Lectures 15 and 16 - NUS Physics Department
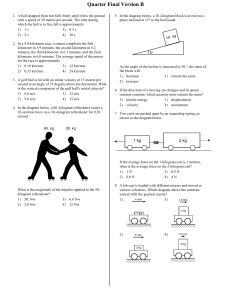
... along the plane, which is inclined at an angle of 30.0° to the horizontal. For this motion determine (a) the change in the block's kinetic energy, (b) the change in the potential energy of the block-Earth system, and (c) the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant). (d) What is t ...
... along the plane, which is inclined at an angle of 30.0° to the horizontal. For this motion determine (a) the change in the block's kinetic energy, (b) the change in the potential energy of the block-Earth system, and (c) the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant). (d) What is t ...
Introduction to reaction dynamics
... detected as a function of angle and time-of-flight (and therefore velocity) using a rotatable mass spectrometer in the simplest case. In this case all product quantum states are detected at the same time and the three dimensional product velocity distribution obtained is averaged over all product in ...
... detected as a function of angle and time-of-flight (and therefore velocity) using a rotatable mass spectrometer in the simplest case. In this case all product quantum states are detected at the same time and the three dimensional product velocity distribution obtained is averaged over all product in ...
File - Elements of Mechanical Engineering
... isothermally until the volume is halved and subsequently it goes further compression at constant pressure till volume is halved again. Calculate the total work done and total heat interaction for the two processes. Assume ideal gas behavior for air and take Cp = 1.005 KJ/Kg K. Q6. 1.5kg nitrogen co ...
... isothermally until the volume is halved and subsequently it goes further compression at constant pressure till volume is halved again. Calculate the total work done and total heat interaction for the two processes. Assume ideal gas behavior for air and take Cp = 1.005 KJ/Kg K. Q6. 1.5kg nitrogen co ...
Consequences of the relation between temperature, heat, and
... There’s not much more to add to this right now- we will come back to the third law when we examine the molecular origins of thermodynamic behavior in the second part of the term. We’ve stated (without trying to demonstrate it) that entropy is a measure of disorder on the molecular scale- thus the th ...
... There’s not much more to add to this right now- we will come back to the third law when we examine the molecular origins of thermodynamic behavior in the second part of the term. We’ve stated (without trying to demonstrate it) that entropy is a measure of disorder on the molecular scale- thus the th ...
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT – I BASIC
... called throttling. During this process, pressure and velocity are reduced. 15. Define – Sensible Heat and Latent Heat (N/D 2013) Sensible heat is the heat that changes the temperature of the substance when added to it or when abstracted from it. Latent heat is the heat that does not affect the tempe ...
... called throttling. During this process, pressure and velocity are reduced. 15. Define – Sensible Heat and Latent Heat (N/D 2013) Sensible heat is the heat that changes the temperature of the substance when added to it or when abstracted from it. Latent heat is the heat that does not affect the tempe ...
Ppt
... A small block slides inside a hoop of radius r. The walls of the hoop are frictionless but the horizontal floor has a coefficient of sliding friction of m. The block’s initial velocity is v and is entirely tangential. How far, in angle around the circle does the block travel before coming to rest ? ...
... A small block slides inside a hoop of radius r. The walls of the hoop are frictionless but the horizontal floor has a coefficient of sliding friction of m. The block’s initial velocity is v and is entirely tangential. How far, in angle around the circle does the block travel before coming to rest ? ...
genius by Pradeep Kshetrapal Problems based on Q, U and W 1
... (a) – 340 kJ (b) – 170 kJ (c) 170 kJ (d) 340 kJ A vessel contains an ideal monoatomic gas which expands at constant pressure, when heat Q is supplied to it. Then work done by the gas in the expansion is (a) Q (b) 3Q/5 (c) 2Q/5 (d) 2Q/3 ...
... (a) – 340 kJ (b) – 170 kJ (c) 170 kJ (d) 340 kJ A vessel contains an ideal monoatomic gas which expands at constant pressure, when heat Q is supplied to it. Then work done by the gas in the expansion is (a) Q (b) 3Q/5 (c) 2Q/5 (d) 2Q/3 ...
Calculation of the Fermi wave vector for thin films, T. B
... surfaces. Thus, the interplanar distance is equal to d = a/2 = 1.805 Å, whereas the dimensionless electronic density ρ is 0.5. The choice of copper is connected to the view that the Fermi surface for this metal is quite similar to a spherical surface [9], therefore our model is more realistic than f ...
... surfaces. Thus, the interplanar distance is equal to d = a/2 = 1.805 Å, whereas the dimensionless electronic density ρ is 0.5. The choice of copper is connected to the view that the Fermi surface for this metal is quite similar to a spherical surface [9], therefore our model is more realistic than f ...
NSCC Chem 121 chapter6
... KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of ...
... KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF MATTER • The kinetic molecular theory of matter is a useful tool for explaining the observed properties of matter in the three different states of solid, liquid and gas. • Postulate 1: Matter is made up of tiny particles called molecules. • Postulate 2: The particles of ...
2003
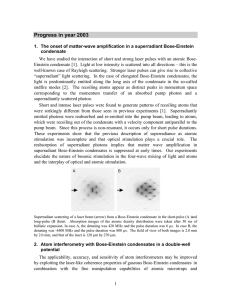
... The characteristic feature of Bose-Einstein condensation is the accumulation of a macroscopic number of particles in the lowest quantum state. Condensate fragmentation, the macroscopic occupation of two or more quantum states, is usually prevented by interactions [16]. However, multiple condensates ...
... The characteristic feature of Bose-Einstein condensation is the accumulation of a macroscopic number of particles in the lowest quantum state. Condensate fragmentation, the macroscopic occupation of two or more quantum states, is usually prevented by interactions [16]. However, multiple condensates ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.