Chapter One :- Concepts and Definitions
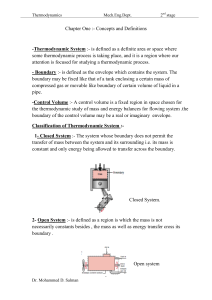
... - Homogeneous and Heterogeneous :- A substance exist at a single phase called a homogeneous , while one consists of two or more phase is called ...
... - Homogeneous and Heterogeneous :- A substance exist at a single phase called a homogeneous , while one consists of two or more phase is called ...
Simulation of the influence of preheating on stress - Purdue e-Pubs
... defects because of stress concentration. In order to obtain the heating parameters, it is important to calculate the stress distribution under various preheating conditions. In this study, a thermal-mechanical computational procedure based on thermal elastic-plasticity theory was developed to unders ...
... defects because of stress concentration. In order to obtain the heating parameters, it is important to calculate the stress distribution under various preheating conditions. In this study, a thermal-mechanical computational procedure based on thermal elastic-plasticity theory was developed to unders ...
8POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
... 2.A force acts between a particle-like object (tomato or block) in the system and the rest of the system. 3.When the system configuration changes, the force does work (call it W1) on the particle-like object, transferring energy between the kinetic energy K of the object and some other type of energ ...
... 2.A force acts between a particle-like object (tomato or block) in the system and the rest of the system. 3.When the system configuration changes, the force does work (call it W1) on the particle-like object, transferring energy between the kinetic energy K of the object and some other type of energ ...
Presentation453.08
... drag defines a certain velocity as the steady state speed at which the particles move under the influence of an acting external force and of the viscosity of the medium. Friction increases with speed, so that the speed of the particle will only increase up to a point, until it will reach a steady st ...
... drag defines a certain velocity as the steady state speed at which the particles move under the influence of an acting external force and of the viscosity of the medium. Friction increases with speed, so that the speed of the particle will only increase up to a point, until it will reach a steady st ...
Thermodynamic Properties of a single component fluid PV UH += TS
... we have a total of 83 = 512 different partial derivatives. The Bridgeman Tables can give us any of these partials, although some are not as useful as others. The Bridgeman Tables require (i) an equation of state, (ii) an expression for the heat capacity (either , Cv or Cp) and a single reference ent ...
... we have a total of 83 = 512 different partial derivatives. The Bridgeman Tables can give us any of these partials, although some are not as useful as others. The Bridgeman Tables require (i) an equation of state, (ii) an expression for the heat capacity (either , Cv or Cp) and a single reference ent ...
Laboratory Exercises in Physical Chemistry
... In this experiment a thermos bottle is used as a calorimeter. The thermos bottle is closed with a lid. Determination of the calorimeter constant, C: 1) fill the thermos bottle with 300 ml of distilled water, put a stirrer into it and take temperature-time readings at 10-second intervals until the di ...
... In this experiment a thermos bottle is used as a calorimeter. The thermos bottle is closed with a lid. Determination of the calorimeter constant, C: 1) fill the thermos bottle with 300 ml of distilled water, put a stirrer into it and take temperature-time readings at 10-second intervals until the di ...
EXCESS HEAT DURING DIFFUSION OF DEUTERIUM THROUGH PALLADIUM
... The main idea behind our calorimeter design is the use of a mass flow calorimetric method so that no calibration is necessary. Its design has been improved over time and it can be described in two different designs described below. 2.1 - First design Figure 1 shows a view of the first system. The va ...
... The main idea behind our calorimeter design is the use of a mass flow calorimetric method so that no calibration is necessary. Its design has been improved over time and it can be described in two different designs described below. 2.1 - First design Figure 1 shows a view of the first system. The va ...
Thermodynamics
... heat, or matter between the system and the surroundings In classical thermodynamics, the second law is a basic take place across this boundary. postulate applicable to any system involving heat energy In practice, the boundary is simply an imaginary dotted transfer; in statistical thermodynamics, th ...
... heat, or matter between the system and the surroundings In classical thermodynamics, the second law is a basic take place across this boundary. postulate applicable to any system involving heat energy In practice, the boundary is simply an imaginary dotted transfer; in statistical thermodynamics, th ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.