Experimental Brain Research 221(1)
... cortex near the junction of the dorsal parieto-occipital sulcus, POS) (Fattori et al. 2001, 2009a; Galletti et al. 2003) and a putative ‘parietal reach region’ (PRR) that straddles the boundary between MIP and V6A (Batista et al. 1999; Buneo et al. 2002; Chang et al. 2008; Andersen and Cui 2009). PR ...
... cortex near the junction of the dorsal parieto-occipital sulcus, POS) (Fattori et al. 2001, 2009a; Galletti et al. 2003) and a putative ‘parietal reach region’ (PRR) that straddles the boundary between MIP and V6A (Batista et al. 1999; Buneo et al. 2002; Chang et al. 2008; Andersen and Cui 2009). PR ...
Chapter 14:The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... – Cranial dura mater is pressed closely against cranial ...
... – Cranial dura mater is pressed closely against cranial ...
Animal responses to the environment
... fibres. Nerve fibres are bundled together with some connective tissue. Nerve fibres and connective tissue make up nerve tissue. ...
... fibres. Nerve fibres are bundled together with some connective tissue. Nerve fibres and connective tissue make up nerve tissue. ...
After all, it`s still replication: A reply to Jacob on simulation and mirror
... left hand to drink) what are the observer’s MNs coding? Are the observer’s MNs coding the agent’s kinematic instructions, or the agent’s motor intention, or the agent’s prior intention? According to the classical model of MNs, MNs code the agent’s motor intention. In the remainder of this section, I ...
... left hand to drink) what are the observer’s MNs coding? Are the observer’s MNs coding the agent’s kinematic instructions, or the agent’s motor intention, or the agent’s prior intention? According to the classical model of MNs, MNs code the agent’s motor intention. In the remainder of this section, I ...
Network structure underlying resolution of conflicting non
... Social judgments often require resolution of incongruity in communication contents. Although previous studies revealed that such conflict resolution recruits brain regions including the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and posterior inferior frontal gyrus (pIFG), functional relationships and networks ...
... Social judgments often require resolution of incongruity in communication contents. Although previous studies revealed that such conflict resolution recruits brain regions including the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and posterior inferior frontal gyrus (pIFG), functional relationships and networks ...
A COMMON REFERENCE FRAME FOR MOVEMENT PLANS IN
... Figure 3 | A PRR neuron that encodes reaches to visual targets in an eye-centred reference frame. A monkey faced a panel that contained touch-sensitive buttons. Within each button was a red and a green light-emitting diode (LED). Red lights indicated where the monkey should look; green lights indica ...
... Figure 3 | A PRR neuron that encodes reaches to visual targets in an eye-centred reference frame. A monkey faced a panel that contained touch-sensitive buttons. Within each button was a red and a green light-emitting diode (LED). Red lights indicated where the monkey should look; green lights indica ...
The evolution of brains from early mammals to humans
... grasp maternal hair and nurse.29 As placental mammals could have long gestation periods for brain development, they thereby escaped this restriction. Overall, the comparative evidence indicates that early mammals had on the order of 15–20 cortical areas (see Figure 1) that were specialized for diffe ...
... grasp maternal hair and nurse.29 As placental mammals could have long gestation periods for brain development, they thereby escaped this restriction. Overall, the comparative evidence indicates that early mammals had on the order of 15–20 cortical areas (see Figure 1) that were specialized for diffe ...
Kandel ch. 42 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... together form the body of the cerebellum. The posterolateral fissure on the ventral surface separates the body from the much smaller flocculonodular lobe (Figure 422). Sagittal section through the midline shows that shallower fissures further subdivide each lobe into several lobules comprising a var ...
... together form the body of the cerebellum. The posterolateral fissure on the ventral surface separates the body from the much smaller flocculonodular lobe (Figure 422). Sagittal section through the midline shows that shallower fissures further subdivide each lobe into several lobules comprising a var ...
Patterning and axon guidance of cranial motor neurons
... in a particular rhombomere, as well as the timing of the onset of the expression and the expression level, dictates segmentation and segment identity at that axial level. The patterns of Hox gene expression in the hindbrain are established, at least in part, by the diffusible action of FGF8 and reti ...
... in a particular rhombomere, as well as the timing of the onset of the expression and the expression level, dictates segmentation and segment identity at that axial level. The patterns of Hox gene expression in the hindbrain are established, at least in part, by the diffusible action of FGF8 and reti ...
CN V - Trigeminal
... Cochlear ganglion to CN VIII CN VIII synapses in the cochlear nuclei Cochlear nuclei project to the superior olivary nucleus and inferior colliculus Superior olivary nucleus is also receiving input from contralateral cochlear nuclei Superior olivary nucleus projects to inferior colliculus Inferior c ...
... Cochlear ganglion to CN VIII CN VIII synapses in the cochlear nuclei Cochlear nuclei project to the superior olivary nucleus and inferior colliculus Superior olivary nucleus is also receiving input from contralateral cochlear nuclei Superior olivary nucleus projects to inferior colliculus Inferior c ...
Modulation of Neuronal Activity in the Monkey Putamen Associated
... dorsolateral part of the striatum that receives inputs from motor cortical areas constitutes the site for the learning and retention of overlearned skilled behaviors, whereas the dorsomedial part connected to association cortices is critical for acquiring new associations between stimuli and movemen ...
... dorsolateral part of the striatum that receives inputs from motor cortical areas constitutes the site for the learning and retention of overlearned skilled behaviors, whereas the dorsomedial part connected to association cortices is critical for acquiring new associations between stimuli and movemen ...
21. Basal ganglion
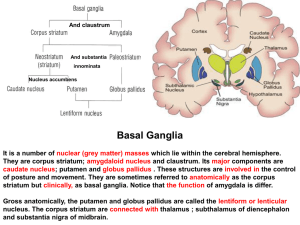
... caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal ganglia. Notice that the function of amygdala is differ. Gross anatomically, the putamen an ...
... caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal ganglia. Notice that the function of amygdala is differ. Gross anatomically, the putamen an ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... 25. Compare the major functional areas (sensory and motor) of the cerebral cortex in terms of location and function (a diagram may help here). 26. Explain what is meant by an association area of the cerebral cortex and name a few association traits. 27. Name the term referring to the measurement of ...
... 25. Compare the major functional areas (sensory and motor) of the cerebral cortex in terms of location and function (a diagram may help here). 26. Explain what is meant by an association area of the cerebral cortex and name a few association traits. 27. Name the term referring to the measurement of ...
Evolution of Specialized Pyramidal Neurons in
... 1978; Meyer, 1987; Hof and Morrison, 1995; Hof et al., 2000; Kaas, 2000]. Although comparable neurons have been described in other mammals, their exceptionally large size in primates [Le Gros Clark, 1942; Zilles, 1990; Kaas, 2000], for whom dexterous digital movement and vision are important [Le Gro ...
... 1978; Meyer, 1987; Hof and Morrison, 1995; Hof et al., 2000; Kaas, 2000]. Although comparable neurons have been described in other mammals, their exceptionally large size in primates [Le Gros Clark, 1942; Zilles, 1990; Kaas, 2000], for whom dexterous digital movement and vision are important [Le Gro ...
Neuroanatomy Final Review Notes by Russ Beach
... facial nucleus (lower face portion of facial nucleus) -UMN lesion would paralyze lower half of face on contralateral side -LMN lesion would paralyze complete half of face on ipsilateral side -Corticobulbar lesions are only represented by these facial effects, because all other cranial nuclei are pro ...
... facial nucleus (lower face portion of facial nucleus) -UMN lesion would paralyze lower half of face on contralateral side -LMN lesion would paralyze complete half of face on ipsilateral side -Corticobulbar lesions are only represented by these facial effects, because all other cranial nuclei are pro ...
fromkin-9-computers
... Bottom-up processing relates to decoding. You start with the actual sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. and figure out the words, phrases, clauses, sentences, paragraphs, etc. Top-down processing is based on reasoning. You make a generalization and see how well the sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. supp ...
... Bottom-up processing relates to decoding. You start with the actual sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. and figure out the words, phrases, clauses, sentences, paragraphs, etc. Top-down processing is based on reasoning. You make a generalization and see how well the sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. supp ...
Lecture notes for week 6
... PREDICATE SYMBOLS – that represent relationships between objects in the sense that objects are mapped to TRUE or FALSE. E.g., Brother(Rick,Father(John)) – Rick and John are constant symbols (objects), Fasther is a function symbol and Brother is a predicate symbol returning TRUE or FALSE. ...
... PREDICATE SYMBOLS – that represent relationships between objects in the sense that objects are mapped to TRUE or FALSE. E.g., Brother(Rick,Father(John)) – Rick and John are constant symbols (objects), Fasther is a function symbol and Brother is a predicate symbol returning TRUE or FALSE. ...
Cortical interactions underlying the production of speech sounds
... articulator movements are used to produce auditory and somatosensory feedback. This combination of articulatory, auditory, and somatosensory information is used to tune the synaptic projections between the sensory error maps and the model’s motor cortex. The learning in this stage is not phoneme- or ...
... articulator movements are used to produce auditory and somatosensory feedback. This combination of articulatory, auditory, and somatosensory information is used to tune the synaptic projections between the sensory error maps and the model’s motor cortex. The learning in this stage is not phoneme- or ...
CYTOARCHITECTURE OF CEREBRAL CORTEX
... • Cell-surface markers • Ion-channels • Connexins • Transporters: plasma membrane; vesicular • Others ...
... • Cell-surface markers • Ion-channels • Connexins • Transporters: plasma membrane; vesicular • Others ...
then
... status of commitment to joint goal changes status of commitment to attaining joint goal in the team context changes status of commitment of another team member changes R1: if status of commitment to joint goal changes or status of commitment in the team context changes then inform all other team ...
... status of commitment to joint goal changes status of commitment to attaining joint goal in the team context changes status of commitment of another team member changes R1: if status of commitment to joint goal changes or status of commitment in the team context changes then inform all other team ...
document
... Bottom-up processing relates to decoding. You start with the actual sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. and figure out the words, phrases, clauses, sentences, paragraphs, etc. Top-down processing is based on reasoning. You make a generalization and see how well the sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. supp ...
... Bottom-up processing relates to decoding. You start with the actual sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. and figure out the words, phrases, clauses, sentences, paragraphs, etc. Top-down processing is based on reasoning. You make a generalization and see how well the sounds, letters, morphemes, etc. supp ...
Properties of spike train spectra in two parietal reach areas
... Fairchild Building, Room D209, Stanford, CA 94305, USA ...
... Fairchild Building, Room D209, Stanford, CA 94305, USA ...
Investigation of the central regulation of taste perception and
... theories have emerged, and the most popular theory stated that antagonistic centers play role in the regulation of food intake. The stimulation of the so-called hungercenter, localized in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), causes complex foodsearching and consummative responses, so the animal rec ...
... theories have emerged, and the most popular theory stated that antagonistic centers play role in the regulation of food intake. The stimulation of the so-called hungercenter, localized in the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA), causes complex foodsearching and consummative responses, so the animal rec ...
CASE 47
... subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefrontal cortex) and send their output to the thalamus, which then feeds back to the cortex. Although the functions of the basal ganglia are not well under ...
... subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefrontal cortex) and send their output to the thalamus, which then feeds back to the cortex. Although the functions of the basal ganglia are not well under ...