ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... Second largest part of brain Coordinates body movements 2 Hemispheres (just like the cerebrum) Covered with cerebellar cortex (just like the cerebrum) Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that keep you alive Most cranial nerves attach to brainstem Processes information between spinal ...
... Second largest part of brain Coordinates body movements 2 Hemispheres (just like the cerebrum) Covered with cerebellar cortex (just like the cerebrum) Brainstem: Controls the daily functions that keep you alive Most cranial nerves attach to brainstem Processes information between spinal ...
Alternate Version with Animations
... transduced automatically into articulated words structured by the gestural programs. The meanings of words were automatically linked to the actions, sounds and shapes to which the gestures referred. ...
... transduced automatically into articulated words structured by the gestural programs. The meanings of words were automatically linked to the actions, sounds and shapes to which the gestures referred. ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... measured by amount of radioactivity present • This technique shows the pattern of neural activation is Figure 15.10 These molecules have the same related to both chemical chemical formula, but the molecular group at the structure and to perception bottom is rotated to a different position. The black ...
... measured by amount of radioactivity present • This technique shows the pattern of neural activation is Figure 15.10 These molecules have the same related to both chemical chemical formula, but the molecular group at the structure and to perception bottom is rotated to a different position. The black ...
Spinal Cord
... Dorsal and ventral roots fuse laterally to form spinal nerves Four zones are evident within the gray matter – somatic sensory (SS), visceral sensory (VS), visceral motor (VM), and somatic motor (SM) ...
... Dorsal and ventral roots fuse laterally to form spinal nerves Four zones are evident within the gray matter – somatic sensory (SS), visceral sensory (VS), visceral motor (VM), and somatic motor (SM) ...
Unit 3 - Mayfield City Schools
... -location of reticular activating system -controls heart rate, swallowing, breathing, and digestion -processes visual input -travel cross optic chiasma on the way to opposing hemisphere -involved in learning and memory formation -damages does not eliminate existing memories but prevents formation of ...
... -location of reticular activating system -controls heart rate, swallowing, breathing, and digestion -processes visual input -travel cross optic chiasma on the way to opposing hemisphere -involved in learning and memory formation -damages does not eliminate existing memories but prevents formation of ...
Nervous System
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
Growth and Development
... things for different lengths of time – They look at preferred objects longer ...
... things for different lengths of time – They look at preferred objects longer ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... • Neurons - nerve cells that transmit signals to/from the brain at up to 200 mph. – consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a long projection called an axon, which conducts the signal. The signal terminates at the axon terminals which transmits an electro-c ...
... • Neurons - nerve cells that transmit signals to/from the brain at up to 200 mph. – consists of a cell body (or soma) with branching dendrites (signal receivers) and a long projection called an axon, which conducts the signal. The signal terminates at the axon terminals which transmits an electro-c ...
7-4_DescendingPathways_HubaT
... In this picture you can see the 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are grouped according to the place where they emerge from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for carrying information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is the center of ...
... In this picture you can see the 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Spinal nerves are grouped according to the place where they emerge from the spinal cord. Spinal nerves are responsible for carrying information between the central nervous system and other parts of the body. The spinal cord is the center of ...
Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System
... If enough of the chemical builds up In the next neuron Impulse is sent on ...
... If enough of the chemical builds up In the next neuron Impulse is sent on ...
Motor Cortex, Basal Ganglia, Cerebellum
... 1. Projects to primary motor cortex and brain stem (particularly descending reticular formation) 2. Associated with assembling movements into coordinated actions. Lesions impair ability to develop appropriate sequences of muscle contractions 3. Participates in movements that involve several joints a ...
... 1. Projects to primary motor cortex and brain stem (particularly descending reticular formation) 2. Associated with assembling movements into coordinated actions. Lesions impair ability to develop appropriate sequences of muscle contractions 3. Participates in movements that involve several joints a ...
Orbitofrontal Cortex and Its Contribution to Decision
... The 13 region acts as a bridge between the lateral and medial layers of the brain. Primary olfactory and gustatory cortex project to this region. The 11 region is involved in planning, reasoning, and decision making. ...
... The 13 region acts as a bridge between the lateral and medial layers of the brain. Primary olfactory and gustatory cortex project to this region. The 11 region is involved in planning, reasoning, and decision making. ...
