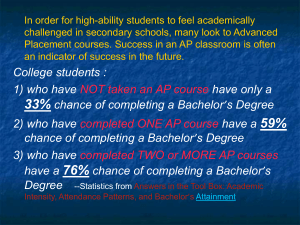
Computational models for prediction of fire behaviour
... - influence of convection, diffusion, volumetric (buoyancy) force - transport equation for thermal radiation ...
... - influence of convection, diffusion, volumetric (buoyancy) force - transport equation for thermal radiation ...
Chapter 10 Cycles
... Figure 10.8: Sketch of diverging isobars for CPIG in T − s plane. There are other classes of Brayton cycle plants. Schematics are shown next. • Turbojet. In the turbojet, the kinetic energy of the fluid becomes important at two points in the cycle. In the compression, the freestream fluid, entering ...
... Figure 10.8: Sketch of diverging isobars for CPIG in T − s plane. There are other classes of Brayton cycle plants. Schematics are shown next. • Turbojet. In the turbojet, the kinetic energy of the fluid becomes important at two points in the cycle. In the compression, the freestream fluid, entering ...
The O 1s and V 2p X-ray Absorption Spectra of Vanadium Oxides
... Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 24, no. 3, September, 1994 TRANSMISSION ...
... Brazilian Journal of Physics, vol. 24, no. 3, September, 1994 TRANSMISSION ...
Basic Principles of Shock Loading
... Fatigue loading occurs when the member experiences alternating, repeated, or fluctuating stresses. Fatigue loading generally is classified by the number of loading cycles on the member and the stress level. Low cycle fatigue usually is associated with stress levels above the yield point, and fractur ...
... Fatigue loading occurs when the member experiences alternating, repeated, or fluctuating stresses. Fatigue loading generally is classified by the number of loading cycles on the member and the stress level. Low cycle fatigue usually is associated with stress levels above the yield point, and fractur ...
Settling and Sedimentation
... For other shapes of particles, drag coefficients will be different If the particles are quite small, Brownian motion is present. Brownian motion is the random motion imparted to the particle by collisions between the molecules of the fluid surrounding the particle and the particle. This movement is ...
... For other shapes of particles, drag coefficients will be different If the particles are quite small, Brownian motion is present. Brownian motion is the random motion imparted to the particle by collisions between the molecules of the fluid surrounding the particle and the particle. This movement is ...
Chemisorption of acrylonitrile on the Cu(100) Linköping University Post Print
... tionally demanding than the gradient-corrected approximations, it allows us to consider rather large clusters with all 3d, 4d, and 4p atomic orbitals of Cu included in the basis set. The charge analysis used in this work comes from the Hirshfeld scheme, which is directly based on the electronic dens ...
... tionally demanding than the gradient-corrected approximations, it allows us to consider rather large clusters with all 3d, 4d, and 4p atomic orbitals of Cu included in the basis set. The charge analysis used in this work comes from the Hirshfeld scheme, which is directly based on the electronic dens ...
Influence of magmatism on mantle cooling, surface heat flow and
... 2006; Korenaga, 2008), and although a crucial component of this scaling—constant slab bending radius—is arguably invalid (as argued by Davies (2009) and Leng and Zhong (2010) and observed by Buffett and Heuret (2011)), isochemical numerical convection calculations (Korenaga, 2010) do indicate a subs ...
... 2006; Korenaga, 2008), and although a crucial component of this scaling—constant slab bending radius—is arguably invalid (as argued by Davies (2009) and Leng and Zhong (2010) and observed by Buffett and Heuret (2011)), isochemical numerical convection calculations (Korenaga, 2010) do indicate a subs ...
- Lancaster EPrints
... density. Such approaches are appealing since they are not directly influenced by the theoretical methodology employed in the obtention of the density to be analysed: in fact, such analyses can be applied to experimental densities derived from low temperature X-ray diffraction (XRD) data [6]. The mos ...
... density. Such approaches are appealing since they are not directly influenced by the theoretical methodology employed in the obtention of the density to be analysed: in fact, such analyses can be applied to experimental densities derived from low temperature X-ray diffraction (XRD) data [6]. The mos ...
Physics 4B Thermodynamics Laboratory Manual
... half ice, we can also determine the amount of heat energy needed to melt a gram of ice. This energy is known as the latent heat of fusion. You can also determine the amount of heat energy needed to turn a gram of boiling water into steam. This energy is known as the latent heat of vaporization. It i ...
... half ice, we can also determine the amount of heat energy needed to melt a gram of ice. This energy is known as the latent heat of fusion. You can also determine the amount of heat energy needed to turn a gram of boiling water into steam. This energy is known as the latent heat of vaporization. It i ...
Basic Concepts
... • The energy stored in the system by virtue of the configuration and motion of molecules constituting the system is called internal energy (U). The energy due to mass motion of the system as a whole (the kinetic energy), and that due to its external position in gravitational, electrical, or magnetic ...
... • The energy stored in the system by virtue of the configuration and motion of molecules constituting the system is called internal energy (U). The energy due to mass motion of the system as a whole (the kinetic energy), and that due to its external position in gravitational, electrical, or magnetic ...
Thesis-KM-oct11
... data matrix. This data matrix can be turned into a detailed 2D map of the measured area using commercial software such as Igor Pro and Labview which enables us to see important connections between formations of the various ions (in terms of relative intensities). Thus 2D data for HX show you how I(H ...
... data matrix. This data matrix can be turned into a detailed 2D map of the measured area using commercial software such as Igor Pro and Labview which enables us to see important connections between formations of the various ions (in terms of relative intensities). Thus 2D data for HX show you how I(H ...
XeCu Covalent Bonding in XeCuF and XeCuCl, Characterized by
... Abstract: XeCu covalent bonding has been found in the complexes XeCuF and XeCuCl. The molecules were characterized by Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy, supported by MP2 ab initio calculations. The complexes were prepared by laser ablation of Cu in the presence of Xe and SF6 or Cl2 and stabil ...
... Abstract: XeCu covalent bonding has been found in the complexes XeCuF and XeCuCl. The molecules were characterized by Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy, supported by MP2 ab initio calculations. The complexes were prepared by laser ablation of Cu in the presence of Xe and SF6 or Cl2 and stabil ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.