Chapter 2 Notes Packet (Part 1)
... Called ________________________________ Law However, the neuron is more likely to fire more often when stimulated by a strong signal _________________________________Period: After a neuron fires, for the next thousandth of a second it will not fire again regardless of the strength of the incom ...
... Called ________________________________ Law However, the neuron is more likely to fire more often when stimulated by a strong signal _________________________________Period: After a neuron fires, for the next thousandth of a second it will not fire again regardless of the strength of the incom ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... Top-down processing lets us use the general loudness of sounds, as well as differences in the signals received from each ear, to determine location of a sound. Different pitches are represented in a tonotopic map in the auditory cortex of the brain. Association areas of the cortex help us recognize ...
... Top-down processing lets us use the general loudness of sounds, as well as differences in the signals received from each ear, to determine location of a sound. Different pitches are represented in a tonotopic map in the auditory cortex of the brain. Association areas of the cortex help us recognize ...
heledius - Society for the Advancement of Sexual Health
... Must have support from nearby glial cells. Must have nutrients from the blood. Must be able to establish connections with already ...
... Must have support from nearby glial cells. Must have nutrients from the blood. Must be able to establish connections with already ...
File parts of the brain
... = controls language expression that directs the muscle movements involved in speech. ...
... = controls language expression that directs the muscle movements involved in speech. ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... g. Synapse – Junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. h. There is lots of variety among Neurons, so not all neurons contain all these parts. 2. Glia – Cells in Nervous System that provides various support for neurons. a. Glial cells supply nourishment to neurons, remove ...
... g. Synapse – Junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. h. There is lots of variety among Neurons, so not all neurons contain all these parts. 2. Glia – Cells in Nervous System that provides various support for neurons. a. Glial cells supply nourishment to neurons, remove ...
Unit Three- The Brain
... Similarly, in the _______________________, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion of the ___________________. This part of the cortex receives information about the individual's current position from several other parts. Then, like the ship's captain, it issues its com ...
... Similarly, in the _______________________, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion of the ___________________. This part of the cortex receives information about the individual's current position from several other parts. Then, like the ship's captain, it issues its com ...
Brain Imaging Jigsaw Articles
... Positron emission tomography (PET), or “PET scanning”, was the first functional brain imaging technology to become available. It was developed in the mid-1970s. The physiological phenomenon on which both PET and fMRI are based was discovered in the late 19th century, when neurosurgeons found that th ...
... Positron emission tomography (PET), or “PET scanning”, was the first functional brain imaging technology to become available. It was developed in the mid-1970s. The physiological phenomenon on which both PET and fMRI are based was discovered in the late 19th century, when neurosurgeons found that th ...
INTRODUCTION: LANGUAGE DISORDERS IN ADULTS
... could not speak, Wernicke's patient could speak but could not fully comprehend. Wernicke's new type of aphasia also had a different locus from that described by Broca: it was located in the posterior part of the temporal lobe. ...
... could not speak, Wernicke's patient could speak but could not fully comprehend. Wernicke's new type of aphasia also had a different locus from that described by Broca: it was located in the posterior part of the temporal lobe. ...
to the ms word version of these notes.
... This demonstrates that the two hemispheres are functional different, each having some strengths and weaknesses not shared by the other hemisphere. It also demonstrates that information flow between the two hemispheres is necessary for the full range of human responses. For most people the left hemis ...
... This demonstrates that the two hemispheres are functional different, each having some strengths and weaknesses not shared by the other hemisphere. It also demonstrates that information flow between the two hemispheres is necessary for the full range of human responses. For most people the left hemis ...
accepted manuscript - Radboud Repository
... Euclidean space, so that one can refer to a particular activity pattern by specifying its spatial coordinates. Since each of these methods has limited resolution in either the time or spatial domain, incorporating additional data, such as those obtained from invasive animal studies, would be highly ...
... Euclidean space, so that one can refer to a particular activity pattern by specifying its spatial coordinates. Since each of these methods has limited resolution in either the time or spatial domain, incorporating additional data, such as those obtained from invasive animal studies, would be highly ...
PPT
... inspection systems, beer testing, welding quality analysis, paper quality prediction, computer chip quality analysis, analysis of grinding operations, chemical product design analysis, machine maintenance analysis, project bidding, planning and management, dynamic modeling of chemical process system ...