The Nervous System
... Frontal lobes control motor functions, memory, reasoning, and judgment Parietal lobes control sensory reception and integration, as well as taste. Temporal lobes receives auditory information Occipital lobes receive information from the eyes ...
... Frontal lobes control motor functions, memory, reasoning, and judgment Parietal lobes control sensory reception and integration, as well as taste. Temporal lobes receives auditory information Occipital lobes receive information from the eyes ...
Understanding mirror neurons: a bio-robotic
... Some F5 neurons in addition to their motor discharge, respond also to the presentation of visual stimuli. F5 visuomotor neurons pertain to two completely different categories. Neurons of the first category discharge when the monkey observes graspable objects (“canonical” F5 neurons, (Murata et al., ...
... Some F5 neurons in addition to their motor discharge, respond also to the presentation of visual stimuli. F5 visuomotor neurons pertain to two completely different categories. Neurons of the first category discharge when the monkey observes graspable objects (“canonical” F5 neurons, (Murata et al., ...
Document
... Show how expert systems can be used when a human expert is not available. Show how an artificial agent can be used to simulate mundane tasks performed by human beings. Show how expert systems and mundane systems can use different search techniques to solve problems. Show how the learning pro ...
... Show how expert systems can be used when a human expert is not available. Show how an artificial agent can be used to simulate mundane tasks performed by human beings. Show how expert systems and mundane systems can use different search techniques to solve problems. Show how the learning pro ...
The Peripheral Nervous System The P.N.S.
... cord to the hand muscles, telling them to draw away. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
... cord to the hand muscles, telling them to draw away. __________________________________________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
Document
... – Here, the child applies a word to a broader class of objects or actions than in adult usage ...
... – Here, the child applies a word to a broader class of objects or actions than in adult usage ...
• In vertebrates
... neurons are distributed according to the body part that generates sensory input or receives motor input Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... neurons are distributed according to the body part that generates sensory input or receives motor input Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
lower motor neurons
... (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal muscular atrophy) • Fasciculation occasionally develops due to anterior root lesion (disc herniation), compression- and other neuropathies • If large number of axons are affected fasciculation may be more prominent (even cramps can appear) ...
... (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal muscular atrophy) • Fasciculation occasionally develops due to anterior root lesion (disc herniation), compression- and other neuropathies • If large number of axons are affected fasciculation may be more prominent (even cramps can appear) ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Forebrain has two cerebral hemispheres which make up the cerebral cortex Basal ganglia is believed to facilitate movements involving power, speed, direction, and amplitude in movement preparation. Hypothalamus controls body temperature and regulates carbohydrate energy use. Thalamus is a relay stati ...
... Forebrain has two cerebral hemispheres which make up the cerebral cortex Basal ganglia is believed to facilitate movements involving power, speed, direction, and amplitude in movement preparation. Hypothalamus controls body temperature and regulates carbohydrate energy use. Thalamus is a relay stati ...
How does the Teenage Brain Work? (Teacher Version)
... 1. Do you feel teenagers have a lack of control over their impulses? truthfulness of Why or why not? arguments set forth in (Student’s answers will vary.) public documents; their 2. According to researchers, why are teenagers not able to make appeal to both friendly decisions the same way adults do? ...
... 1. Do you feel teenagers have a lack of control over their impulses? truthfulness of Why or why not? arguments set forth in (Student’s answers will vary.) public documents; their 2. According to researchers, why are teenagers not able to make appeal to both friendly decisions the same way adults do? ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous system that allows animals to respond to external and internal signals. Include: function of myelin sheath, function of Schwann cells, description of action potential and pr ...
... 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous system that allows animals to respond to external and internal signals. Include: function of myelin sheath, function of Schwann cells, description of action potential and pr ...
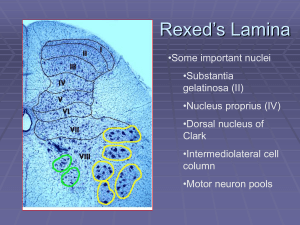
Rexed`s Lamina
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
... Spinocerebellar Pathway Proprioceptive signals from limbs and trunk travel up to the cerebellum Second order nerves ascend in ipsilateral lateral column ...
Slide 1
... • Sensory input can evoke motor response regardless of point of integration – Spinal cord – Lower region of brain – Motor area of cerebral cortex ...
... • Sensory input can evoke motor response regardless of point of integration – Spinal cord – Lower region of brain – Motor area of cerebral cortex ...