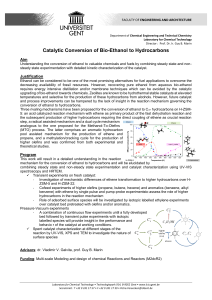
Page|1 - askIITians
... Right Answer Explanation: C A calorimeter (from Latin calor, meaning heat) is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorime ...
... Right Answer Explanation: C A calorimeter (from Latin calor, meaning heat) is an object used for calorimetry, or the process of measuring the heat of chemical reactions or physical changes as well as heat capacity. Differential scanning calorimeters, isothermal micro calorimeters, titration calorime ...
Thermochemistry - Parkway C-2
... • There are four ways to measure the heat of a chemical reaction: – Calorimetry – using a calorimeter to experimentally measure the heat released or absorbed from a reaction – Hess’ Law – using other chemical reactions to algebraically solve for the heat of a reaction – Heats of formation – using a ...
... • There are four ways to measure the heat of a chemical reaction: – Calorimetry – using a calorimeter to experimentally measure the heat released or absorbed from a reaction – Hess’ Law – using other chemical reactions to algebraically solve for the heat of a reaction – Heats of formation – using a ...
Chapter 4: Chemical Reaction Dynamics
... general changes for different approach angles. If more energy is stored in the reactants, the barrier can also be crossed for approach angels differing from the optimal value. Thus, the cone of acceptance of the reaction can be increased. ...
... general changes for different approach angles. If more energy is stored in the reactants, the barrier can also be crossed for approach angels differing from the optimal value. Thus, the cone of acceptance of the reaction can be increased. ...
Slide 1
... Lecture 15 The Redox Sequence Oxidation State Half-Reactions Balanced Oxidation-Reduction reactions Predicted Sequence of Redox Reactions Tracers for these reactions ...
... Lecture 15 The Redox Sequence Oxidation State Half-Reactions Balanced Oxidation-Reduction reactions Predicted Sequence of Redox Reactions Tracers for these reactions ...
Thermodynamics
... Third Law of Thermodynamics In a perfect crystal (diamond), the entropy at 0K is 0 J/K. Can use third law to develop standard molar entropy values ...
... Third Law of Thermodynamics In a perfect crystal (diamond), the entropy at 0K is 0 J/K. Can use third law to develop standard molar entropy values ...
Annexure `CD-01` L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 2 1 2 0 4
... 3. “Organic Chemistry”, R. T. Morrison and R. N. Boyd, 6th Edition (1992), Prentice-Hall of India (P) Ltd., New Delhi. 4. “Organic Chemistry”, S. M. Mukherjee, S. P. Singh, and R. P. Kapoor, 1st Edition (1985), New Age International (P) Ltd. ...
... 3. “Organic Chemistry”, R. T. Morrison and R. N. Boyd, 6th Edition (1992), Prentice-Hall of India (P) Ltd., New Delhi. 4. “Organic Chemistry”, S. M. Mukherjee, S. P. Singh, and R. P. Kapoor, 1st Edition (1985), New Age International (P) Ltd. ...
Document
... An unknown white solid is discovered on the lab counter in room 2101. Miss Allen wants to know if it is ionic or covalent. Describe how you could use its properties to determine if it is ionic or covalent. Be sure to use at least 3 specific examples of properties (3 marks) ...
... An unknown white solid is discovered on the lab counter in room 2101. Miss Allen wants to know if it is ionic or covalent. Describe how you could use its properties to determine if it is ionic or covalent. Be sure to use at least 3 specific examples of properties (3 marks) ...
Lecture 10 Activity of chemical components
... where Z is the charge on the ion and I is called as net ionic strength, ci is the concentration of the i th ion. The factor –0.0509 depends on the solvent dielectric constant and temperature. Thus we can see that Debye model predicts a reduction in activity coefficients. (1) Higher the charge, lower ...
... where Z is the charge on the ion and I is called as net ionic strength, ci is the concentration of the i th ion. The factor –0.0509 depends on the solvent dielectric constant and temperature. Thus we can see that Debye model predicts a reduction in activity coefficients. (1) Higher the charge, lower ...
9.2 Redox reactions
... Electrons are removed from the reactant (appear as product) Balance number of atoms ...
... Electrons are removed from the reactant (appear as product) Balance number of atoms ...
C. - Knights of The Periodic Table
... An alien astronaut landed on Earth and created the periodic table shown. The astronaut was trying to determine what type of bond would be present in several compounds. The type of bond in a compound containing G and E would be — ...
... An alien astronaut landed on Earth and created the periodic table shown. The astronaut was trying to determine what type of bond would be present in several compounds. The type of bond in a compound containing G and E would be — ...
Week 10 Problem Set (Answers) (4/17, 4/18, 4/19) Reactions and
... another bond is broken? Well, E2 reactions occur via this same mechanism. A new pi bond is formed at the same time a leaving group leaves. Something similar may be occurring here. Additionally, we have to examine the reagent. tBuOK is a strong bulky base that favors E2 elimination towards the less-s ...
... another bond is broken? Well, E2 reactions occur via this same mechanism. A new pi bond is formed at the same time a leaving group leaves. Something similar may be occurring here. Additionally, we have to examine the reagent. tBuOK is a strong bulky base that favors E2 elimination towards the less-s ...