FREE Sample Here
... C. School - The school is intentionally designed to socialize children. There is a strict hierarchy in place within the classroom, and school is the child’s first experience with formal and public evaluation of performance. Schools teach more than academics. IV. Processes of Socialization A. Instrum ...
... C. School - The school is intentionally designed to socialize children. There is a strict hierarchy in place within the classroom, and school is the child’s first experience with formal and public evaluation of performance. Schools teach more than academics. IV. Processes of Socialization A. Instrum ...
operant behavior1
... shown in the so-called stimulus generalization gradient. Hypothetical gradients in mental, neurological, or conceptual inner systems have been discussed for years, but thanks to the work of Guttman (1963) and his students, and others, behavioral gradients are now directly observed. A pigeon, reinfor ...
... shown in the so-called stimulus generalization gradient. Hypothetical gradients in mental, neurological, or conceptual inner systems have been discussed for years, but thanks to the work of Guttman (1963) and his students, and others, behavioral gradients are now directly observed. A pigeon, reinfor ...
Expression and Functional Interaction of Hepatocyte Growth Factor
... During the development, HGF-SF signals were first detected in El2 mouse brain. At that time and throughout further development, HGF-SF mRNA was prominently expressed in the neuroepithelial layer of the telencephalic vesicle. Furthermore, expression was seen in the developing cortical plate, most pro ...
... During the development, HGF-SF signals were first detected in El2 mouse brain. At that time and throughout further development, HGF-SF mRNA was prominently expressed in the neuroepithelial layer of the telencephalic vesicle. Furthermore, expression was seen in the developing cortical plate, most pro ...
State-Dependent TMS Reveals a Hierarchical
... induced a selective shortening of reaction times (RTs) to stimuli showing a repeated (adapted) action, regardless of the effector performing it. In a second experiment, TMS applied over the left STS induced shortening of RTs for adapted actions but only if also the effector was repeated. The results ...
... induced a selective shortening of reaction times (RTs) to stimuli showing a repeated (adapted) action, regardless of the effector performing it. In a second experiment, TMS applied over the left STS induced shortening of RTs for adapted actions but only if also the effector was repeated. The results ...
At the root of embodied cognition: Cognitive science meets
... set of ‘‘rules for control’’, which he says are not ‘‘orders’’ or ‘‘commands,’’ but ‘‘rules not formulated by words.’’ The discovery of canonical neurons allows clarification of this point and further specification of the concept ...
... set of ‘‘rules for control’’, which he says are not ‘‘orders’’ or ‘‘commands,’’ but ‘‘rules not formulated by words.’’ The discovery of canonical neurons allows clarification of this point and further specification of the concept ...
Getting to Know You: Reputation and Trust in a Two
... time effects associated with the 14-s time shift are shown in Fig. 4A and summarized in the bar graphs in Fig. 4B. In early rounds of the task (rounds 3 and 4), the peak of the response for intended increases in trust (i.e., an increase in next repayment) occurs after the investor’s decision is reve ...
... time effects associated with the 14-s time shift are shown in Fig. 4A and summarized in the bar graphs in Fig. 4B. In early rounds of the task (rounds 3 and 4), the peak of the response for intended increases in trust (i.e., an increase in next repayment) occurs after the investor’s decision is reve ...
Unipolar depression
... Antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) increase active levels of noradrenaline and serotonin in depressed patients, and typically reduce symptoms of depression Drugs rapidly affect neurotransmitter levels, but take much loner to reduce symptoms of depression or mania It’s ...
... Antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) increase active levels of noradrenaline and serotonin in depressed patients, and typically reduce symptoms of depression Drugs rapidly affect neurotransmitter levels, but take much loner to reduce symptoms of depression or mania It’s ...
Hypothalamus
... Hypothalamus • “Older” part of the brain (Primitive) – Maintenance of homeostasis • Reception of external and internal signals • Incorporation of signals to generate appropriate responses – Endocrine – Autonomic – Behavioral ...
