is key to many of its properties, including its albedo and thermal emission. A measured radius is especially important for classifying new kinds of planets such as super Earths, ocean planets, and planets around non-solar type stars (e.g., Kuchner 2003). Figure 2 shows the masse ...
... The size of a planet is key to many of its properties, including its albedo and thermal emission. A measured radius is especially important for classifying new kinds of planets such as super Earths, ocean planets, and planets around non-solar type stars (e.g., Kuchner 2003). Figure 2 shows the masse ...
Enhanced lithium depletion in Sun-like stars with orbiting planets.
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
... 451 stars in the HARPS high precision (better than 1 m/s) radial velocity exoplanet survey11 spanning the effective temperature range between 4900 and 6500 K. These are unevolved, slowly rotating non-active stars from a CORALIE catalogue11. These stars have been monitored with high precision spectro ...
Kepler Mission: The Search for Earth-sized Planets
... A transit occurs when a planet crosses the line of sight between an observer and a star and blocks a small amount of light from the star, causing the light from the star to dim slightly for a few hours. ...
... A transit occurs when a planet crosses the line of sight between an observer and a star and blocks a small amount of light from the star, causing the light from the star to dim slightly for a few hours. ...
Exploring Space—The Universe: The Vast
... 3. Discuss with students the location of the solar system within the Milky Way galaxy. What are the three types of galaxies? Discuss answers from the video. (The universe contains spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies.) What type of galaxy is the Milky Way (A spiral galaxy.) Do they think there ...
... 3. Discuss with students the location of the solar system within the Milky Way galaxy. What are the three types of galaxies? Discuss answers from the video. (The universe contains spiral, elliptical, and irregular galaxies.) What type of galaxy is the Milky Way (A spiral galaxy.) Do they think there ...
Latitude and Longitude - Harvard University Laboratory for
... Latitude sailing • Accurate longitude determination only came when chronometers were available • Before this, many voyages involved latitude sailing: sail along the coast until one reaches the latitude of the destination, then sail east or west along this latitude across the sea (checking position ...
... Latitude sailing • Accurate longitude determination only came when chronometers were available • Before this, many voyages involved latitude sailing: sail along the coast until one reaches the latitude of the destination, then sail east or west along this latitude across the sea (checking position ...
01_test_bank
... A) Earth's speed of revolution about the Sun, typical speeds of stars in the local solar neighborhood relative to us, Earth's speed of rotation on its axis, the speed of our solar system orbiting the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, the speeds of very distant galaxies relative to us B) Earth's speed ...
... A) Earth's speed of revolution about the Sun, typical speeds of stars in the local solar neighborhood relative to us, Earth's speed of rotation on its axis, the speed of our solar system orbiting the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, the speeds of very distant galaxies relative to us B) Earth's speed ...
Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 1. Source of word
... Both Ptolemy and Copernicus had to explain the nonuniform motion of the planets in their orbits. Planets move faster when they are closer to the sun. Ptolemy “explained” this by a nonuniform motion of the guiding center of the epicycle about the guiding center circle. Copernicus, perhaps rediscover ...
... Both Ptolemy and Copernicus had to explain the nonuniform motion of the planets in their orbits. Planets move faster when they are closer to the sun. Ptolemy “explained” this by a nonuniform motion of the guiding center of the epicycle about the guiding center circle. Copernicus, perhaps rediscover ...
Dark Matter -24-------------------------------~-----------R-E-S-O-N-A-N-C
... A spiral galaxy is seen as an agglomeration of a very large number of stars and some gas distributed in a rotating disk. In the Milky Way, a typical spiral galaxy, there are over 1011 stars distributed in a disk about 100,000 light years across and 3000 light years thick. The gas is mostly pure hydr ...
... A spiral galaxy is seen as an agglomeration of a very large number of stars and some gas distributed in a rotating disk. In the Milky Way, a typical spiral galaxy, there are over 1011 stars distributed in a disk about 100,000 light years across and 3000 light years thick. The gas is mostly pure hydr ...
ppt - Institute for Astronomy
... star scenario is that it can solve the time scale problem: how does it happen that two stars next to each other can both turn into FUors but being too far apart to affect each other? The solution is that FUor pairs are really quadruple systems which transformed from an unstable nonhierarchical confi ...
... star scenario is that it can solve the time scale problem: how does it happen that two stars next to each other can both turn into FUors but being too far apart to affect each other? The solution is that FUor pairs are really quadruple systems which transformed from an unstable nonhierarchical confi ...
Leo Powerpoint
... Adhafera (Zeta Leo) Chort (Theta Leo) Al Minliar al Asad (Kappa Leo) Alterf (Lambda Leo) Ras Elased Borealis (Mu Leo) Subra (Omicron Leo) ...
... Adhafera (Zeta Leo) Chort (Theta Leo) Al Minliar al Asad (Kappa Leo) Alterf (Lambda Leo) Ras Elased Borealis (Mu Leo) Subra (Omicron Leo) ...
Chapter 11
... Jupiter is surrounded by belts of charged particles, much like the Van Allen belts but vastly larger Magnetosphere is 30 million km across ...
