PoNS Fact Sheet - Helius Medical Technologies
... the electrochemical environment of the brain. Neuromodulation enhances neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to restructure or relearn in response to new experiences, sensory input and functional demands.2 The process of neuroplasticity underlies all cerebral learning, training, and rehabilitation. O ...
... the electrochemical environment of the brain. Neuromodulation enhances neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to restructure or relearn in response to new experiences, sensory input and functional demands.2 The process of neuroplasticity underlies all cerebral learning, training, and rehabilitation. O ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... The stimulus is received by a receptor. It is transmitted by nerves or hormones, and an effector brings about the response. • Animals have two systems of coordination, the nervous system and the endocrine system. • The nervous system coordinates rapid responses to external stimuli. The endocrine sys ...
... The stimulus is received by a receptor. It is transmitted by nerves or hormones, and an effector brings about the response. • Animals have two systems of coordination, the nervous system and the endocrine system. • The nervous system coordinates rapid responses to external stimuli. The endocrine sys ...
The Nervous System
... Homeostasis It means to keep things in balance. Homeostasis keeps internal conditions relatively constant despite change to external environments. ...
... Homeostasis It means to keep things in balance. Homeostasis keeps internal conditions relatively constant despite change to external environments. ...
Worksheet for Nervous Systems
... 13. Interneurons are constantly _____. What does this active provide the context for? 14. Ganglia and nuclei are collections of ______ ______. How do they differ from one another? 15. Supporting cells, called ______ __________ are ____ 16. Which glial cells provide structural and metabolic support f ...
... 13. Interneurons are constantly _____. What does this active provide the context for? 14. Ganglia and nuclei are collections of ______ ______. How do they differ from one another? 15. Supporting cells, called ______ __________ are ____ 16. Which glial cells provide structural and metabolic support f ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... encased in a myelin sheath. Neurons receive signals from other cells through their branching dendrites and their cell body. If the combined signals are strong enough, the neuron fires, transmitting an electrical impulse (the action potential) down its axon, by means of a chemistry-to-electricity pro ...
... encased in a myelin sheath. Neurons receive signals from other cells through their branching dendrites and their cell body. If the combined signals are strong enough, the neuron fires, transmitting an electrical impulse (the action potential) down its axon, by means of a chemistry-to-electricity pro ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... • Less than 20% of the CNS is extracellular space which means that the cells are densely packed and tightly intertwined • Nervous tissue is made up of just two principal types of cells – Neuroglia (glial cells): supporting cells for neurons – Neurons: excitable nerve cells that transmit info. ...
... • Less than 20% of the CNS is extracellular space which means that the cells are densely packed and tightly intertwined • Nervous tissue is made up of just two principal types of cells – Neuroglia (glial cells): supporting cells for neurons – Neurons: excitable nerve cells that transmit info. ...
Networks of computers analyze how networks of nerves in your
... to the brain, the research continues, with no signs of letting up anytime soon. This research looks at how impulses travel between nerve cells in the brain, which allows messages to be sent to muscles throughout the body. Understanding how this communication works could help doctors figure out how t ...
... to the brain, the research continues, with no signs of letting up anytime soon. This research looks at how impulses travel between nerve cells in the brain, which allows messages to be sent to muscles throughout the body. Understanding how this communication works could help doctors figure out how t ...
Chapter 3 Section 2 - 6th
... Chapter 3 Section 1 The Nervous System - Regulates our internal functions and is involved in how we react to the external world Two main parts: 1. central nervous system- consists of brain and spinal cord 2. peripheral nervous system- made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central ner ...
... Chapter 3 Section 1 The Nervous System - Regulates our internal functions and is involved in how we react to the external world Two main parts: 1. central nervous system- consists of brain and spinal cord 2. peripheral nervous system- made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central ner ...
Nerve
... Histology SSN October 16, 2002 Sara Nash ([email protected]) and Sue Lee ([email protected]) Nerve Tissue I. The Neuron (slide #85, H&E; see Ross Fig. 11.1, p258) A. Basics -the neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system -highly polarized cells: dendrites are neuronal p ...
... Histology SSN October 16, 2002 Sara Nash ([email protected]) and Sue Lee ([email protected]) Nerve Tissue I. The Neuron (slide #85, H&E; see Ross Fig. 11.1, p258) A. Basics -the neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system -highly polarized cells: dendrites are neuronal p ...
