Magic Sand - studentorg
... • Move the magnet both horizontally and vertically past the copper coil, as shown. • The movement of the magnet induces current in the copper coil. ...
... • Move the magnet both horizontally and vertically past the copper coil, as shown. • The movement of the magnet induces current in the copper coil. ...
File - Science with Ms. C
... A generator produces an electric current when a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is rotated _____________ __________________ Generators at power plants produce electric energy for our homes. ...
... A generator produces an electric current when a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core is rotated _____________ __________________ Generators at power plants produce electric energy for our homes. ...
Tesla_04 - StealthSkater
... making such devices more compact and more efficient. Making no waves The idea of transmitting energy wirelessly isn't new. For almost 2 centuries, scientists have known that rapidly changing magnetic fields (such as those produced by an alternating current flowing through a wire) can induce an elect ...
... making such devices more compact and more efficient. Making no waves The idea of transmitting energy wirelessly isn't new. For almost 2 centuries, scientists have known that rapidly changing magnetic fields (such as those produced by an alternating current flowing through a wire) can induce an elect ...
B.Sc. Part - II (Physics) Paper I – Electricity, Magnetism Electrostatics
... Magnetic field , Magnetic force on a current , Magnetic Induction and Bit – Savart Law , Lorentz Force , Vector and Scalar Magnetic potentials , Magnetic Dipole , Magnetomotive force and Ampere’s Circuital theorem and its applications to calculate magnetic field due to wire carrying current and sole ...
... Magnetic field , Magnetic force on a current , Magnetic Induction and Bit – Savart Law , Lorentz Force , Vector and Scalar Magnetic potentials , Magnetic Dipole , Magnetomotive force and Ampere’s Circuital theorem and its applications to calculate magnetic field due to wire carrying current and sole ...
Understanding Vocabulary Section 17.1 1. coil 2. solenoid Section
... proper time in the rotation of the rotor. 12. The commutator reverses the polarity of the electromagnets at the proper time in the sequence of rotation. 13. The current must be continually reversed so the electromagnets will continually change polarity. 14. The main parts of all electric motors are ...
... proper time in the rotation of the rotor. 12. The commutator reverses the polarity of the electromagnets at the proper time in the sequence of rotation. 13. The current must be continually reversed so the electromagnets will continually change polarity. 14. The main parts of all electric motors are ...
why alternating current??
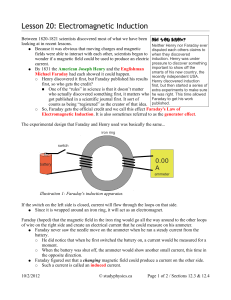
... • When the magnet is moved close to the coil, the magnetic field lines come into contact with the electrons in the coil. • This creates a potential difference. This potential difference causes the electrons to move (what we call current) • The coil now has its own magnetic field which opposes the ap ...
... • When the magnet is moved close to the coil, the magnetic field lines come into contact with the electrons in the coil. • This creates a potential difference. This potential difference causes the electrons to move (what we call current) • The coil now has its own magnetic field which opposes the ap ...
Document
... What are magnetic domains? Magnetic substances like iron, cobalt, and nickel are composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when ...
... What are magnetic domains? Magnetic substances like iron, cobalt, and nickel are composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when ...
Motors and Generators
... Back EMF is an electromagnetic force that opposes the main current flow in a circuit. When the coil of a motor rotates, it is cutting magnetic flux, which will induce an EMF that opposes the cause of induction. Thus, the induced current will flow in the opposite direction of the input current that l ...
... Back EMF is an electromagnetic force that opposes the main current flow in a circuit. When the coil of a motor rotates, it is cutting magnetic flux, which will induce an EMF that opposes the cause of induction. Thus, the induced current will flow in the opposite direction of the input current that l ...
Faraday Disk
... in the winter of 1819 during a demonstration to his students of the heating of a platinum wire by the electric current from a voltaic pile. He had planned to demonstrate both the heating of the wire and to also to carry out some general demonstrations of magnetism, for which he had provided a compas ...
... in the winter of 1819 during a demonstration to his students of the heating of a platinum wire by the electric current from a voltaic pile. He had planned to demonstrate both the heating of the wire and to also to carry out some general demonstrations of magnetism, for which he had provided a compas ...
Magnetism PowerPoint Template
... Over Head High Voltage (OH-HV) OH-HV radiate Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields ( ELF-EMF) ...
... Over Head High Voltage (OH-HV) OH-HV radiate Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields ( ELF-EMF) ...
MAGNETIC INDUCTION AND FARADAY`S LAW
... A square coil of wire with side 5.0 cm contains 100 loops and is perpendicular to a uniform 0.60 T magnetic field. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field to a region where B drops to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is at the edge of the field. It takes 0.100 s to move the whole ...
... A square coil of wire with side 5.0 cm contains 100 loops and is perpendicular to a uniform 0.60 T magnetic field. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field to a region where B drops to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is at the edge of the field. It takes 0.100 s to move the whole ...
Slide 1
... • Iron atoms can easily rotate their magnetic poles to line up with neighboring atoms. ...
... • Iron atoms can easily rotate their magnetic poles to line up with neighboring atoms. ...