Ch18
... An air pump has a cylinder 0.250 m long with a movable piston. The pump is used to compress air from the atmosphere at absolute pressure 1.01 x 105 Pa into a very large tank at 4.20 x 105 Pa gauge pressure. For air, CV=20.8 J/(mol K). (a) The piston begins the compression stroke at the open end of t ...
... An air pump has a cylinder 0.250 m long with a movable piston. The pump is used to compress air from the atmosphere at absolute pressure 1.01 x 105 Pa into a very large tank at 4.20 x 105 Pa gauge pressure. For air, CV=20.8 J/(mol K). (a) The piston begins the compression stroke at the open end of t ...
GCSE P2 2.2.1 Forces and Energy
... When the bowstring is drawn back, it stores ………………………………. ……………………………………. energy. This is transferred to …………………………………………………. energy as the arrow is released and flies into the air. As the arrow rises, it gains ……………………………………………… …………………………………………. energy and loses ……………………………………………………. energy. As th ...
... When the bowstring is drawn back, it stores ………………………………. ……………………………………. energy. This is transferred to …………………………………………………. energy as the arrow is released and flies into the air. As the arrow rises, it gains ……………………………………………… …………………………………………. energy and loses ……………………………………………………. energy. As th ...
Ch 18: Fluids
... Pascal’s Principle reminds us that, for a fluid of uniform pressure, the force exerted on a small area in contact with the fluid will be smaller than the force exerted on a large area. Thus, a small force applied to a small area in a fluid can create a large force on a larger area. This is the princ ...
... Pascal’s Principle reminds us that, for a fluid of uniform pressure, the force exerted on a small area in contact with the fluid will be smaller than the force exerted on a large area. Thus, a small force applied to a small area in a fluid can create a large force on a larger area. This is the princ ...
Lecture 11 DFT for periodic crystalline solids CHEM6085: Density
... lattice because the G vectors are reciprocal lattice vectors • The basis set is limited to all the plane waves with wavector lengths less than some value Gmax, i.e. all vectors within as sphere of radius Gmax • In practical calculations the basis set is input in terms of the “kinetic energy cut-off” ...
... lattice because the G vectors are reciprocal lattice vectors • The basis set is limited to all the plane waves with wavector lengths less than some value Gmax, i.e. all vectors within as sphere of radius Gmax • In practical calculations the basis set is input in terms of the “kinetic energy cut-off” ...
Document
... An air pump has a cylinder 0.250 m long with a movable piston. The pump is used to compress air from the atmosphere at absolute pressure 1.01 x 105 Pa into a very large tank at 4.20 x 105 Pa gauge pressure. For air, CV=20.8 J/(mol K). (a) The piston begins the compression stroke at the open end of t ...
... An air pump has a cylinder 0.250 m long with a movable piston. The pump is used to compress air from the atmosphere at absolute pressure 1.01 x 105 Pa into a very large tank at 4.20 x 105 Pa gauge pressure. For air, CV=20.8 J/(mol K). (a) The piston begins the compression stroke at the open end of t ...
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS BY COMPUTER SIMULATION (*)
... (such as shear forces, temperature gradients, electric fields, etc.) and that it attains equilibrium before the calculation of any properties. Even the calculation of transport coefficients by means of time correlation functions referred to in 3.1., assume the system to be in equilibrium when the co ...
... (such as shear forces, temperature gradients, electric fields, etc.) and that it attains equilibrium before the calculation of any properties. Even the calculation of transport coefficients by means of time correlation functions referred to in 3.1., assume the system to be in equilibrium when the co ...
Chapter 6 - DePaul University Department of Chemistry
... and therefore possess kinetic energy. • Postulate 3: The particles possess potential energy as a result of repelling or attracting each other. • Postulate 4: The average particle speed increases as the temperature increases. • Postulate 5: The particles transfer energy from one to another during col ...
... and therefore possess kinetic energy. • Postulate 3: The particles possess potential energy as a result of repelling or attracting each other. • Postulate 4: The average particle speed increases as the temperature increases. • Postulate 5: The particles transfer energy from one to another during col ...
Lecture 2 - MyCourses
... curves E(k) for one line (0 -> π/a) In 3D solids, k is called the wave vector and has three components (kx, ky, kz) E(k) needs to be considered for several lines within the first Brillouin zone – Primitive cell in reciprocal space, uniquely defined for all Bravais lattices Where do the band energies ...
... curves E(k) for one line (0 -> π/a) In 3D solids, k is called the wave vector and has three components (kx, ky, kz) E(k) needs to be considered for several lines within the first Brillouin zone – Primitive cell in reciprocal space, uniquely defined for all Bravais lattices Where do the band energies ...
Heat transfer physics

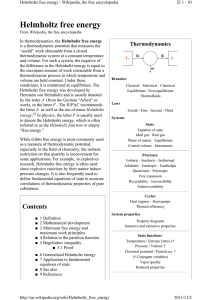
Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.