LT2Ch6
... Punishment can intensify inappropriate behavior when it elicits a response compatible with the punished response. Contiguity is essential to prevent conditioning of competing associations. Not all environmental cues are noticed. ...
... Punishment can intensify inappropriate behavior when it elicits a response compatible with the punished response. Contiguity is essential to prevent conditioning of competing associations. Not all environmental cues are noticed. ...
Selection by Consequences as a Causal Mode
... • Invoke unobservable O to mediate relation between S and R • Rise of mediational neobehaviorism: S – O – R • Operational definitions of O made it all acceptable ...
... • Invoke unobservable O to mediate relation between S and R • Rise of mediational neobehaviorism: S – O – R • Operational definitions of O made it all acceptable ...
File - Shifa Students Corner
... movement, the striatum becomes active and inhibits the pallidum, allowing more excitation of motor thalamic nuclei and cortex The corpus striatum may normally be the site in which instructions for parts of learned movements are remembered and from which they are transmitted to the motor cortex for ...
... movement, the striatum becomes active and inhibits the pallidum, allowing more excitation of motor thalamic nuclei and cortex The corpus striatum may normally be the site in which instructions for parts of learned movements are remembered and from which they are transmitted to the motor cortex for ...
Basic Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
... Limitations of Natural Observation • Observer effect: changes in subject’s behavior caused by an awareness of being observed • Observer bias: occurs when observers see what they expect to see or record only selected details • Anthropomorphic fallacy: attributing human thoughts, feelings, or motives ...
... Limitations of Natural Observation • Observer effect: changes in subject’s behavior caused by an awareness of being observed • Observer bias: occurs when observers see what they expect to see or record only selected details • Anthropomorphic fallacy: attributing human thoughts, feelings, or motives ...
November 12
... Basal ganglia loop (near thalamus) gives the “go” signal Cerebellar loop – tells the motor cortex how to carry out the planned activity ...
... Basal ganglia loop (near thalamus) gives the “go” signal Cerebellar loop – tells the motor cortex how to carry out the planned activity ...
Animal Behaviors
... Any time an animal learns to make a connection between a certain behavior and a given reward or punishment. ...
... Any time an animal learns to make a connection between a certain behavior and a given reward or punishment. ...
Eye Movement Control by the Cerebral Cortex Charles Pierrot
... – Projects to both FEF and the superior colliculus • Parieto-FEF projection: visual fixation • Parieto-superior colliculus projection: saccadic involvement ...
... – Projects to both FEF and the superior colliculus • Parieto-FEF projection: visual fixation • Parieto-superior colliculus projection: saccadic involvement ...
Coming to Attention
... a result of their intentional, conscious focus on the task. If the black X appeared very soon-within a third of a second--after the green letter, about half the time the participants did not notice it. If there was a longer period after the first stimulus, their recognition rate improved. 13. At the ...
... a result of their intentional, conscious focus on the task. If the black X appeared very soon-within a third of a second--after the green letter, about half the time the participants did not notice it. If there was a longer period after the first stimulus, their recognition rate improved. 13. At the ...
Neurobiologically Inspired Robotics: Enhanced Autonomy through
... task that unifies the theoretical principles of DAC with biologically constrained models of several brain areas, they show that efficient goal-oriented behavior results from the interaction of parallel learning mechanisms accounting for motor adaptation, spatial encoding and decision-making. Human–R ...
... task that unifies the theoretical principles of DAC with biologically constrained models of several brain areas, they show that efficient goal-oriented behavior results from the interaction of parallel learning mechanisms accounting for motor adaptation, spatial encoding and decision-making. Human–R ...
Physiology 2 - Sheet #6 - Dr.Loai Al-Zgoul - Done by: Yara
... motion. However, his personality and behavior changed severely as a result of his injury. Note: The subcortical is responsible for one’s emotion but what controls the emotion is mainly the prefrontal cortex. An example to get a better understanding of this is when you feel angry-- it’s the subcortic ...
... motion. However, his personality and behavior changed severely as a result of his injury. Note: The subcortical is responsible for one’s emotion but what controls the emotion is mainly the prefrontal cortex. An example to get a better understanding of this is when you feel angry-- it’s the subcortic ...
Attack and Escape Behaviors
... • Psychoneuroimmunology is the study of the relationship between the nervous system and the immune system. • Deals with the way in which experiences, especially stressful ones, alter the immune system. • Also deals with how the immune system influences the central nervous system. ...
... • Psychoneuroimmunology is the study of the relationship between the nervous system and the immune system. • Deals with the way in which experiences, especially stressful ones, alter the immune system. • Also deals with how the immune system influences the central nervous system. ...