... Jupiter is surrounded by belts of charged particles, much like the Van Allen belts but vastly larger Magnetosphere is 30 million km across ...
List of Astronomical Events for 2017
... or ice particles, similar to grains of sand. As Earth collides with these particles, they streak through the atmosphere, resulting in bright flashes as they burn up. We see these bright flashes as meteors. Timings & Rates: Meteor showers are best viewed between midnight and sunrise on the peak dates ...
... or ice particles, similar to grains of sand. As Earth collides with these particles, they streak through the atmosphere, resulting in bright flashes as they burn up. We see these bright flashes as meteors. Timings & Rates: Meteor showers are best viewed between midnight and sunrise on the peak dates ...
Lecture 2
... Your friend in Brazil is farther North, at 22 degrees South. So a star that passes overhead for her is at 54-22=32 degrees above your horizon. ...
... Your friend in Brazil is farther North, at 22 degrees South. So a star that passes overhead for her is at 54-22=32 degrees above your horizon. ...
April 2015 Astronomy Calendar by Dave Mitsky
... Brilliant Venus is positioned high in the west at sunset. It sets about three hours after the Sun in early April and three-and-one-half hours after sunset by month’s end. Venus is at perihelion on April 18th. During the second week of April, the planet passes between the Hyades (Melotte 25) and Plei ...
... Brilliant Venus is positioned high in the west at sunset. It sets about three hours after the Sun in early April and three-and-one-half hours after sunset by month’s end. Venus is at perihelion on April 18th. During the second week of April, the planet passes between the Hyades (Melotte 25) and Plei ...
OBSERVATIONS (1)
... Let’s think about these things one (or three) at a time. • Every day the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west. This is evidently what the Sun is doing, and there are still people who “believe” that it does exactly that. They have elaborate explanations for why all the observations that scienc ...
... Let’s think about these things one (or three) at a time. • Every day the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west. This is evidently what the Sun is doing, and there are still people who “believe” that it does exactly that. They have elaborate explanations for why all the observations that scienc ...
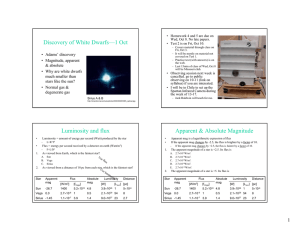
Discovery of White Dwarfs—1 Oct • Adams’ discovery
... Abs mag of a star is its apparent mag if the star is moved to a distance of 10 pc. If the abs mag changes by -2.5 mag, the luminosity is brighter by a factor of 10. ...
... Abs mag of a star is its apparent mag if the star is moved to a distance of 10 pc. If the abs mag changes by -2.5 mag, the luminosity is brighter by a factor of 10. ...
THE INNER CORE OF A NEUTRON STAR Part 1
... star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles without net electrical charge. Neutron stars are very hot and are supported a ...
... star composition makes it so heavy that its density is at least twice the mass of Earth’s Sun. Current thinking subscribes to the possibility that a neutron star is primarily made up of almost entirely sub-atomic particles without net electrical charge. Neutron stars are very hot and are supported a ...
A Human-Powered Orrery: Connecting Learners with the Night Sky*
... you should not do with the real Sun). Ask them what constellations are behind the Sun and if they would expect to see these constellations in the real sky (no, they are “up” during the day and “behind” the bright Sun). Have the student rotate 1/4 turn counterclockwise and ask them what constellation ...
... you should not do with the real Sun). Ask them what constellations are behind the Sun and if they would expect to see these constellations in the real sky (no, they are “up” during the day and “behind” the bright Sun). Have the student rotate 1/4 turn counterclockwise and ask them what constellation ...
Chapter 12
... • How massive are newborn stars? —Stars greater than about 150MSun would be so luminous that radiation pressure would blow them apart. —Degeneracy pressure stops the contraction of objects <0.08MSun before fusion starts. ...
... • How massive are newborn stars? —Stars greater than about 150MSun would be so luminous that radiation pressure would blow them apart. —Degeneracy pressure stops the contraction of objects <0.08MSun before fusion starts. ...
Constraints on the Birth Aggregate of the Solar System
... ndt < 3 × 104 pc−3 Myr. In this present work, we constrain the size of the solar birth aggregate from both directions: It must be large enough to provide a sufficiently massive star for enrichment and small enough to allow for well-ordered planetary orbits. We must keep in mind, however, another pos ...
... ndt < 3 × 104 pc−3 Myr. In this present work, we constrain the size of the solar birth aggregate from both directions: It must be large enough to provide a sufficiently massive star for enrichment and small enough to allow for well-ordered planetary orbits. We must keep in mind, however, another pos ...
main sequence stars of a open cluster
... 5. Discussion: Print out the CM diagram and discuss your result. Q.1. Find the main sequence from the printed-out CM diagram. Enclose the main sequence by line with a width as narrow as possible. Q.2. What are the characteristics of the main-sequence stars? Explain considering meanings of absolute m ...
... 5. Discussion: Print out the CM diagram and discuss your result. Q.1. Find the main sequence from the printed-out CM diagram. Enclose the main sequence by line with a width as narrow as possible. Q.2. What are the characteristics of the main-sequence stars? Explain considering meanings of absolute m ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.