The Neural Mechanisms of Learning
... More evidence for the role of LTP in learning comes from studies indicating that drugs which enhance synaptic transmission tend to enhance learning NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) a neurotransmitter receptor found on dendrites particularly in the hippocampal region NMDA is specialised to receive th ...
... More evidence for the role of LTP in learning comes from studies indicating that drugs which enhance synaptic transmission tend to enhance learning NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) a neurotransmitter receptor found on dendrites particularly in the hippocampal region NMDA is specialised to receive th ...
Keeping the Nervous System Healthy Quiz Answers
... Vitamins B1 and B12 are important for a healthy nervous system. ...
... Vitamins B1 and B12 are important for a healthy nervous system. ...
UNIT 2: Internal geological agents
... and the inside of the organism itself, and the ability to produce responses. There are two coordination systems which regulate all the human body funtions: A – The nervous system B – The endocrine system Differences between the nervous system and the endocrine system: The nervous system The endocrin ...
... and the inside of the organism itself, and the ability to produce responses. There are two coordination systems which regulate all the human body funtions: A – The nervous system B – The endocrine system Differences between the nervous system and the endocrine system: The nervous system The endocrin ...
Methods in Cognitive Neuroscience I
... • WADA procedure – Injection of sodium amytal (a barbituate), into one and then the other carotid artery temporarily (5-10min) puts half the brain to sleep allowing neurologists to assess function in the awake hemisphere ...
... • WADA procedure – Injection of sodium amytal (a barbituate), into one and then the other carotid artery temporarily (5-10min) puts half the brain to sleep allowing neurologists to assess function in the awake hemisphere ...
Intr to NS 2015
... (A) Central Nervous System (CNS) : consisting of the brain and spinal cord , and (B) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS ) : Fibers outside the CNS ...
... (A) Central Nervous System (CNS) : consisting of the brain and spinal cord , and (B) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS ) : Fibers outside the CNS ...
File
... •Coordinates between the brain and the other body structures •Reflexes are processed in spinal cord ...
... •Coordinates between the brain and the other body structures •Reflexes are processed in spinal cord ...
Central Nervous System
... differences between things or events. In the posterior portion of the frontal lobe lies the precentral gyrus which is also known as the somatomotor or primary motor cortex. This is where voluntary motions are processed. The motor homunculus (little person) represents the portions of the body which ...
... differences between things or events. In the posterior portion of the frontal lobe lies the precentral gyrus which is also known as the somatomotor or primary motor cortex. This is where voluntary motions are processed. The motor homunculus (little person) represents the portions of the body which ...
Describe how action potentials are generated
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... These axons become embedded in the Schwann cell, which provides structural support and nutrients. ...
... These axons become embedded in the Schwann cell, which provides structural support and nutrients. ...
Describe how action potentials are generated and
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
Slide ()
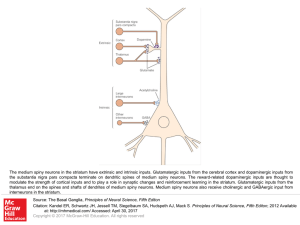
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... • Identify and give functions for each of the following: dendrite, cell body, axon • Distinguish among sensory, motor and interneuron with respect to structure and function • Contrast the locations and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems • Differentiate between the functions of t ...
... • Identify and give functions for each of the following: dendrite, cell body, axon • Distinguish among sensory, motor and interneuron with respect to structure and function • Contrast the locations and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems • Differentiate between the functions of t ...
The Nervous System
... 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system does this body part belong? 5. Explain how the peripheral nervous system connects to the central nervous system. 6. If a spider ...
... 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system does this body part belong? 5. Explain how the peripheral nervous system connects to the central nervous system. 6. If a spider ...
Lecture 6 - Wiki Index
... Detection of medical phenomena. A variety of health-related indices (e.g., a combination of heart rate, levels of various substances in the blood, respiration rate) can be monitored. The onset of a particular medical condition could be associated with a very complex (e.g., nonlinear and interactive) ...
... Detection of medical phenomena. A variety of health-related indices (e.g., a combination of heart rate, levels of various substances in the blood, respiration rate) can be monitored. The onset of a particular medical condition could be associated with a very complex (e.g., nonlinear and interactive) ...
Take the 10-item multiple choice quiz to check
... permits passage of foreign substances from the blood to the neurons. prohibits the transport of amino acids and glucose to the neurons. prohibits the removal of waste materials from the neurons. protects neurons from toxic substances in the blood. does not prevent fluctuations in the composition of ...
... permits passage of foreign substances from the blood to the neurons. prohibits the transport of amino acids and glucose to the neurons. prohibits the removal of waste materials from the neurons. protects neurons from toxic substances in the blood. does not prevent fluctuations in the composition of ...
Intro Nervous System and Neurons
... – monitor changes inside and outside the body – changes = stimuli – sensory receptors responsible for input ...
... – monitor changes inside and outside the body – changes = stimuli – sensory receptors responsible for input ...
chapter nervous system i: basig strugture and function
... Continuous stimulation ofa neuron on the distal side ofthisjunction is prevented by ...
... Continuous stimulation ofa neuron on the distal side ofthisjunction is prevented by ...
Nervous System Notes Outline
... 13. Name 3 structurally different neurons. 1. _______________ – one input (dendrite), one output (axon); eyes, nose, ears 2. _______________ – one output with 2 branches (fused dendrites and axon); most ___________ neurons of ________ 3. _______________ – many inputs (dendrites), one output (axon); ...
... 13. Name 3 structurally different neurons. 1. _______________ – one input (dendrite), one output (axon); eyes, nose, ears 2. _______________ – one output with 2 branches (fused dendrites and axon); most ___________ neurons of ________ 3. _______________ – many inputs (dendrites), one output (axon); ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... The Control Center of the Body The nervous system is your body’s control center Carries messages to and from your brain and the rest of your body. Controls senses Smell, touch, hearing, tasting, and sight ...
... The Control Center of the Body The nervous system is your body’s control center Carries messages to and from your brain and the rest of your body. Controls senses Smell, touch, hearing, tasting, and sight ...
nervesendocrine ppttwo
... spinal cord not the brain. Reflexes protect the body before the brain knows what is going on. ...
... spinal cord not the brain. Reflexes protect the body before the brain knows what is going on. ...
4.27.05 Respiration and Nervous
... Nervous Tissue • The nervous system is divided into a central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and a peripheral nervous system (PNS), consisting of nerves carrying sensory and motor information between the CNS and muscles and glands. • Both systems have two types of ce ...
... Nervous Tissue • The nervous system is divided into a central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and a peripheral nervous system (PNS), consisting of nerves carrying sensory and motor information between the CNS and muscles and glands. • Both systems have two types of ce ...
Nervous Tissue
... – Inside (+) ions move from stimuli site to neighboring () areas – Outside (+) ions move toward stimuli site ...
... – Inside (+) ions move from stimuli site to neighboring () areas – Outside (+) ions move toward stimuli site ...
NSC 201/BCS 240 Basic Neurobiology
... • Orient students to the research environment (set realistic expectations) • Arrange for some basic training to increase their marketability and likelihood of success in finding and carrying out undergraduate research. • We have a network of labs and clinical research groups ...
... • Orient students to the research environment (set realistic expectations) • Arrange for some basic training to increase their marketability and likelihood of success in finding and carrying out undergraduate research. • We have a network of labs and clinical research groups ...