- Reppert Lab
... acid, or dopamine in Bn-SA/HRP labeling assays (Immunostar, Hudson, WI; histochemical serotonin antisera specification sheet). The specificity of the anti-5HT antiserum on monarch brain sections was tested by preadsorption of the diluted antiserum (1:4,000, with 1% normal goat serum [NGS], in 0.1 M ...
... acid, or dopamine in Bn-SA/HRP labeling assays (Immunostar, Hudson, WI; histochemical serotonin antisera specification sheet). The specificity of the anti-5HT antiserum on monarch brain sections was tested by preadsorption of the diluted antiserum (1:4,000, with 1% normal goat serum [NGS], in 0.1 M ...
CASE 47
... The basal ganglia, located near the thalamus in the diencephalon, are composed of five pairs of nuclei: the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefro ...
... The basal ganglia, located near the thalamus in the diencephalon, are composed of five pairs of nuclei: the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefro ...
Reinforcement, and Punishment Striatal Mechanisms Underlying
... and make no conclusions about an organism’s hedonic state or whether it “likes” or “dislikes” the stimuli. Instead, the hedonic state of an organism can be described by the terms reward and aversion. Rewarding stimuli are those to which an animal assigns a positive hedonic value, whereas aversive st ...
... and make no conclusions about an organism’s hedonic state or whether it “likes” or “dislikes” the stimuli. Instead, the hedonic state of an organism can be described by the terms reward and aversion. Rewarding stimuli are those to which an animal assigns a positive hedonic value, whereas aversive st ...
The spinal cord is a complex cable of nerves that connects the brain
... nerves called the cauda equina. The upper end of the conus medullaris is usually not well defined. The spinal cord is the connection center for the reflexes as well as the afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) pathways for most of the body below the head and neck. The spinal cord begins at the bra ...
... nerves called the cauda equina. The upper end of the conus medullaris is usually not well defined. The spinal cord is the connection center for the reflexes as well as the afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) pathways for most of the body below the head and neck. The spinal cord begins at the bra ...
Nonlinear brain dynamics as macroscopic manifestation of
... on the neuropsychological field theories of Lashley (1929), Köhler (1940) and Pribram (1971). Karl Lashley wrote: "Generalization [stimulus equivalence] is one of the primitive basic functions of organized nervous tissue. … Here is the dilemma. Nerve impulses are transmitted from cell to cell throug ...
... on the neuropsychological field theories of Lashley (1929), Köhler (1940) and Pribram (1971). Karl Lashley wrote: "Generalization [stimulus equivalence] is one of the primitive basic functions of organized nervous tissue. … Here is the dilemma. Nerve impulses are transmitted from cell to cell throug ...
Control of Wake and Sleep States
... Slow oscillations is generated within cortex and strongly influences thalamus through CT projections. They consist of prolonged depolarizations associated with extracellular gamma activity (up) ...
... Slow oscillations is generated within cortex and strongly influences thalamus through CT projections. They consist of prolonged depolarizations associated with extracellular gamma activity (up) ...
Congenital blindness affects diencephalic but not mesencephalic
... and Ptito 2012). Among these structures, the thalamus plays an important part in the sensory processing and integration, given its key position in establishing input– output connections between multiple sensory and motor cortical areas (Cappe et al. 2009). In conditions of early visual deprivation, ...
... and Ptito 2012). Among these structures, the thalamus plays an important part in the sensory processing and integration, given its key position in establishing input– output connections between multiple sensory and motor cortical areas (Cappe et al. 2009). In conditions of early visual deprivation, ...
An Introduction to the ANS and Higher
... • Controls during resting conditions • “Rest and digest” ...
... • Controls during resting conditions • “Rest and digest” ...
a Primer on the Brain and Nervous System
... central nervous system and are thought to be important for reward mechanisms and mood. The hindbrain includes the pons and the medulla oblongata, which control respiration, heart rhythms, and blood glucose levels. Another part of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which, like the cerebrum, also has two ...
