Lab Activity 14 - Portland Community College
... • The delay between stimulus and the response is minimized. • The synapse is considered the integration center ...
... • The delay between stimulus and the response is minimized. • The synapse is considered the integration center ...
Comparison of Quantities: Core and Format
... et al. 2010). Whereas in an analogue stimulus the magnitude is a perceptually accessible aspect of the stimulus, in a symbolic stimulus the magnitude being coded is independent from physical characteristics. For example, 3 dots and the Arabic digit ‘‘3’’ both implement the notion of 3 but the visual ...
... et al. 2010). Whereas in an analogue stimulus the magnitude is a perceptually accessible aspect of the stimulus, in a symbolic stimulus the magnitude being coded is independent from physical characteristics. For example, 3 dots and the Arabic digit ‘‘3’’ both implement the notion of 3 but the visual ...
(fMRI) in Brain Tumour Patients
... and lip pouting, for somatotopic mapping along the motor cortex. Commonly used tasks to activate the language areas are verb-to-noun generation (Figure 2), passive listening, and picture naming [7]. The baseline condition can simply consist of no activity or stimulus presentation, but may also be us ...
... and lip pouting, for somatotopic mapping along the motor cortex. Commonly used tasks to activate the language areas are verb-to-noun generation (Figure 2), passive listening, and picture naming [7]. The baseline condition can simply consist of no activity or stimulus presentation, but may also be us ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... of type I muscle fibers. To produce a given amount of force, a muscle that has a large number of type I muscle fibers will recruit a proportionally large number of motor units. ...
... of type I muscle fibers. To produce a given amount of force, a muscle that has a large number of type I muscle fibers will recruit a proportionally large number of motor units. ...
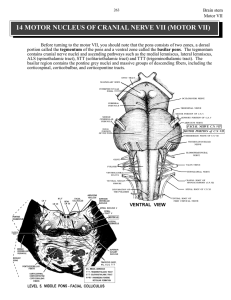
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... body. Lesions of the corticopontine projection and the basilar pontine grey result in CONTRALATERAL deficits in muscle coordination. This incoordination/ataxia involves both the arm and the leg. In contrast, a lesion of the middle cerebellar PEDUNCLE results in IPSILATERAL deficits in motor coordina ...
... body. Lesions of the corticopontine projection and the basilar pontine grey result in CONTRALATERAL deficits in muscle coordination. This incoordination/ataxia involves both the arm and the leg. In contrast, a lesion of the middle cerebellar PEDUNCLE results in IPSILATERAL deficits in motor coordina ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... the focus. The image is focused on the retina, a sheet of photo receptors that process vision. The retina is lined with neurons that line the line the back of the eye. As in a camera, the image on the retina is reversed: Objects to the right of center project images to the left part of the retina an ...
... the focus. The image is focused on the retina, a sheet of photo receptors that process vision. The retina is lined with neurons that line the line the back of the eye. As in a camera, the image on the retina is reversed: Objects to the right of center project images to the left part of the retina an ...
primary motor Cortex
... Voltage-gated ion channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Initially, a stimulus will cause the membrane to depolarize toward threshold. When this occurs, voltage-gated Na+ channels begin to open. As a result, Na+ ions enter the cell down their concentration and electri ...
... Voltage-gated ion channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential. Initially, a stimulus will cause the membrane to depolarize toward threshold. When this occurs, voltage-gated Na+ channels begin to open. As a result, Na+ ions enter the cell down their concentration and electri ...
Basal Ganglia
... neurons continue firing and change their activities according to certain adjustments made to each movement. Such BG activity influences VL thalamic projections back to area 4 (primary motor cortex), allowing for more discrete regulation of individual muscles. Additional targets of BG output are te ...
... neurons continue firing and change their activities according to certain adjustments made to each movement. Such BG activity influences VL thalamic projections back to area 4 (primary motor cortex), allowing for more discrete regulation of individual muscles. Additional targets of BG output are te ...
Towards natural stimulation in fMRI—Issues of data analysis
... identify neuronal networks related to seeing, hearing, and language processing: viewing of a 20-min movie led to increased correlations within these networks and to decreased correlations between non-connected regions. ICA has also revealed neural correlates of other complex human behaviors, such as ...
... identify neuronal networks related to seeing, hearing, and language processing: viewing of a 20-min movie led to increased correlations within these networks and to decreased correlations between non-connected regions. ICA has also revealed neural correlates of other complex human behaviors, such as ...
differentiation of brain vesicles
... hills) that show a great amount of variation in size among various species. Give examples for each pair. (You may want to refer to chapter 6 also.) 6) Name two pathways that originate in the midbrain and descend to the spinal cord. 7) At the base of the midbrain (ventral side) one finds a fiber bund ...
... hills) that show a great amount of variation in size among various species. Give examples for each pair. (You may want to refer to chapter 6 also.) 6) Name two pathways that originate in the midbrain and descend to the spinal cord. 7) At the base of the midbrain (ventral side) one finds a fiber bund ...
