Astronomy 1010 - The University of Toledo
... Every mass attracts every other mass through the force called gravity The force of attraction is directly proportional to the product of their masses The force of attraction is inversely proportional to the distance between the objects ...
... Every mass attracts every other mass through the force called gravity The force of attraction is directly proportional to the product of their masses The force of attraction is inversely proportional to the distance between the objects ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... solar system is shown in the image. The image is brighter to the upper right -- the side of the nebula nearest the Earth -- where there is less obscuring material to block the X-ray emission. NGC 7027 is the remains of a sun-like star that has ejected much of its mass to expose its hot core. The X-r ...
... solar system is shown in the image. The image is brighter to the upper right -- the side of the nebula nearest the Earth -- where there is less obscuring material to block the X-ray emission. NGC 7027 is the remains of a sun-like star that has ejected much of its mass to expose its hot core. The X-r ...
University Mohamed Khider- Biskra Faculty of letters and
... 10. Which planet has a surface and atmosphere most like the Earth? a. Mars b. Neptune c. Mercury 11. What is the brightest star in the night sky at any time? a. Sirius b. Orion c. Venus 12. A natural satellite that orbits a planet? a. Star b. Sun c. Moon 13. About how many stars are in our galaxy? a ...
... 10. Which planet has a surface and atmosphere most like the Earth? a. Mars b. Neptune c. Mercury 11. What is the brightest star in the night sky at any time? a. Sirius b. Orion c. Venus 12. A natural satellite that orbits a planet? a. Star b. Sun c. Moon 13. About how many stars are in our galaxy? a ...
Space Science Unit - World of Teaching
... • This chart uses surface temperature of the star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). Th ...
... • This chart uses surface temperature of the star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). Th ...
THE LIBERAL ARTS AND SCIENCES The liberal arts and sciences
... over time of the earth’s axis of rotation, the sun does not rise in those constellations that your birthday falls upon now. In addition, on the same day each year, the earth may be up to 22,000 miles further or closer to the sun due to the shape of its orbit, which is not perfectly circular. That is ...
... over time of the earth’s axis of rotation, the sun does not rise in those constellations that your birthday falls upon now. In addition, on the same day each year, the earth may be up to 22,000 miles further or closer to the sun due to the shape of its orbit, which is not perfectly circular. That is ...
Space Science Unit
... • This chart uses surface temperature of the star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). Th ...
... • This chart uses surface temperature of the star and the absolute magnitude (brightness) of the star to help astronomers decide which phase of the star’s life cycle the star is in and other important information about the star. • Most stars are what we consider main sequence (including our sun). Th ...
Homework 4
... 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
... 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
Spiral Elliptical Irregular - SMS 8th Grade Astronomy Unit
... jet 17 years to travel this far!) Pluto is 39 AU from the sun…How many miles is that? _____________________ Anything farther than objects in our solar system has to be measured in light years A light year (ly) is the distance light can travel in one year. Light travels _________________ per second. ...
... jet 17 years to travel this far!) Pluto is 39 AU from the sun…How many miles is that? _____________________ Anything farther than objects in our solar system has to be measured in light years A light year (ly) is the distance light can travel in one year. Light travels _________________ per second. ...
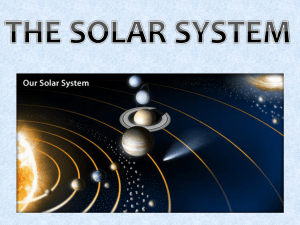
The Solar System
... the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go around it. We say that the planets are in orbit around the Sun. ...
... the heliocentric model. This just means that the Sun is at the centre of the solar system, and the Earth and other planets go around it. We say that the planets are in orbit around the Sun. ...
Chapter 15 part 1
... The closest star to Earth (besides the Sun) is called Proxima Centauri. It has the largest known stellar parallax, 0.76'', which means that it is about 1/0.76 = 1.3 pc away— about 270,000 A.U., or 4.3 light-years. ...
... The closest star to Earth (besides the Sun) is called Proxima Centauri. It has the largest known stellar parallax, 0.76'', which means that it is about 1/0.76 = 1.3 pc away— about 270,000 A.U., or 4.3 light-years. ...
Chapter 2: The Sky
... • If the Earth did not rotate about its axis, could we define a celestial sphere as we do now? • Could we even define a set of poles and equator? • What is the difference between a constellation and an asterism? Examples? • What does the word apparent mean in the context of “apparent visual magnitud ...
... • If the Earth did not rotate about its axis, could we define a celestial sphere as we do now? • Could we even define a set of poles and equator? • What is the difference between a constellation and an asterism? Examples? • What does the word apparent mean in the context of “apparent visual magnitud ...
Astronomy 1010 final review sample topics
... a.) its radius increases and its rotation rate stays the same b.) its radius decreases and its rotation rate decreases c.) its radius decreases, but its rotation rate stays the same d.) its radius decreases, but its rotation rate increases 6. Based on Newton’s version of Kepler’s 3rd Law [p2 = 4π 2 ...
... a.) its radius increases and its rotation rate stays the same b.) its radius decreases and its rotation rate decreases c.) its radius decreases, but its rotation rate stays the same d.) its radius decreases, but its rotation rate increases 6. Based on Newton’s version of Kepler’s 3rd Law [p2 = 4π 2 ...
EM review
... 4 % of an estimated population of 966 ± 45 NEAs 8501 NEAs are known with D < 1000 m The estimated total population of all NEAs with D > 140 m (H < 22.0 mag) is ~ 15,000; observed: 5456 (~ 37 %) The estimated total population of all NEAs with D > 100 m (H < 22.75 mag) is ~ 20,000; observed: 6059 (~ 3 ...
... 4 % of an estimated population of 966 ± 45 NEAs 8501 NEAs are known with D < 1000 m The estimated total population of all NEAs with D > 140 m (H < 22.0 mag) is ~ 15,000; observed: 5456 (~ 37 %) The estimated total population of all NEAs with D > 100 m (H < 22.75 mag) is ~ 20,000; observed: 6059 (~ 3 ...
Solar System - Spring Branch ISD
... Our solar system is located in an outward spiral of the __________ Milky Way galaxy. ...
... Our solar system is located in an outward spiral of the __________ Milky Way galaxy. ...
Homework 5 (stellar properties)
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
Classification_of_Stars_By_Luminosity
... He called the brightest stars in the sky first magnitude and the dimmest visible to the naked eye sixth magnitude. Stars of intermediate brightness were given intermediate values. ...
... He called the brightest stars in the sky first magnitude and the dimmest visible to the naked eye sixth magnitude. Stars of intermediate brightness were given intermediate values. ...
MAUI STARGAZING MAY OBSERVING LIST DEEP SPACE
... a reference to The Milky Way. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few thousand stars to giants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting their galaxy's own center of mass. ...
... a reference to The Milky Way. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few thousand stars to giants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting their galaxy's own center of mass. ...
Calculating Main Sequence Lifetimes
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
... At the beginning of the twentieth century two astronomers, the Danish E. Hertzsprung and the American H. N. Russell, established a correlation between two important stellar parameters: brightness and color. Since ancient times, the brightness of a star is indicated by "magnitudes": 1, 2 and so on, w ...
Aquarius (constellation)
Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for ""water-carrier"" or ""cup-carrier"", and its symbol is 20px (Unicode ♒), a representation of water.Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac (the sun's apparent path). It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century AD astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river.