... central nervous system and are thought to be important for reward mechanisms and mood. The hindbrain includes the pons and the medulla oblongata, which control respiration, heart rhythms, and blood glucose levels. Another part of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which, like the cerebrum, also has two ...
primer on brain facts - Chicago Society of Neuroscience
... central nervous system and are thought to be important for reward mechanisms and mood. The hindbrain includes the pons and the medulla oblongata, which control respiration, heart rhythms, and blood glucose levels. Another part of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which, like the cerebrum, also has two ...
... central nervous system and are thought to be important for reward mechanisms and mood. The hindbrain includes the pons and the medulla oblongata, which control respiration, heart rhythms, and blood glucose levels. Another part of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which, like the cerebrum, also has two ...
BrainFacts.org A P R I M E R ...
... central nervous system and are thought to be important for reward mechanisms and mood. The hindbrain includes the pons and the medulla oblongata, which control respiration, heart rhythms, and blood glucose levels. Another part of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which, like the cerebrum, also has two ...
... central nervous system and are thought to be important for reward mechanisms and mood. The hindbrain includes the pons and the medulla oblongata, which control respiration, heart rhythms, and blood glucose levels. Another part of the hindbrain is the cerebellum which, like the cerebrum, also has two ...
Module 5 – Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nerves The Spinal Cord
... The cell bodies of neurons within the grey matter are organised into functional groups called nuclei: ...
... The cell bodies of neurons within the grey matter are organised into functional groups called nuclei: ...
Elephant brain Part I
... We report morphological data on brains of four African, Loxodonta africana, and three Asian elephants, Elephas maximus, and compare findings to literature. Brains exhibit a gyral pattern more complex and with more numerous gyri than in primates, humans included, and in carnivores, but less complex t ...
... We report morphological data on brains of four African, Loxodonta africana, and three Asian elephants, Elephas maximus, and compare findings to literature. Brains exhibit a gyral pattern more complex and with more numerous gyri than in primates, humans included, and in carnivores, but less complex t ...
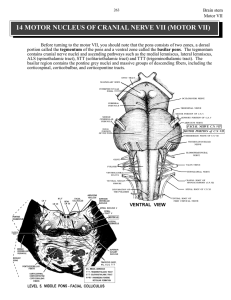
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... CONTRALATERAL deficits in muscle coordination. This incoordination/ataxia involves both the arm and the leg. In contrast, a lesion of the middle cerebellar PEDUNCLE results in IPSILATERAL deficits in motor coordination of the arm and leg. Why?? What about a Romberg sign following a lesion of the mid ...
... CONTRALATERAL deficits in muscle coordination. This incoordination/ataxia involves both the arm and the leg. In contrast, a lesion of the middle cerebellar PEDUNCLE results in IPSILATERAL deficits in motor coordination of the arm and leg. Why?? What about a Romberg sign following a lesion of the mid ...
The Nervous System
... The brain stem functions as a. a location for memory and learning. b. the control site responsible for heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. c. the location where all sensory information is processed and delivered to the cerebrum. d. an area that recognizes hunger, thirst, and body temperature. ...
... The brain stem functions as a. a location for memory and learning. b. the control site responsible for heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. c. the location where all sensory information is processed and delivered to the cerebrum. d. an area that recognizes hunger, thirst, and body temperature. ...
Maturation of Layer V Pyramidal Neurons in the Rat Prefrontal
... 1994; Weinberger and Berman 1996). Although the causes for such malfunction may be complex, many studies suggest abnormalities that occur during early postnatal development (Jones 1997; Lewis and Levitt 2002; Raedler et al. 1998). Electrical activities play important roles in developmental processes ...
... 1994; Weinberger and Berman 1996). Although the causes for such malfunction may be complex, many studies suggest abnormalities that occur during early postnatal development (Jones 1997; Lewis and Levitt 2002; Raedler et al. 1998). Electrical activities play important roles in developmental processes ...