... Hypothalamus • “Older” part of the brain (Primitive) – Maintenance of homeostasis • Reception of external and internal signals • Incorporation of signals to generate appropriate responses – Endocrine – Autonomic – Behavioral ...
When Is an Adolescent an Adult? - Waisman Laboratory for Brain
... All analyses were performed on the data from the 110 subjects with usable imaging and behavioral data. We examined responses to the debriefing questions and the SCR data to assess the efficacy of our emotionalstate manipulation. A 1-Hz filter was applied to the raw SCR data. Data were smoothed for e ...
... All analyses were performed on the data from the 110 subjects with usable imaging and behavioral data. We examined responses to the debriefing questions and the SCR data to assess the efficacy of our emotionalstate manipulation. A 1-Hz filter was applied to the raw SCR data. Data were smoothed for e ...
Cognitive Architectures: Where do we go from here?
... Another area that poses remarkable challenge to AI is word games, and in particular the 20-questions game. Word games require extensive knowledge about objects and their properties, but not about complex relations between objects. Different methods of knowledge representation may be used in differen ...
... Another area that poses remarkable challenge to AI is word games, and in particular the 20-questions game. Word games require extensive knowledge about objects and their properties, but not about complex relations between objects. Different methods of knowledge representation may be used in differen ...
Vertebrate brains and evolutionary connectomics: on the origins of
... The organization of the non-mammalian forebrain had long puzzled neurobiologists. Unlike typical mammalian brains, the telencephalon is not organized in a laminated ‘cortical’ manner, with distinct cortical areas dedicated to individual sensory modalities or motor functions. The two major regions of ...
... The organization of the non-mammalian forebrain had long puzzled neurobiologists. Unlike typical mammalian brains, the telencephalon is not organized in a laminated ‘cortical’ manner, with distinct cortical areas dedicated to individual sensory modalities or motor functions. The two major regions of ...
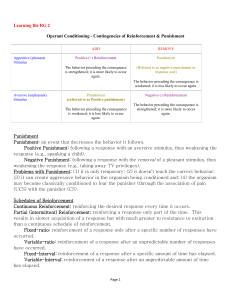
negative reinforcement - sfhs
... Punishment - Any consequence that decreases the future likelihood of a behavior The subject determines if a consequence is reinforcing or ...
... Punishment - Any consequence that decreases the future likelihood of a behavior The subject determines if a consequence is reinforcing or ...
A Model of Prefrontal Cortical Mechanisms for Goal-directed Behavior Michael E. Hasselmo Abstract
... of the next appropriate action. Simulations demonstrate how these mechanisms can guide performance in a range of goaldirected tasks, and provide a functional framework for some of the neuronal responses previously observed in the medial prefrontal cortex during performance of spatial memory tasks in ...
... of the next appropriate action. Simulations demonstrate how these mechanisms can guide performance in a range of goaldirected tasks, and provide a functional framework for some of the neuronal responses previously observed in the medial prefrontal cortex during performance of spatial memory tasks in ...
TINS04
... impaired auditory function following microgyri or ectopias[26,27]. Indeed, female rats showed normal auditory performance and did not show a similar anatomical disruption of the MGN in response to the microgyri, even though their cortical lesions were as widely distributed[22]. It was then found tha ...
... impaired auditory function following microgyri or ectopias[26,27]. Indeed, female rats showed normal auditory performance and did not show a similar anatomical disruption of the MGN in response to the microgyri, even though their cortical lesions were as widely distributed[22]. It was then found tha ...
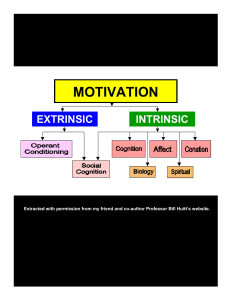
Learning file RG 2
... Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation performing ...
... Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest, as the motivation performing ...
File
... Operant Conditioning Processes Primary Reinforcement is unlearned and usually necessary for survival. Food is the best example of a primary reinforcer. Secondary Reinforcement is anything that comes to represent a primary reinforcer such as praise from a friend or a gold star on a homework assignme ...