Slide ()
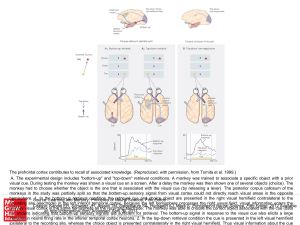
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
Slide ()
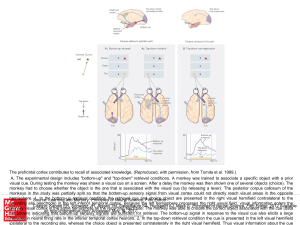
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
31.1 The Neuron The Neuron
... Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. ...
... Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the nervous system. Describe the function of neurons. Describe how a nerve impulse is transmitted. ...
Chapter 6 - Learning
... – What happens when the reinforcement stops? As in when the person leaves the institutuion – Ethical concerns… • Is it right for one human to control another human being’s behavior? ...
... – What happens when the reinforcement stops? As in when the person leaves the institutuion – Ethical concerns… • Is it right for one human to control another human being’s behavior? ...
Psy101 Learning.lst
... Differentiate between primary and secondary reinforcers and give an example of each as they relate to you. ...
... Differentiate between primary and secondary reinforcers and give an example of each as they relate to you. ...
Document
... • Controls automatic functions at subconscious level • Sympathetic nervous system - nerves emerge from thoracic and lumbar ...
... • Controls automatic functions at subconscious level • Sympathetic nervous system - nerves emerge from thoracic and lumbar ...
Term - Manhasset Schools
... awareness to which we have ready access) and unconsciousness (mental processes to which we do not normally have access) -stresses importance of childhood in development of personality -behavior is directed by chemical and biological forces, such as neurotransmitters and the brain -cultural values va ...
... awareness to which we have ready access) and unconsciousness (mental processes to which we do not normally have access) -stresses importance of childhood in development of personality -behavior is directed by chemical and biological forces, such as neurotransmitters and the brain -cultural values va ...
document
... Physical punishment may teach discrimination instead of stopping a behavior Physical punishment can teach fear of the person and place, not just the behavior Physical punishment models aggression as a solution for problems Physical punishment works best as an occasional back-up that is combined with ...
... Physical punishment may teach discrimination instead of stopping a behavior Physical punishment can teach fear of the person and place, not just the behavior Physical punishment models aggression as a solution for problems Physical punishment works best as an occasional back-up that is combined with ...
Physiology Unit Objectives and Assignments
... Using the table below, put an X in the box for the each objective. If you really understand the concept and think you could explain it to someone, mark the Green Light Box. If you kind of get it but still have some questions or need to a study a little more to memorize it, put an X in the Orange Lig ...
... Using the table below, put an X in the box for the each objective. If you really understand the concept and think you could explain it to someone, mark the Green Light Box. If you kind of get it but still have some questions or need to a study a little more to memorize it, put an X in the Orange Lig ...
AP Psychology - Coshocton City Schools
... and scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of human beings and other animals. Students are exposed to the psychological facts, principles, and phenomena associated with each of the major subfields within psychology. They also learn about the ethics and methods psychologists use in the ...
... and scientific study of the behavior and mental processes of human beings and other animals. Students are exposed to the psychological facts, principles, and phenomena associated with each of the major subfields within psychology. They also learn about the ethics and methods psychologists use in the ...
Coming to Attention How the brain decides what to focus conscious
... awareness of a stimulus, and a second, in which the same stimulus did not penetrate the consciousness. They used a phenomenon called attention blink. In the experiment they once again displayed a series of letters to subjects and observed them with fMRI. This time, however, only a single green lette ...
... awareness of a stimulus, and a second, in which the same stimulus did not penetrate the consciousness. They used a phenomenon called attention blink. In the experiment they once again displayed a series of letters to subjects and observed them with fMRI. This time, however, only a single green lette ...
Nervous System
... 4. Ependymal cells – lines cavities (Ventricles) of brain & spinal cord, helps form CSF, ciliated 5. Schwann cells – forms myelin in PNS ...
... 4. Ependymal cells – lines cavities (Ventricles) of brain & spinal cord, helps form CSF, ciliated 5. Schwann cells – forms myelin in PNS ...
Structure and functions of the Human Nervous system
... a) Tectum : 2 structures : reflex centre for vision = superior colliculus Reflex centre for hearing = inferior colliculus b) Tegmentum: structures are mainly involved in regulation of motor movement ...
... a) Tectum : 2 structures : reflex centre for vision = superior colliculus Reflex centre for hearing = inferior colliculus b) Tegmentum: structures are mainly involved in regulation of motor movement ...