neural control of respiration
... Skeletal muscles provide the motive force for respiration. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle, they have no rhythmic "beat" of their own; they depend entirely on the nervous system for a stimulus to contract. Two separate neural systems control respiration: (1) Voluntary control originates in cerebral ...
... Skeletal muscles provide the motive force for respiration. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle, they have no rhythmic "beat" of their own; they depend entirely on the nervous system for a stimulus to contract. Two separate neural systems control respiration: (1) Voluntary control originates in cerebral ...
Nervous System
... incredibly compact, weighing just 3 pounds. Its many folds and grooves, though, provide it with the additional surface area necessary for storing all of the body's important information. ...
... incredibly compact, weighing just 3 pounds. Its many folds and grooves, though, provide it with the additional surface area necessary for storing all of the body's important information. ...
Neural Cell Assemblies for Practical
... again be used to associate concepts so that synapses between associated concepts have a lower weight than synapses within concepts, but a higher weight than synapses between unassociated concepts. An associative memory based on this type of learning would be able to implement host of practical appli ...
... again be used to associate concepts so that synapses between associated concepts have a lower weight than synapses within concepts, but a higher weight than synapses between unassociated concepts. An associative memory based on this type of learning would be able to implement host of practical appli ...
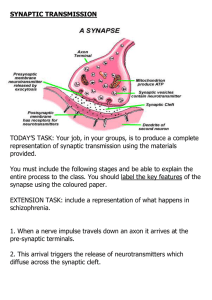
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along ...
... immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along ...
The Nervous System
... changes, called stimuli, which occur inside and outside the body. – They monitor such things as temperature, light, and sound from the external environment. – Inside the body (the internal environment), receptors detect variations in pressure, pH, carbon dioxide concentration, and the levels of vari ...
... changes, called stimuli, which occur inside and outside the body. – They monitor such things as temperature, light, and sound from the external environment. – Inside the body (the internal environment), receptors detect variations in pressure, pH, carbon dioxide concentration, and the levels of vari ...
Do Now 03/03-04 - Ed White Anatomy and Physiology
... your newly acquired knowledge O Expectations: ...
... your newly acquired knowledge O Expectations: ...
File
... • 3. Brain structures associated with sleep – a. The superchiasmatic nucleus – influences the entire sleep cycle. In rats with damage to this structure they will still sleep the same number of hours but the length and frequency of the their sleep episodes will be disrupted. It uses specialized opt ...
... • 3. Brain structures associated with sleep – a. The superchiasmatic nucleus – influences the entire sleep cycle. In rats with damage to this structure they will still sleep the same number of hours but the length and frequency of the their sleep episodes will be disrupted. It uses specialized opt ...
Biology 12 Name: Nervous System Practice Exam Types of Neurons
... d) The frequency of action potentials would be increased. 20. Why can an impulse traveling along an axon not reverse its direction? a) The myelin sheath will only permit one-way travel of an impulse. b) Sodium gates remain closed until the impulse reaches the synapse. c) The threshold required to cr ...
... d) The frequency of action potentials would be increased. 20. Why can an impulse traveling along an axon not reverse its direction? a) The myelin sheath will only permit one-way travel of an impulse. b) Sodium gates remain closed until the impulse reaches the synapse. c) The threshold required to cr ...
Eagleman Ch 1. Introduction
... can be implanted in the brain to record the electrical activity of individual neurons or groups of neurons. Microdialysis samples the chemical makeup and concentration of fluid in the brain. Voltammetry measures the levels of neurotransmitters in a tissue by monitoring voltage changes in the pro ...
... can be implanted in the brain to record the electrical activity of individual neurons or groups of neurons. Microdialysis samples the chemical makeup and concentration of fluid in the brain. Voltammetry measures the levels of neurotransmitters in a tissue by monitoring voltage changes in the pro ...
Intelligence and Patterns - Paradigm Shift International
... Wondering whether the command center responsible for generating fixational eye movements resides within the same brain structure that is in charge of initiating and directing large voluntary eye movements, Hafed decided to measure neural activity in the superior colliculus before and during microsac ...
... Wondering whether the command center responsible for generating fixational eye movements resides within the same brain structure that is in charge of initiating and directing large voluntary eye movements, Hafed decided to measure neural activity in the superior colliculus before and during microsac ...
General anatomy [edit]
... frequently, parts of the diencephalon are included. The brain stem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via thecranial nerves. Though small, this is an extremely important part of the brain as the nerve connections of the motor and sensory systems from the main part o ...
... frequently, parts of the diencephalon are included. The brain stem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via thecranial nerves. Though small, this is an extremely important part of the brain as the nerve connections of the motor and sensory systems from the main part o ...