... Operant Conditioning Processes Primary Reinforcement is unlearned and usually necessary for survival. Food is the best example of a primary reinforcer. Secondary Reinforcement is anything that comes to represent a primary reinforcer such as praise from a friend or a gold star on a homework assignme ...
Neural Mechanisms of Addiction
... properties (Table 1). Humans and animals rapidly learn cues and contexts that predict the availability of these “addictive drugs”; once learned, these cues motivate drug seeking in humans and animal models. In the conditioned place preference model, rats or mice will spend more time in a location in ...
... properties (Table 1). Humans and animals rapidly learn cues and contexts that predict the availability of these “addictive drugs”; once learned, these cues motivate drug seeking in humans and animal models. In the conditioned place preference model, rats or mice will spend more time in a location in ...
Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... Example: B.F. Skinner put rats in a box with a lever connected to a feeder. It only provided a reinforcement after 60 seconds. The rats quickly learned that it didn’t matter how early or often it pushed the lever, it had to wait a set amount of time. As the set amount of time came to an end, the rat ...
... Example: B.F. Skinner put rats in a box with a lever connected to a feeder. It only provided a reinforcement after 60 seconds. The rats quickly learned that it didn’t matter how early or often it pushed the lever, it had to wait a set amount of time. As the set amount of time came to an end, the rat ...
Novel cyclic AMP signalling avenues in learning and memory
... densities and plays an important role in synaptic function. Several studies suggested that AKAP79/150 anchored PKA contributes to mechanisms associated with synaptic plasticity and memory processes, but the precise role of AKAPs in these processes is still unknown. In this study we established the m ...
... densities and plays an important role in synaptic function. Several studies suggested that AKAP79/150 anchored PKA contributes to mechanisms associated with synaptic plasticity and memory processes, but the precise role of AKAPs in these processes is still unknown. In this study we established the m ...
0474 ch 10(200-221).
... than in any other organism, lies anterior to the central sulcus. The gyrus just anterior to the central sulcus in this lobe contains a primary motor area, which provides conscious control of skeletal muscles. Note that the more detailed the action, the greater the amount of cortical tissue involved ...
... than in any other organism, lies anterior to the central sulcus. The gyrus just anterior to the central sulcus in this lobe contains a primary motor area, which provides conscious control of skeletal muscles. Note that the more detailed the action, the greater the amount of cortical tissue involved ...
Parietal cortex neurons of the monkey related to the visual guidance
... the head fixed. They were trained to manipulate various types of objects connected with microswitches that required different patterns of hand movement (object-manipulation task). They were also trained to fixate their gaze on the object without manipulating it, in order to assess visual responses o ...
... the head fixed. They were trained to manipulate various types of objects connected with microswitches that required different patterns of hand movement (object-manipulation task). They were also trained to fixate their gaze on the object without manipulating it, in order to assess visual responses o ...
Stress Slides Class 5
... Stress: The Importance of Allostasis The term came into being in the 1980’s as a newer more appreciative way to view the body’s rapid and efficient methods of dealing with stress. Allostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain stability amidst change. M Lu, N Halfon ...
... Stress: The Importance of Allostasis The term came into being in the 1980’s as a newer more appreciative way to view the body’s rapid and efficient methods of dealing with stress. Allostasis refers to the body’s ability to maintain stability amidst change. M Lu, N Halfon ...
The role of the medial prefrontal cortex in learning and reward Ph.D
... 1994). Behavior of humans and animals is often goal directed and can be flexibly modulated by motivation. Flexible representations are created in experimental animals during instrumental conditioning. Pavlovian CSs may modulate instrumental performance, this is the Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (P ...
... 1994). Behavior of humans and animals is often goal directed and can be flexibly modulated by motivation. Flexible representations are created in experimental animals during instrumental conditioning. Pavlovian CSs may modulate instrumental performance, this is the Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (P ...