Slide ()
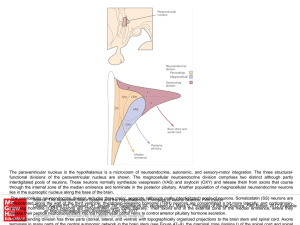
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Slide ()
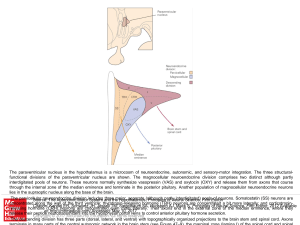
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
... The paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus is a microcosm of neuroendocrine, autonomic, and sensory-motor integration. The three structuralfunctional divisions of the paraventricular nucleus are shown. The magnocellular neuroendocrine division comprises two distinct although partly interdigitat ...
Quiz - Web Adventures
... A Plaguing Problem Episode 4 – Mystery of Morpheus: Quiz 1) Which scientist won a Nobel Prize for discovering how nerve cells communicate? a) Friedrich Serturner b) Hippocrates c) Linnaeus d) Otto Loewi 2) The part of a neuron where the receptors are located is the: a) Axon b) Cell body c) Dendrite ...
... A Plaguing Problem Episode 4 – Mystery of Morpheus: Quiz 1) Which scientist won a Nobel Prize for discovering how nerve cells communicate? a) Friedrich Serturner b) Hippocrates c) Linnaeus d) Otto Loewi 2) The part of a neuron where the receptors are located is the: a) Axon b) Cell body c) Dendrite ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful ...
... when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful ...
Nervous System ppt
... Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. Caused by loss of dopamine producing cells in brain (substantia niagra) Dopamine helps control muscle movement by releasing inhibitory function of substantia nia ...
... Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. Caused by loss of dopamine producing cells in brain (substantia niagra) Dopamine helps control muscle movement by releasing inhibitory function of substantia nia ...
Introduction to Financial Prediction using Artificial Intelligent Method
... processing/memory abstraction of human information processing. neural networks are based on the parallel architecture of animal brains. ...
... processing/memory abstraction of human information processing. neural networks are based on the parallel architecture of animal brains. ...
pre02
... • Switched Capacitor (SC) is a circuit made of one capacitor and two switches which connect the capacitor with a given frequency alternately to the input an output of the SC. This simulates the behaviors of a resistor, so SCs are used in integrated circuits instead of resistors. The resistance is se ...
... • Switched Capacitor (SC) is a circuit made of one capacitor and two switches which connect the capacitor with a given frequency alternately to the input an output of the SC. This simulates the behaviors of a resistor, so SCs are used in integrated circuits instead of resistors. The resistance is se ...
The Nervous System
... Name the two main divisions of the nervous system Identify the CNS and PNS on a diagram of the body's Nervous System Explain the term receptor Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicle ...
... Name the two main divisions of the nervous system Identify the CNS and PNS on a diagram of the body's Nervous System Explain the term receptor Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicle ...
Nervous System - Gordon State College
... The spinal cord transmits information from sensory neurons to the brain, and from the brain to motor neurons that initiate movement. The upper segments of the spinal cord control the upper parts of the body, while the lower segments control the ...
... The spinal cord transmits information from sensory neurons to the brain, and from the brain to motor neurons that initiate movement. The upper segments of the spinal cord control the upper parts of the body, while the lower segments control the ...
Nervous System - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
... Axon: Tail of the neuron that carries electrical information away from the body towards the next neuron Insulated with myelin ...
... Axon: Tail of the neuron that carries electrical information away from the body towards the next neuron Insulated with myelin ...
ntro to Nervous system study guide
... Nervous system Quiz Review 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
... Nervous system Quiz Review 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
The Nervous System
... Sensory receptors collect and monitor stimuli (sensory input) Control center processes and interprets sensory input and makes decisions about what to (integration) Sends a response by activating a system to take care of business, usually muscles or glands (motor output) ...
... Sensory receptors collect and monitor stimuli (sensory input) Control center processes and interprets sensory input and makes decisions about what to (integration) Sends a response by activating a system to take care of business, usually muscles or glands (motor output) ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
... Nodes of Ravier—allow for movement of ions into extracellular fluid. 2. Neuralgia—protect and nourish neurons. Different types review: 1434. ...
... Nodes of Ravier—allow for movement of ions into extracellular fluid. 2. Neuralgia—protect and nourish neurons. Different types review: 1434. ...
What is an adult stem cell?
... can give rise to mature cell types that have characteristic morphologies, specialized functions. Evidence for the presence of adult SC Three methods are used to determine whether candidate adult SC give rise to specialized cells. 1. candidate adult SC can be labeled in vivo and then they can be ...
... can give rise to mature cell types that have characteristic morphologies, specialized functions. Evidence for the presence of adult SC Three methods are used to determine whether candidate adult SC give rise to specialized cells. 1. candidate adult SC can be labeled in vivo and then they can be ...