Brain-implantable biomimetic electronics as the next era in neural
... The computational properties of the prosthetic being developed are based on the hippocampus, a cortical region of the brain involved in the formation of new long-term memories. The hippocampus lies beneath the phylogenetically more recent neocortex, and is composed of several different subsystems th ...
... The computational properties of the prosthetic being developed are based on the hippocampus, a cortical region of the brain involved in the formation of new long-term memories. The hippocampus lies beneath the phylogenetically more recent neocortex, and is composed of several different subsystems th ...
Hierarchical somatosensory processing
... SII: a higher level of processing? The notion that SII is higher than SI in hierarchy was proposed on the basis of their anatomical relationships: SI sends projections to SII, while SII projects back to the superficial layers of SI [8,42,43]. Physiological studies have shown that compared to SI neur ...
... SII: a higher level of processing? The notion that SII is higher than SI in hierarchy was proposed on the basis of their anatomical relationships: SI sends projections to SII, while SII projects back to the superficial layers of SI [8,42,43]. Physiological studies have shown that compared to SI neur ...
The ventricles are structures that produce cerebrospinal fluid
... Similar cross-sectional structures at all spinal cord levels. -It carries sensory information (sensations) from the body and some from the head to the central nervous system (CNS) via afferent fibers, and it performs the initial processing of this information. -Motor neurons in the ventral horn proj ...
... Similar cross-sectional structures at all spinal cord levels. -It carries sensory information (sensations) from the body and some from the head to the central nervous system (CNS) via afferent fibers, and it performs the initial processing of this information. -Motor neurons in the ventral horn proj ...
Chapter 14 Part 1
... correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory. It also directs our behavior towards others. In this chapter we will consider the principal parts of the brain, how the brain ...
... correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory. It also directs our behavior towards others. In this chapter we will consider the principal parts of the brain, how the brain ...
Skeletal System
... The white matter on each side of the column is divided into three white columns or funiculi and labeled according to their position (posterior, lateral, anterior) Each funiculi contains several fiber tracts, and each tract is made up of axons with similar destinations and functions ...
... The white matter on each side of the column is divided into three white columns or funiculi and labeled according to their position (posterior, lateral, anterior) Each funiculi contains several fiber tracts, and each tract is made up of axons with similar destinations and functions ...
Integrated model of visual processing
... necessity of computing with high spatial precision and reaching out to distant regions in the visual field is difficult to achieve with horizontal connections within a single cortical area. Areas such as V1 and V2 that contain neurons coding with high precision the visual scene also have very high m ...
... necessity of computing with high spatial precision and reaching out to distant regions in the visual field is difficult to achieve with horizontal connections within a single cortical area. Areas such as V1 and V2 that contain neurons coding with high precision the visual scene also have very high m ...
Ch. 3–Biological Basis of Behavior PPT
... Evolutionary psychologists use several strategies to develop and test hypotheses about whether a psychological trait is likely to be an evolved adaptation. Cross-cultural Consistency. Characteristics that have been demonstrated to be cross cultural human universals such as smiling, crying, facial ex ...
... Evolutionary psychologists use several strategies to develop and test hypotheses about whether a psychological trait is likely to be an evolved adaptation. Cross-cultural Consistency. Characteristics that have been demonstrated to be cross cultural human universals such as smiling, crying, facial ex ...
brain –computer interface - Nexus Academic Publishers
... The brain is incredibly complex. To say that all thoughts or actions are the result of simple electric signals in the brain is a gross understatement. There are about 100 billion neurons in a human brain. Each neuron is constantly sending and receiving signals through a complex web of connections. T ...
... The brain is incredibly complex. To say that all thoughts or actions are the result of simple electric signals in the brain is a gross understatement. There are about 100 billion neurons in a human brain. Each neuron is constantly sending and receiving signals through a complex web of connections. T ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.