... inspection systems, beer testing, welding quality analysis, paper quality prediction, computer chip quality analysis, analysis of grinding operations, chemical product design analysis, machine maintenance analysis, project bidding, planning and management, dynamic modeling of chemical process system ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... Alzheimer’s Disease • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
... Alzheimer’s Disease • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
HCLSIG_BioRDF_Subgroup$$Meetings$$2008-11
... • Properties: attributes that are used to annotate page contents and relate pages – E.g., Address, Age, Sex, Email, and Friends are properties of Jone Smith ...
... • Properties: attributes that are used to annotate page contents and relate pages – E.g., Address, Age, Sex, Email, and Friends are properties of Jone Smith ...
Nervous System
... Identify the parts of the rat’s brain: olfactory bulbs, cerebral cortex, and cerebellum. The rat brain is different from the human brain in several ways. First, the human brain has many folds called gyri; the rat’s brain is smooth in appearance. Second, the olfactory bulbs (for smelling) of the rat ...
... Identify the parts of the rat’s brain: olfactory bulbs, cerebral cortex, and cerebellum. The rat brain is different from the human brain in several ways. First, the human brain has many folds called gyri; the rat’s brain is smooth in appearance. Second, the olfactory bulbs (for smelling) of the rat ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... communicate with the rest of the body, specifically the neuron Neurons are highly specialized cells that receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another They communicate information in electrical and chemical form Your entire brain has an estimated 100 billion neurons Glial Cel ...
... communicate with the rest of the body, specifically the neuron Neurons are highly specialized cells that receive and transmit information from one part of the body to another They communicate information in electrical and chemical form Your entire brain has an estimated 100 billion neurons Glial Cel ...
Cell body
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
Biological Impact
... • The cerebral cortex is a higher-level brain structure…it’s responsible for higher-level cognitive processes • The cerebral cortex covers the two hemispheres of the brain with wrinkled folds (sort of like a cauliflower)….these “wrinkles” increase the entire surface area of the cortex. • The cerebra ...
... • The cerebral cortex is a higher-level brain structure…it’s responsible for higher-level cognitive processes • The cerebral cortex covers the two hemispheres of the brain with wrinkled folds (sort of like a cauliflower)….these “wrinkles” increase the entire surface area of the cortex. • The cerebra ...
The basic unit of computation - Zador Lab
... more general models of network computation14–16, and it has been rigorously proven that such networks can implement a very rich class of computations17. Common to all these models is the notion that synapses do more than just provide a substrate for the long-lasting changes underlying learning and m ...
... more general models of network computation14–16, and it has been rigorously proven that such networks can implement a very rich class of computations17. Common to all these models is the notion that synapses do more than just provide a substrate for the long-lasting changes underlying learning and m ...
Neuropsychology
... ▫ Invasive methods: Lesion studies, electrical stimulation ▫ Non-invasive methods: EEG, MEG, MRI, fMRI, CT, ...
... ▫ Invasive methods: Lesion studies, electrical stimulation ▫ Non-invasive methods: EEG, MEG, MRI, fMRI, CT, ...
November 1 CNS INTRO
... 15. Motor tracts descending from the cortex to motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord will descend through the brainstem in the following order: A. Myelencephalon, Metencephalon, Mesencephalon B. Metencephalon, Myelencephalon, Mesencephalon C. Mesencephalon, Metencephalon, Myelencephal ...
... 15. Motor tracts descending from the cortex to motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord will descend through the brainstem in the following order: A. Myelencephalon, Metencephalon, Mesencephalon B. Metencephalon, Myelencephalon, Mesencephalon C. Mesencephalon, Metencephalon, Myelencephal ...
Slide ()
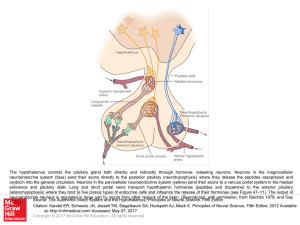
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
Nervous_System_PowerPoint
... Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord White matter: propagates sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the periphery Gray matter: receives and integrates incoming and outgoing info ...
... Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord White matter: propagates sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the periphery Gray matter: receives and integrates incoming and outgoing info ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.