Practice questions 1. How are functionalism and behaviourism
... is done: when they monitored the activity of dendrites and axons they found evidence for __________ transmission of signals. When they monitored the synaptic gaps, they found evidence for ___________ transmission of signals. This now well-know phenomenon allows to explain the _____________ of respon ...
... is done: when they monitored the activity of dendrites and axons they found evidence for __________ transmission of signals. When they monitored the synaptic gaps, they found evidence for ___________ transmission of signals. This now well-know phenomenon allows to explain the _____________ of respon ...
The Mammalian Nervous System: Structure and
... The three regions of embryonic brain develop into adult brain structures. The hindbrain becomes the medulla, the pons, and the cerebellum. Physiological functions, such as breathing and swallowing, are controlled by the medulla and pons. Muscle control is coordinated in the ...
... The three regions of embryonic brain develop into adult brain structures. The hindbrain becomes the medulla, the pons, and the cerebellum. Physiological functions, such as breathing and swallowing, are controlled by the medulla and pons. Muscle control is coordinated in the ...
Homeostasis Review Definitions
... • The nervous system senses the outside environment and initiates a series of reactions in the body to allow the body to respond. The endocrine contributes to homeostasis by producing hormones or chemical messengers that carry out a process that helps restore balance in the body. ...
... • The nervous system senses the outside environment and initiates a series of reactions in the body to allow the body to respond. The endocrine contributes to homeostasis by producing hormones or chemical messengers that carry out a process that helps restore balance in the body. ...
heledius - Society for the Advancement of Sexual Health
... A Blue print of what we like and desire sexually. Highly influenced by early life experience. Can be altered by trauma. Is impacted by parental messages during childhood ...
... A Blue print of what we like and desire sexually. Highly influenced by early life experience. Can be altered by trauma. Is impacted by parental messages during childhood ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... – Numbered according to the portion of the vertebral column at which they exit ...
... – Numbered according to the portion of the vertebral column at which they exit ...
Biological Bases of Behavior
... It’s important to note that a genetic predisposition does not mean a person will develop a disease, certain personality trait, or grow to be exactly 5’10’’. It means that genetic markers indicate it could happen. ...
... It’s important to note that a genetic predisposition does not mean a person will develop a disease, certain personality trait, or grow to be exactly 5’10’’. It means that genetic markers indicate it could happen. ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell ret ...
... open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell ret ...
Overview
... 3. Another part of the brain sends a message to motor neurons in muscles in the body. Muscles in the head and neck are activated, and the head turns. ...
... 3. Another part of the brain sends a message to motor neurons in muscles in the body. Muscles in the head and neck are activated, and the head turns. ...
Grasping the Ungraspable: How do motor actions and motor metaphors interact?
... action execution, and during action observation (Gallese et al., 1996). The neural areas active while observing an action (e.g., kicking) are also active during the processing of concrete action descriptions (e.g., she kicked the ball) (Pulvermuller, 2005). These advances raise an interesting possib ...
... action execution, and during action observation (Gallese et al., 1996). The neural areas active while observing an action (e.g., kicking) are also active during the processing of concrete action descriptions (e.g., she kicked the ball) (Pulvermuller, 2005). These advances raise an interesting possib ...
in the central nervous system
... a) It causes an electrical and chemical change →Stimulus activates a receptor →Impulses start across the nerve pathway →Effector responds to the impulse ...
... a) It causes an electrical and chemical change →Stimulus activates a receptor →Impulses start across the nerve pathway →Effector responds to the impulse ...
File
... • Brain: controls breathing, heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, emotions, reasoning, memory, and creativity • Spinal cord: a means of communication between the brain and the peripheral nerves that leave the cord • The brain and spinal cord are wrapped in protective membranes called mening ...
... • Brain: controls breathing, heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, emotions, reasoning, memory, and creativity • Spinal cord: a means of communication between the brain and the peripheral nerves that leave the cord • The brain and spinal cord are wrapped in protective membranes called mening ...
Chapter 9 - Nervous System
... It is attached to the surface of the brain and spinal cord and follows their contours. 9.12 Spinal Cord (p. 221; Fig. 9.21) A. The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends as a slender cord to the level of the intervertebral disk between the first and second lumbar vertebrae. B. Struc ...
