Food for Thought: What Fuels Brain Cells?
... predominantly use lactate as a fuel, and restrict the use of glucose to predominantly produce a form of energy called reducing power. This allows them to buffer the free radicals they produce because of their high oxidative metabolism. Astrocytes in turn, process glucose mostly glycolytically in an ...
... predominantly use lactate as a fuel, and restrict the use of glucose to predominantly produce a form of energy called reducing power. This allows them to buffer the free radicals they produce because of their high oxidative metabolism. Astrocytes in turn, process glucose mostly glycolytically in an ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Action Potential: neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ...
... Action Potential: neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ...
to the ms word version of these notes.
... right side of the brain, the person will see it perfectly well, but may not be able to name it, even though it is a common object. This demonstrates that the two hemispheres are functional different, each having some strengths and weaknesses not shared by the other hemisphere. It also demonstrates t ...
... right side of the brain, the person will see it perfectly well, but may not be able to name it, even though it is a common object. This demonstrates that the two hemispheres are functional different, each having some strengths and weaknesses not shared by the other hemisphere. It also demonstrates t ...
the biology of awareness
... mammalian brains. They control the same activities like breathing and body temperature. But our brains do other things as well. The most interesting is our unique mode of communication called “symbolic language.” We use written and spoken language to express abstract ideas and concepts. We also use ...
... mammalian brains. They control the same activities like breathing and body temperature. But our brains do other things as well. The most interesting is our unique mode of communication called “symbolic language.” We use written and spoken language to express abstract ideas and concepts. We also use ...
Childhood Physical Growth
... The bones of the child continue to grow. The arms and legs get longer. Since the legs now grow faster than the torso, the legs constitute a growing percentage of the height of the child. The bones in the hands and feet also grow, but in a different way. While the one year old typically has only ...
... The bones of the child continue to grow. The arms and legs get longer. Since the legs now grow faster than the torso, the legs constitute a growing percentage of the height of the child. The bones in the hands and feet also grow, but in a different way. While the one year old typically has only ...
Your Child`s Brain
... and rumpled cortex wherein thought and perception originate. The neural cells are so small, and the distance so great, that a neuron striking out for what will be the prefrontal cortex migrates a distance equivalent to a human's walking from New York to California, says developmental neurobiologist ...
... and rumpled cortex wherein thought and perception originate. The neural cells are so small, and the distance so great, that a neuron striking out for what will be the prefrontal cortex migrates a distance equivalent to a human's walking from New York to California, says developmental neurobiologist ...
Chap 2 Outline
... We can use case studies of human brain damage to learn about the brain’s functions, but cannot easily generalize from one case to another. We can study the brain by using deep lesioning to destroy certain areas of the brain in laboratory animals, or by electrically stimulating those areas (ESB). ...
... We can use case studies of human brain damage to learn about the brain’s functions, but cannot easily generalize from one case to another. We can study the brain by using deep lesioning to destroy certain areas of the brain in laboratory animals, or by electrically stimulating those areas (ESB). ...
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS
... fully as possible and may need support to do so. This course will look at some of the more common neurological conditions that you will come across as a carer, and will provide you with the information you need to support these people. In order to understand neurological conditions, it is important ...
... fully as possible and may need support to do so. This course will look at some of the more common neurological conditions that you will come across as a carer, and will provide you with the information you need to support these people. In order to understand neurological conditions, it is important ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
... Neuroscience and the Central Nervous System • The neuron – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – branches that receive messages from other neurons – Axon – trunk of neuron that sends messages to other neurons – Axon terminals – buds at end of axon from which chemical messages are sent – Synapses – small ...
... Neuroscience and the Central Nervous System • The neuron – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – branches that receive messages from other neurons – Axon – trunk of neuron that sends messages to other neurons – Axon terminals – buds at end of axon from which chemical messages are sent – Synapses – small ...
Revised Lesson Plan 1 - The Brain
... Group students by asking them to count 1 – 6. Students with the same number will form a group. There should be at least 3 – 4 members in a group. Ask students to name five ways in which they use their brain every day. Have them write their answers on sticky notes and post them on the poster board pr ...
