Lecture 12 Slides
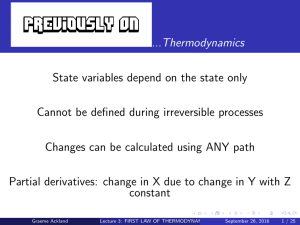
... final states of the system, not on how the change occurred (i.e., changes in state functions are also path-independent) ...
... final states of the system, not on how the change occurred (i.e., changes in state functions are also path-independent) ...
Module - 1: Thermodynamics
... relevant part of the kitchen as the environment (with temperature TE) of that system. Our observation is that if TS is not equal to TE, then TS will change until the two temperatures are equal and thus thermal equilibrium is reached. Such a change in temperature is due to the transfer of energy betw ...
... relevant part of the kitchen as the environment (with temperature TE) of that system. Our observation is that if TS is not equal to TE, then TS will change until the two temperatures are equal and thus thermal equilibrium is reached. Such a change in temperature is due to the transfer of energy betw ...
Practice Exam #2
... B) Zn (s) + 2Br- (aq) → ZnBr2 (aq) C) Zn (s) + 2H+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g) D) Zn (s) + 2HBr (aq) → ZnBr2 (s) + 2H+ (aq) E) Zn (s) + 2HBr (aq) → ZnBr2 (aq) + 2H+ (aq) 12) Which of the following is an oxidation-reduction reaction? A) AgNO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + HNO3 (aq) B) HCl (aq) + NaOH (a ...
... B) Zn (s) + 2Br- (aq) → ZnBr2 (aq) C) Zn (s) + 2H+ (aq) → Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g) D) Zn (s) + 2HBr (aq) → ZnBr2 (s) + 2H+ (aq) E) Zn (s) + 2HBr (aq) → ZnBr2 (aq) + 2H+ (aq) 12) Which of the following is an oxidation-reduction reaction? A) AgNO3 (aq) + HCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + HNO3 (aq) B) HCl (aq) + NaOH (a ...
QUESTION
... What is the substance if 1347.5 J are required to raise the temperature of a 350-g sample by 10 0C? ANSWER: ...
... What is the substance if 1347.5 J are required to raise the temperature of a 350-g sample by 10 0C? ANSWER: ...
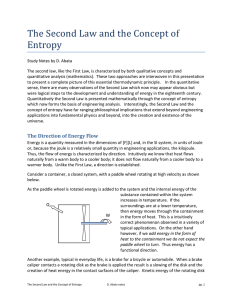
The Second Law and the Concept of Entropy
... Energy accountability in the science of thermodynamics is described through the logical concepts of state and process. A process occurs when the thermodynamic system undergoes a change in state or an energy transfer at steady state. A process can be perfect or reversible or imperfect and irreversibl ...
... Energy accountability in the science of thermodynamics is described through the logical concepts of state and process. A process occurs when the thermodynamic system undergoes a change in state or an energy transfer at steady state. A process can be perfect or reversible or imperfect and irreversibl ...
PPT
... During a phase change, the pressure is constant and equal to the saturation pressure (which is a function of T only). Adding heat to a substance at constant pressure and resulting in a change in physical state, i.e. change in phase, is described by, Starting with First Law in the ...
... During a phase change, the pressure is constant and equal to the saturation pressure (which is a function of T only). Adding heat to a substance at constant pressure and resulting in a change in physical state, i.e. change in phase, is described by, Starting with First Law in the ...
thermochemistry
... – Transfer of energy occuring as a result of the exertion of a force along a certain distance is called “work”. ...
... – Transfer of energy occuring as a result of the exertion of a force along a certain distance is called “work”. ...
g) Chemistry 30 - Mr. Jones LHS Science
... Know the sign convention for heat and work entering or exiting the system. Be able to calculate the internal energy of a system (ΔE = q + w) Be able to relate the change in temperature of a substance to the heat absorbed or released (q = mCΔT) Be able to calculate the specific heat capacity ...