... It is attached to the surface of the brain and spinal cord and follows their contours. 9.12 Spinal Cord (p. 221; Fig. 9.21) A. The spinal cord begins at the base of the brain and extends as a slender cord to the level of the intervertebral disk between the first and second lumbar vertebrae. B. Struc ...
The Peripheral and Autonomic Nervous Systems
... Preganglionic neurons in the CNS send axon to synapse on ganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia outside the CNS The axons of the postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscles, glands, and adipose tissues. ...
... Preganglionic neurons in the CNS send axon to synapse on ganglionic neurons in autonomic ganglia outside the CNS The axons of the postganglionic fibers innervate cardiac muscle, smooth muscles, glands, and adipose tissues. ...
Parts of the Brain - Bellarmine University
... between the brain and spinal cord Various nuclei of the medulla transmits nerve impulses that control: Heart rate Constriction Dilation of blood vessels Blood pressure Swallowing sneezing ...
... between the brain and spinal cord Various nuclei of the medulla transmits nerve impulses that control: Heart rate Constriction Dilation of blood vessels Blood pressure Swallowing sneezing ...
Bio 103 Nervous System
... - adrenergic synapses - released at most SNS post-ganglionic fibers Dopamine Serotonin - not enough may cause depression - SSRI ...
... - adrenergic synapses - released at most SNS post-ganglionic fibers Dopamine Serotonin - not enough may cause depression - SSRI ...
Nervous System
... Sense organs – specialized cells that can detect environmental changes called stimuli. Various sense organs contain receptors. The skin, for example, is a sense organ that contains receptors that sense changes in a wide variety of stimuli for pain, touch, pressure, heat, and cold. See list in the te ...
... Sense organs – specialized cells that can detect environmental changes called stimuli. Various sense organs contain receptors. The skin, for example, is a sense organ that contains receptors that sense changes in a wide variety of stimuli for pain, touch, pressure, heat, and cold. See list in the te ...
Neuron Teacher Key 5-17-16
... 13. What is a synapse? Identify where synapse junctions may occur in the body. A synapse is the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a ...
... 13. What is a synapse? Identify where synapse junctions may occur in the body. A synapse is the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a ...
Brain Development Infancy and Early Childhood Phyllis L
... n Increases conduction of nerve impulses from 10-100 times as rapidly as would occur along a non-myelinated axon. A newborn’s neurons lack dendrites, synaptic connections and myelin sheath needed for conducting impulses. ...
... n Increases conduction of nerve impulses from 10-100 times as rapidly as would occur along a non-myelinated axon. A newborn’s neurons lack dendrites, synaptic connections and myelin sheath needed for conducting impulses. ...
Slide ()
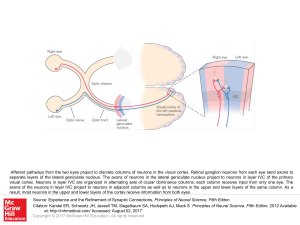
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
... separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the primary visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. Th ...
CV Hilbert Johan Kappen - Radboud University Portal
... • BK has made leading contributions to the development and use of novel approximate inference methods for application in intelligent systems and machine learning, using insights from statistical physics. Examples are the TAP approximation, linear response theory, Cluster Variation Method, and loop c ...
... • BK has made leading contributions to the development and use of novel approximate inference methods for application in intelligent systems and machine learning, using insights from statistical physics. Examples are the TAP approximation, linear response theory, Cluster Variation Method, and loop c ...
The Nervous System Worksheet
... b) The peripheral nervous system connects the CNS to the rest of the body via neurones that run to and from the CNS. Name this neurone and label its parts using the words in the box below. ...
... b) The peripheral nervous system connects the CNS to the rest of the body via neurones that run to and from the CNS. Name this neurone and label its parts using the words in the box below. ...
Neuron
... Receive stimuli from sensory cells and other neurons and transmit them towards the soma. So they can be regarded as major sites of information input into neuron. Axon: Fig.(2) Single, long, cylindrical process of a neuron. So its diameter is uniform. Does not branch profusely; but may give ris ...
... Receive stimuli from sensory cells and other neurons and transmit them towards the soma. So they can be regarded as major sites of information input into neuron. Axon: Fig.(2) Single, long, cylindrical process of a neuron. So its diameter is uniform. Does not branch profusely; but may give ris ...