8Neurotrophins PCD
... Synthesis by Physiological Activity • The transcription of genes for CNS neurotrophins is regulated by various forms of neuronal activity. • It has been observed that levels of BDNF mRNA in hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum can be changed by: - depolarization and Ca2+ influx - excitatory neurotran ...
... Synthesis by Physiological Activity • The transcription of genes for CNS neurotrophins is regulated by various forms of neuronal activity. • It has been observed that levels of BDNF mRNA in hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum can be changed by: - depolarization and Ca2+ influx - excitatory neurotran ...
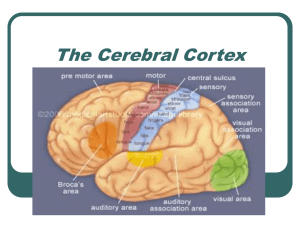
The Cerebral Cortex
... of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
... of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
Modern neuroscience is based on ideas derived
... and outputs of small or large brain areas, a column, layer, or single neurons. Using tracers we learned, for example, that connections between any two structures are generally reciprocal. Initially all but Cortex, (2004) 40, 000-000 ...
... and outputs of small or large brain areas, a column, layer, or single neurons. Using tracers we learned, for example, that connections between any two structures are generally reciprocal. Initially all but Cortex, (2004) 40, 000-000 ...
Central Auditory Pathways
... Neuron specialization The three major types of neurons, depending on their specialization: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons ...
... Neuron specialization The three major types of neurons, depending on their specialization: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons ...
Automated image computing reshapes computational neuroscience Open Access
... potential solutions based on bioimage informatics, especially automated image computing. Computational neuroscience is undergoing a transformation. Traditionally, this field has focused on studying information processing in nervous systems by collecting, analyzing, and simulating neuronal electrophy ...
... potential solutions based on bioimage informatics, especially automated image computing. Computational neuroscience is undergoing a transformation. Traditionally, this field has focused on studying information processing in nervous systems by collecting, analyzing, and simulating neuronal electrophy ...
2/pg
... signal from one cell to another – chemical signal is passed: neurotransmitter – neuron-muscle synapse = neuromuscular junction ...
... signal from one cell to another – chemical signal is passed: neurotransmitter – neuron-muscle synapse = neuromuscular junction ...
Perception - Department of Psychology
... characteristics to tell us how perception works Can also look to perception for how brain is organized ...
... characteristics to tell us how perception works Can also look to perception for how brain is organized ...
What are Neural Networks? - Teaching-WIKI
... cell such as a muscle effector cell or glandular cell. • The axon, is the primary conduit through which the neuron transmits impulses to neurons downstream in the signal chain • Humans: 1011 neurons of > 20 types, 1014 synapses, 1ms10ms cycle time • Signals are noisy “spike trains” of electrical pot ...
... cell such as a muscle effector cell or glandular cell. • The axon, is the primary conduit through which the neuron transmits impulses to neurons downstream in the signal chain • Humans: 1011 neurons of > 20 types, 1014 synapses, 1ms10ms cycle time • Signals are noisy “spike trains” of electrical pot ...
Chapter 49 and 50 Presentations-Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... digestive tract, pancreas, and gall bladder. It can function by itself, but it is largely under the control of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. travismulthaupt.com ...
... digestive tract, pancreas, and gall bladder. It can function by itself, but it is largely under the control of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. travismulthaupt.com ...
Nervous System III – Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... (found in the grey matter of the spinal cord) received the information and interprets it. It then sends out a response signal. 4) The muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be ...
... (found in the grey matter of the spinal cord) received the information and interprets it. It then sends out a response signal. 4) The muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be ...
Effect of varying neurons in the hidden layer of neural
... interconnected processing nodes (neurons) working together to solve specific problems. ANNs, like the human brain, learn by example. An ANN is designed for a specific application, such as pattern recognition or data classification, through a learning process. Learning in biological systems involves ...
... interconnected processing nodes (neurons) working together to solve specific problems. ANNs, like the human brain, learn by example. An ANN is designed for a specific application, such as pattern recognition or data classification, through a learning process. Learning in biological systems involves ...
CHAPTER 14 –NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of
... the superior colliculi, are associated with visual reflexes such as the tracking movements of the eyes. The lower two, or inferior colliculi, are involved with the sense of hearing. • Pons – broad band of white matter located anterior to the cerebellum and between the midbrain and the medulla oblong ...
... the superior colliculi, are associated with visual reflexes such as the tracking movements of the eyes. The lower two, or inferior colliculi, are involved with the sense of hearing. • Pons – broad band of white matter located anterior to the cerebellum and between the midbrain and the medulla oblong ...









![General anatomy [edit]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000712414_1-9f164978a5775158fafd921c8e3d4cef-300x300.png)