2 COMPUTATIONAL MODELLING IN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
... Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science in which methods and techniques are developed that permit intelligent computer systems to be built. These systems allow the simulation of different aspects of human and animal cognition, including perception, action, communication, problem ...
... Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science in which methods and techniques are developed that permit intelligent computer systems to be built. These systems allow the simulation of different aspects of human and animal cognition, including perception, action, communication, problem ...
Spinal Cord - Study Windsor
... What is Pain? “An unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with ...
... What is Pain? “An unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with ...
The suffix –ous Date set: 13th January 2017 Due in: 19th January
... The suffix –ous turns nouns into adjectives. When we add –ous to the end of root words, we have to follow these rules: Just add –ous (root ...
... The suffix –ous turns nouns into adjectives. When we add –ous to the end of root words, we have to follow these rules: Just add –ous (root ...
Lecture 11 - Fredonia.edu
... concrete physical processes by which speech is formed. – Speech is movement? – Study speech movements? ...
... concrete physical processes by which speech is formed. – Speech is movement? – Study speech movements? ...
Neurological Control of Movement. Chapter 3.
... The cerebellum is involved in all rapid and complex movement processes and assists the primary motor cortex and the basal ganglia. ...
... The cerebellum is involved in all rapid and complex movement processes and assists the primary motor cortex and the basal ganglia. ...
Mental Imagery in Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review
... disorders that have a profound impact not only on the life of the people affected but also on their family, caregivers and society at large. It adds on to the financial burden on the health care system as well. According to WHO fact sheet 2013, every year, around the world, between 2,50,000 and 5,00 ...
... disorders that have a profound impact not only on the life of the people affected but also on their family, caregivers and society at large. It adds on to the financial burden on the health care system as well. According to WHO fact sheet 2013, every year, around the world, between 2,50,000 and 5,00 ...
Three Controversial Hypotheses Concerning Computation in the
... 3 provides a complementary and similarly organized cortical interface for the bulk of sensory information related to touch, and other areas provide gateways for other senses. The general trends of modularity and functional localization seemed to hold for more complex functions as well. Brodmann area ...
... 3 provides a complementary and similarly organized cortical interface for the bulk of sensory information related to touch, and other areas provide gateways for other senses. The general trends of modularity and functional localization seemed to hold for more complex functions as well. Brodmann area ...
TRUTH Read
... tie. Do you ever feel queasy when you are in a stress ul situation—such as when your teacher springs a ii prise quiz on you? This is because your sympa thetic nervous system has kicked into ...
... tie. Do you ever feel queasy when you are in a stress ul situation—such as when your teacher springs a ii prise quiz on you? This is because your sympa thetic nervous system has kicked into ...
Nervous System: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... functional groups with limited input sources (sensory) and output locations (motor) ...
... functional groups with limited input sources (sensory) and output locations (motor) ...
Document
... responsible for assembling memories from: 1) inputs to visual, auditory, olfactory, taste and body contact, 2) sensory responses and consequences arising from motor behavior or speech, and 3) emotions associated with sensory and motor events. Memories are distributed in modality cortices, hippocampu ...
... responsible for assembling memories from: 1) inputs to visual, auditory, olfactory, taste and body contact, 2) sensory responses and consequences arising from motor behavior or speech, and 3) emotions associated with sensory and motor events. Memories are distributed in modality cortices, hippocampu ...
The Motor System of the Cortex and the Brain Stem
... art of neural prosthetics; and describe neural mechanisms of proprioception and feedback control of action. The human motor system produces action. It controls goal-directed movement by selecting the targets of action, generating a motor plan, and coordinating the generation of forces needed to achi ...
... art of neural prosthetics; and describe neural mechanisms of proprioception and feedback control of action. The human motor system produces action. It controls goal-directed movement by selecting the targets of action, generating a motor plan, and coordinating the generation of forces needed to achi ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... the axon to the axon terminals. From there, they cross synapses to the dendrites of other neurons. New synapses can develop between neurons that were not previously connected, as when we learn something new. ...
... the axon to the axon terminals. From there, they cross synapses to the dendrites of other neurons. New synapses can develop between neurons that were not previously connected, as when we learn something new. ...
Scrambling and Processing: Dependencies
... grammar. What distinguishes one syntactic theory from another is which the linguistic grounds it uses to argue for a particular structural representation. Often, theories compete with each other over long periods of time because linguistic methods do not strongly favor one theory over the other. One ...
... grammar. What distinguishes one syntactic theory from another is which the linguistic grounds it uses to argue for a particular structural representation. Often, theories compete with each other over long periods of time because linguistic methods do not strongly favor one theory over the other. One ...
The Mirror System, Imitation, and the Evolution of Language
... F5 rather than by visual inputs so that AIP can monitor ongoing activity as well as visual affordances. Here we indicate the case in which the visual input has activated an affordance for a precision pinch, and we here show the AIP activity driving an F5 cell pool that controls the execution of a pr ...
... F5 rather than by visual inputs so that AIP can monitor ongoing activity as well as visual affordances. Here we indicate the case in which the visual input has activated an affordance for a precision pinch, and we here show the AIP activity driving an F5 cell pool that controls the execution of a pr ...