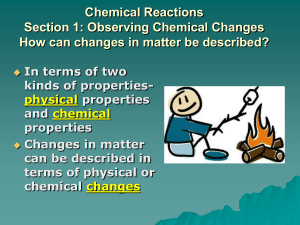
study note 3 33
... An addition of a molecule to a double or triple bond. The molecule is broken down in the reaction; the two parts of the molecule are added to either side of the double bond, leaving a single bond (or leaving a double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are ty ...
... An addition of a molecule to a double or triple bond. The molecule is broken down in the reaction; the two parts of the molecule are added to either side of the double bond, leaving a single bond (or leaving a double bond when the addition is to a triple bond). Halogenation, and hydrogenation are ty ...
Assignment 4 Task 1a
... have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds have unambiguous names. You also need to understand how a combination of element ...
... have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds have unambiguous names. You also need to understand how a combination of element ...
Chapter 6-student notes
... 3. A solid has a mass of 35g. When it is mixed with a solution, a chemical reaction happens. If the total mass of the products is 85g, what was the mass of the solution? 4. Solution A gas a mass of 60g. Solution B has a mass of 40g. When they are mixed, a chemical reaction occurs in which a gas is p ...
... 3. A solid has a mass of 35g. When it is mixed with a solution, a chemical reaction happens. If the total mass of the products is 85g, what was the mass of the solution? 4. Solution A gas a mass of 60g. Solution B has a mass of 40g. When they are mixed, a chemical reaction occurs in which a gas is p ...
Document
... A compound D has the molecular formula C2H4O2 and is obtained from a reaction between methanoic acid and methanol. Write an equation for this reaction and state the name of D. ...
... A compound D has the molecular formula C2H4O2 and is obtained from a reaction between methanoic acid and methanol. Write an equation for this reaction and state the name of D. ...
Workshop 5
... same reaction at a lower temperature. The Pb-C bond energy in (CH3)4Pb is 49 kcal/mol. a. Show the initiation and propagation steps for the chlorination of CH4 using (CH3)4Pb with CH4 and Cl2. Explain why lower temperatures are needed for the halogenation reaction using (CH3)4Pb as the initiator tha ...
... same reaction at a lower temperature. The Pb-C bond energy in (CH3)4Pb is 49 kcal/mol. a. Show the initiation and propagation steps for the chlorination of CH4 using (CH3)4Pb with CH4 and Cl2. Explain why lower temperatures are needed for the halogenation reaction using (CH3)4Pb as the initiator tha ...
Begin Chemical Equations Practice
... • In a chemical reaction, the materials to the left of the arrow are the reactants. Reactants are consumed in the reaction. • The arrow is like an equal sign in math. It can be read “react to produce” or “produces” or “forms”. • The materials to the right of the arrow are the products. They form as ...
... • In a chemical reaction, the materials to the left of the arrow are the reactants. Reactants are consumed in the reaction. • The arrow is like an equal sign in math. It can be read “react to produce” or “produces” or “forms”. • The materials to the right of the arrow are the products. They form as ...
Exercises Chem Eqm
... Suggested Problems – Chemical Equilibrium (Atkins & de Paula: Physical Chemistry 8e; Chapter 7) 7.1(a) At 2257 K and 1.00 atm total pressure, water is 1.77 per cent dissociated at equilibrium by way of the reaction 2 H2O(g) ↔2 H2(g) + O2(g). Calculate (a) K, (b) ∆rGo, and (c) ∆rG at this temperature ...
... Suggested Problems – Chemical Equilibrium (Atkins & de Paula: Physical Chemistry 8e; Chapter 7) 7.1(a) At 2257 K and 1.00 atm total pressure, water is 1.77 per cent dissociated at equilibrium by way of the reaction 2 H2O(g) ↔2 H2(g) + O2(g). Calculate (a) K, (b) ∆rGo, and (c) ∆rG at this temperature ...
Ei otsikkoa
... energy raises an electron from one energy level to another. Since bonding in complex ions involves always d orbitals, the electron transition occurs within the split d orbital. ...
... energy raises an electron from one energy level to another. Since bonding in complex ions involves always d orbitals, the electron transition occurs within the split d orbital. ...
Standard answers: 1 Basic concepts, Fuels, alkanes and alkenes
... More heat energy is given out when new bonds forming the products than taken in to break the bonds of the reactants ...
... More heat energy is given out when new bonds forming the products than taken in to break the bonds of the reactants ...
Word
... Given that ΔHreverse = -10 kJ and Ea forward = +40 kJ Solution: Begin by determining whether the forward reaction (A + B → C + D) is endothermic or exothermic: Since ΔHreverse = -10 kJ you can determine that ΔHforward = +10 kJ (same value, just change the sign). Since ΔHforward is positive you know ...
... Given that ΔHreverse = -10 kJ and Ea forward = +40 kJ Solution: Begin by determining whether the forward reaction (A + B → C + D) is endothermic or exothermic: Since ΔHreverse = -10 kJ you can determine that ΔHforward = +10 kJ (same value, just change the sign). Since ΔHforward is positive you know ...
Unit 1 - Cells: The Functional Unit of Life
... Organisms must store energy in a usable form so again control the rate of chemical reactions ...
... Organisms must store energy in a usable form so again control the rate of chemical reactions ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... G. A change in the number of electrons results in an ion IV. Compounds and mixtures A. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule B. A compound is formed when two or more different atoms bond chemically C. A mixture occurs when compounds can be separated by non-chemical means NO CH ...
... G. A change in the number of electrons results in an ion IV. Compounds and mixtures A. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule B. A compound is formed when two or more different atoms bond chemically C. A mixture occurs when compounds can be separated by non-chemical means NO CH ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
... Ionic- Two elements bond by transferring electrons to create ions that attract together (+ is attracted to - after an electron is transferred) ...
CHEM_2nd_Semester_Final_R eview
... Gases and Their Properties 15. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm an ...
... Gases and Their Properties 15. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm an ...
Chemistry 2nd Semester Final Exam Review Chemical Bonds Give
... Gases and Their Properties 15. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm an ...
... Gases and Their Properties 15. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 16. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 17. Explain diffusion, use KMT to support your answer. 18. Is Boyle’s law direct or inverse? Charles’s Law? Gay-Lussac’s Law? 19. If 735 L of a gas is at 3.11 atm an ...