Table of Content
... are products of human experiential observations to which no exceptions have been found so far, and so are considered to be “laws”. The scope of application of the laws of thermodynamics ranges from the microscopic to the macroscopic order, and indeed to cosmological processes. Thus, all processes ta ...
... are products of human experiential observations to which no exceptions have been found so far, and so are considered to be “laws”. The scope of application of the laws of thermodynamics ranges from the microscopic to the macroscopic order, and indeed to cosmological processes. Thus, all processes ta ...
CONSERVATIVE FORCE SYSTEMS
... 1. Set the scale of the Jolly balance to zero position by adjusting the knurled wheel. Hang the spring on its movable arm if it is not already there. Adjust the pointer tip of the balance to the lowest point of the spring and lock in the position of the pointer. 2. Find the mass of the hanger and pl ...
... 1. Set the scale of the Jolly balance to zero position by adjusting the knurled wheel. Hang the spring on its movable arm if it is not already there. Adjust the pointer tip of the balance to the lowest point of the spring and lock in the position of the pointer. 2. Find the mass of the hanger and pl ...
Chapter 13
... Assume the object is initially pulled to a distance A and released from rest As the object moves toward the equilibrium position, F and a decrease, but v increases At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a maximum The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position ...
... Assume the object is initially pulled to a distance A and released from rest As the object moves toward the equilibrium position, F and a decrease, but v increases At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a maximum The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position ...
(Theory of electromagnetism and the light) Author: Arman
... in the atom is so and there are many stationary circuits so the statistics that the directions of many electrons don’t be to opposite is so less and when the opposite directions arrive to other tense together. In fact because in the electromagnetism theory of the light we consider the electrical fie ...
... in the atom is so and there are many stationary circuits so the statistics that the directions of many electrons don’t be to opposite is so less and when the opposite directions arrive to other tense together. In fact because in the electromagnetism theory of the light we consider the electrical fie ...
1 - GENCHEM
... because the electrons in the lower energy orbitals will “shield” the electrons in the higher energy orbitals from the nucleus. This effect arises because the e-e repulsions tend to offset the attraction of the electron to the nucleus. (b) true. (c) false. The electrons are increasingly less able to ...
... because the electrons in the lower energy orbitals will “shield” the electrons in the higher energy orbitals from the nucleus. This effect arises because the e-e repulsions tend to offset the attraction of the electron to the nucleus. (b) true. (c) false. The electrons are increasingly less able to ...
Chapter 7 AP Physics Set
... 7) Suppose the force required to tow a canal barge is directly proportional to the speed. If it takes 4 horsepower to tow the barge at a speed of 2 mi/hr, what horsepower is required to move the barge at a speed of 6 mi/hr? a) 8 hp b) 12 hp c) 24 hp d) 32 hp e) 36 hp 8) A particle is acted upon by a ...
... 7) Suppose the force required to tow a canal barge is directly proportional to the speed. If it takes 4 horsepower to tow the barge at a speed of 2 mi/hr, what horsepower is required to move the barge at a speed of 6 mi/hr? a) 8 hp b) 12 hp c) 24 hp d) 32 hp e) 36 hp 8) A particle is acted upon by a ...
Physical Science - Blue Valley Schools
... component in a system when the change in energy of the other component(s) and energy flows in and out of the system are known. Science & Engineering Practice(s): Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking: Create a computational model or simulation of a phenomenon, designed device, process, or s ...
... component in a system when the change in energy of the other component(s) and energy flows in and out of the system are known. Science & Engineering Practice(s): Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking: Create a computational model or simulation of a phenomenon, designed device, process, or s ...
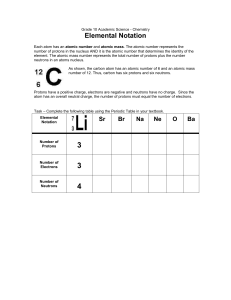
Grade 10 Science – Unit 2
... Lewis Dot Diagrams are very useful. With them, you can (1) determine the type(s) of covalent bonds that an element may make, and (2) predict the type of ion that an atom might make. Each dot diagram consists of an elemental symbol (called the kernel) and a group of 1-8 dots which shows the configura ...
... Lewis Dot Diagrams are very useful. With them, you can (1) determine the type(s) of covalent bonds that an element may make, and (2) predict the type of ion that an atom might make. Each dot diagram consists of an elemental symbol (called the kernel) and a group of 1-8 dots which shows the configura ...
energy 2015 10 25
... • Experimental determination of internal energy. Insulate the closed system to make an adiabatic system. When we do work Wadiabatic to the adiabatic system, the system changes from state A to state B, and the change in internal energy equals the adiabatic work, U(B) – U(A) = Wadiabatic. • Experiment ...
... • Experimental determination of internal energy. Insulate the closed system to make an adiabatic system. When we do work Wadiabatic to the adiabatic system, the system changes from state A to state B, and the change in internal energy equals the adiabatic work, U(B) – U(A) = Wadiabatic. • Experiment ...
Physics TAKS Review
... energies at the level of molecules and atoms. However, those molecules and atoms move around with this energy in very random and un-useful ways. Well, not completely un-usefull. You can use it to keep you warm and to drive chemical reactions. So I guess it’s useful in those ways. It can also be turn ...
... energies at the level of molecules and atoms. However, those molecules and atoms move around with this energy in very random and un-useful ways. Well, not completely un-usefull. You can use it to keep you warm and to drive chemical reactions. So I guess it’s useful in those ways. It can also be turn ...
Heat transfer physics

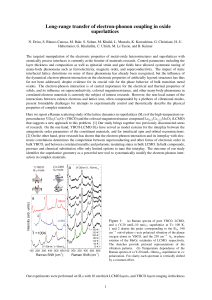
Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.