Apparatus to measure high-temperature thermal conductivity and
... details of instrument fabrication, the method of calibration, and typical measurements on test samples are described. The apparatus can also be used to measure the Seebeck coefficient in the same temperature range. As an example we report the thermal properties of CrSi2, which is a potential candida ...
... details of instrument fabrication, the method of calibration, and typical measurements on test samples are described. The apparatus can also be used to measure the Seebeck coefficient in the same temperature range. As an example we report the thermal properties of CrSi2, which is a potential candida ...
Chapter 2 - Department of Mechanical Engineering
... energy buildup in a space (i.e., car). The surface of the earth, which warms up during the day as a result of the absorption of solar energy, cools down at night by radiating part of its energy into deep space as infrared radiation. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and trace amounts of some other ...
... energy buildup in a space (i.e., car). The surface of the earth, which warms up during the day as a result of the absorption of solar energy, cools down at night by radiating part of its energy into deep space as infrared radiation. Carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and trace amounts of some other ...
Chapter 6 CHEM 121
... • Potential energy is the energy a particle has as a result of being attracted to or repelled by other particles. • COHESIVE FORCE • A cohesive force is an attractive force between particles. It is associated with potential energy. • DISRUPTIVE FORCE • A disruptive force results from particle motion ...
... • Potential energy is the energy a particle has as a result of being attracted to or repelled by other particles. • COHESIVE FORCE • A cohesive force is an attractive force between particles. It is associated with potential energy. • DISRUPTIVE FORCE • A disruptive force results from particle motion ...
Practice Exam
... Problem 13. A steam supply line provides steam at a temperature of 600 oF and a pressure of 500 lbf/in2. The valve is opened, and steam flows through a turbine and into an evacuated tank (volume = 10 ft3). When the pressure in the tank equals the supply line pressure the valve is closed. The work ou ...
... Problem 13. A steam supply line provides steam at a temperature of 600 oF and a pressure of 500 lbf/in2. The valve is opened, and steam flows through a turbine and into an evacuated tank (volume = 10 ft3). When the pressure in the tank equals the supply line pressure the valve is closed. The work ou ...
Lecture 2: Adiabatic Flame Temperature and Chemical Equilibrium
... those that are accepted by modern emission standards which are around 100 ppv or ...
... those that are accepted by modern emission standards which are around 100 ppv or ...
HEALTH, AGEING AND ENTROPY
... carbohydrates and proteins and on the other side we transfer it to the surroundings as heat. Thermodynamically it means that ordered organic molecules are changed to totally unordered form of energy – heat. Highly ordered systems carry low entropy and much stored information. According to second the ...
... carbohydrates and proteins and on the other side we transfer it to the surroundings as heat. Thermodynamically it means that ordered organic molecules are changed to totally unordered form of energy – heat. Highly ordered systems carry low entropy and much stored information. According to second the ...
17 Energy in SHM - Blue Valley Schools
... Motion Detector directly below the hanging mass, taking care that no extraneous objects could send echoes back to the detector. Protect the Motion Detector by placing a wire basket over the detector. The mass should be at least 20 cm above the detector when it is at rest. Using amplitudes of 10 cm o ...
... Motion Detector directly below the hanging mass, taking care that no extraneous objects could send echoes back to the detector. Protect the Motion Detector by placing a wire basket over the detector. The mass should be at least 20 cm above the detector when it is at rest. Using amplitudes of 10 cm o ...
org - thermal physics ib2 09
... When thermal energy is added to a solid, the molecules gain kinetic energy as they vibrate at an increased rate. This is seen macroscopically as an increase in temperature. At the melting point, a temperature is reached at which the kinetic energy of the molecules is so great that they begin to brea ...
... When thermal energy is added to a solid, the molecules gain kinetic energy as they vibrate at an increased rate. This is seen macroscopically as an increase in temperature. At the melting point, a temperature is reached at which the kinetic energy of the molecules is so great that they begin to brea ...
Crystal Defects – Enhancing Silicon Semiconductor Properties by
... The N-type impurity loses its extra valence electron easily when added to a semiconductor material, and in so doing, increases the conductivity of the material by contributing a free electron. This type of impurity has 5 valence electrons and is called a PENTAVALENT impurity. Arsenic, antimony, bism ...
... The N-type impurity loses its extra valence electron easily when added to a semiconductor material, and in so doing, increases the conductivity of the material by contributing a free electron. This type of impurity has 5 valence electrons and is called a PENTAVALENT impurity. Arsenic, antimony, bism ...
Lect13
... Which of the following statements are true? A. You increased the gravitational potential energy and performed negative work on the bag. B. You increased the gravitational potential energy and the earth performed positive work on the bag. C. You increased the gravitational potential energy and the ea ...
... Which of the following statements are true? A. You increased the gravitational potential energy and performed negative work on the bag. B. You increased the gravitational potential energy and the earth performed positive work on the bag. C. You increased the gravitational potential energy and the ea ...
EnergyWorkPower_
... Power is the rate of doing work B. Power is the rate of change of velocity C. Power is a vector D. Power is the potential energy gained when the mass is raised ...
... Power is the rate of doing work B. Power is the rate of change of velocity C. Power is a vector D. Power is the potential energy gained when the mass is raised ...
chapter12
... • Wenv is used to denote the work done by the gas – The focus would be on harnessing a system’s internal energy to do work on something external to the gas ...
... • Wenv is used to denote the work done by the gas – The focus would be on harnessing a system’s internal energy to do work on something external to the gas ...
Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Structure
... Negatively charged particles are emitted from the negative electrode (cathode). These “cathode rays” are accelerated toward and through the positive electrode (anode) and smash against the far end of the tube. They leave tracks by the light emitted by the residual gas along their path. The electrons ...
... Negatively charged particles are emitted from the negative electrode (cathode). These “cathode rays” are accelerated toward and through the positive electrode (anode) and smash against the far end of the tube. They leave tracks by the light emitted by the residual gas along their path. The electrons ...
E. The atomic model describes the electrically neutral atom a
... the stars and the universe (e.g., chemical composition, temperature, age of stars, location of black holes, motion of celestial bodies) 1. Science understanding is developed through the use of science process skills, scientific knowledge, scientific investigation, reasoning, and critical thinking A. ...
... the stars and the universe (e.g., chemical composition, temperature, age of stars, location of black holes, motion of celestial bodies) 1. Science understanding is developed through the use of science process skills, scientific knowledge, scientific investigation, reasoning, and critical thinking A. ...
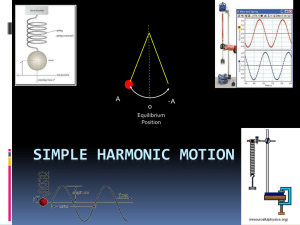
Simple Harmonic motion
... Since no mass is present in either formula, the period or frequency of a pendulum is independent of its mass! ...
... Since no mass is present in either formula, the period or frequency of a pendulum is independent of its mass! ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.