... Group students by asking them to count 1 – 6. Students with the same number will form a group. There should be at least 3 – 4 members in a group. Ask students to name five ways in which they use their brain every day. Have them write their answers on sticky notes and post them on the poster board pr ...
Jenny - Brookings School District
... • When a neuron is at rest, it is in a state of polarization and contains membrane potential. There is an excess of sodium (Na+) ions outside of the cell membrane that create a positive charge. Similarly, there is an excess of potassium (K+) ions inside the cell along with negatively charged molecul ...
... • When a neuron is at rest, it is in a state of polarization and contains membrane potential. There is an excess of sodium (Na+) ions outside of the cell membrane that create a positive charge. Similarly, there is an excess of potassium (K+) ions inside the cell along with negatively charged molecul ...
Chapter 8 - Cloudfront.net
... Consists of nerves The twelve nerves branching from brain The thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves Most nerves contain both sensory and motor nerves ...
... Consists of nerves The twelve nerves branching from brain The thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves Most nerves contain both sensory and motor nerves ...
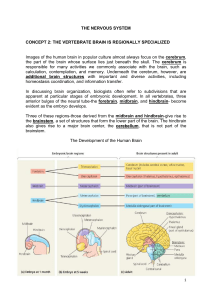
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... Emotional experiences are often stored as memories that can be recalled by similar circumstances. In the case of fear, emotional memory is stored separately from the memory system that supports explicit recall of events. The focus of emotional memory is the amygdala, which is located in the temporal ...
... Emotional experiences are often stored as memories that can be recalled by similar circumstances. In the case of fear, emotional memory is stored separately from the memory system that supports explicit recall of events. The focus of emotional memory is the amygdala, which is located in the temporal ...
Brain Functions
... glial cells we wouldn't have working neurons, and without neurons there would be no point of glial cells. About 90 percent of your brain cells are glial cells (the other 10 percent are neurons) which means that we have about 1,000 billion of them. Did you know that glial means "glue?" These cells ar ...
... glial cells we wouldn't have working neurons, and without neurons there would be no point of glial cells. About 90 percent of your brain cells are glial cells (the other 10 percent are neurons) which means that we have about 1,000 billion of them. Did you know that glial means "glue?" These cells ar ...
Biological Bases of Behavior - Mrs. Short`s AP Psychology Class
... 1. sensory neurons are located in the body’s sense organs (for example, the eye, ear, or nose) and send information from these organs to the brain 2. motor neurons– convey information from the nervous system to the body’s organs, glands, and muscles 3. interneurons (association neurons) transmit inf ...
... 1. sensory neurons are located in the body’s sense organs (for example, the eye, ear, or nose) and send information from these organs to the brain 2. motor neurons– convey information from the nervous system to the body’s organs, glands, and muscles 3. interneurons (association neurons) transmit inf ...
Psychology Chapter 3
... -If we think of the nervous system as long “chains” of communicating cells, then neurons are the links. -Neurons come in many different shapes and sizes, but the most consist of four basic parts. ...
... -If we think of the nervous system as long “chains” of communicating cells, then neurons are the links. -Neurons come in many different shapes and sizes, but the most consist of four basic parts. ...
Understanding the Brain`s Emergent Properties
... brain, the correlation models that are required may be too complex and may require more sophisticated learning methods than what we have tried with rule abstraction. Finally, it could be the case that the system we are trying to understand simply has no “midpoints.” That is, emergent behavior result ...
... brain, the correlation models that are required may be too complex and may require more sophisticated learning methods than what we have tried with rule abstraction. Finally, it could be the case that the system we are trying to understand simply has no “midpoints.” That is, emergent behavior result ...
Nervous System
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom and glandular ...
Slides
... Though it seems self-evident to us, the realization that the brain is the physical organ that underlies cognition is fairly recent. The ancient Egyptians thought that the heart was the seat of human intelligence and routinely removed the brain in the course of mummification, presumably on the ground ...
... Though it seems self-evident to us, the realization that the brain is the physical organ that underlies cognition is fairly recent. The ancient Egyptians thought that the heart was the seat of human intelligence and routinely removed the brain in the course of mummification, presumably on the ground ...
The Biology of Mind 2011-12
... Language Aphasia is an impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). ...
... Language Aphasia is an impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding). ...
Exercises and Tests
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...