... Know the sign convention for heat and work entering or exiting the system. Be able to calculate the internal energy of a system (ΔE = q + w) Be able to relate the change in temperature of a substance to the heat absorbed or released (q = mCΔT) Be able to calculate the specific heat capacity ...
Fundamentals of chemical thermodynamics and bioenergetics
... the bulb of a flashlight), and surface work (blowing up a soap bubble). When gas ...
... the bulb of a flashlight), and surface work (blowing up a soap bubble). When gas ...
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
... tubes can be calculated approximately from Gnielinski relation or Chilton– Colburn analogy by using the friction factor determined from the Moody chart or the Colebrook equation. ...
... tubes can be calculated approximately from Gnielinski relation or Chilton– Colburn analogy by using the friction factor determined from the Moody chart or the Colebrook equation. ...
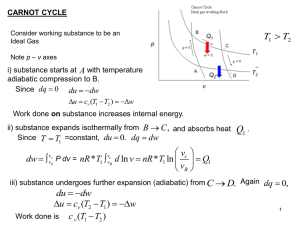
Lecture 3: FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
... Calculate the final temperature when cold ice is dropped into hot water. Proceed by assuming a series of processes in which the energy goes into some unspecified storage reservoir The water cools to 0◦ . The ice warms to 0◦ . The ice melts. Finally, the sum of these energies is put back into the sys ...
... Calculate the final temperature when cold ice is dropped into hot water. Proceed by assuming a series of processes in which the energy goes into some unspecified storage reservoir The water cools to 0◦ . The ice warms to 0◦ . The ice melts. Finally, the sum of these energies is put back into the sys ...
Chapter 20 Problems
... all. The passive solar energy collector can consist simply of very large windows in a room facing south. Sunlight shining in during the daytime is absorbed by the floor, interior walls, and objects in the room, raising their temperature to 38C. As the sun goes down, insulating draperies or shutters ...
... all. The passive solar energy collector can consist simply of very large windows in a room facing south. Sunlight shining in during the daytime is absorbed by the floor, interior walls, and objects in the room, raising their temperature to 38C. As the sun goes down, insulating draperies or shutters ...
Tutorial Questions
... a pressure increase of 1 GPa. What will be its new temperature in relation to its initial temperature? You can make use of the fact that CP for Al is 24 Jmol-1K-1 (about 3R) and its volume expansivity () is 3 x 10-6 K-1. The density of Al is 2.7 x 103 kgm-3, and its atomic weight is 27 gmol-1. (4) ...
... a pressure increase of 1 GPa. What will be its new temperature in relation to its initial temperature? You can make use of the fact that CP for Al is 24 Jmol-1K-1 (about 3R) and its volume expansivity () is 3 x 10-6 K-1. The density of Al is 2.7 x 103 kgm-3, and its atomic weight is 27 gmol-1. (4) ...
File - SRIT - MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
... So far, no attempt has been made to relate these interactions between themselves and with the energy content of the system. First law of thermodynamics, often called as law of conservation of energy, relating work, heat, and energy content of the system will be discussed in detail in this chapter. ...
... So far, no attempt has been made to relate these interactions between themselves and with the energy content of the system. First law of thermodynamics, often called as law of conservation of energy, relating work, heat, and energy content of the system will be discussed in detail in this chapter. ...
Heat transfer

Heat transfer is the exchange of thermal energy between physical systems, depending on the temperature and pressure, by dissipating heat. The fundamental modes of heat transfer are conduction or diffusion, convection and radiation.Heat transfer always occurs from a region of high temperature to another region of lower temperature. Heat transfer changes the internal energy of both systems involved according to the First Law of Thermodynamics. The Second Law of Thermodynamics defines the concept of thermodynamic entropy, by measurable heat transfer.Thermal equilibrium is reached when all involved bodies and the surroundings reach the same temperature. Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change in volume in response to a change in temperature.