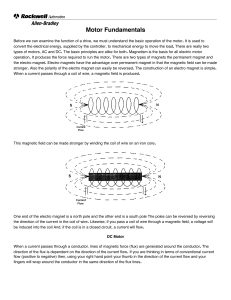
Magnetism and Electricity - Bloomsburg Area School District
... the poles on the magnet labeled “N” are touching, or both of the poles on the magnet labeled “S.” ...
... the poles on the magnet labeled “N” are touching, or both of the poles on the magnet labeled “S.” ...
Thermal Agitation of Electric Charge in Conductors
... as indicated in Fig. 2 and resonant within the range A. Since there is equilibrium between the amounts of power transferred in the two directions before inserting the network, it follows that after the network is inserted more power would be transferred from conductor II to the conductor I than in t ...
... as indicated in Fig. 2 and resonant within the range A. Since there is equilibrium between the amounts of power transferred in the two directions before inserting the network, it follows that after the network is inserted more power would be transferred from conductor II to the conductor I than in t ...
Induction and Inductance
... • Just as capacitors can be used to produce electric field, an inductor can be used to produce a desired magnetic field. • The inductance of an inductor is given as (Tesla sq meter per Ampere) ...
... • Just as capacitors can be used to produce electric field, an inductor can be used to produce a desired magnetic field. • The inductance of an inductor is given as (Tesla sq meter per Ampere) ...
Applications
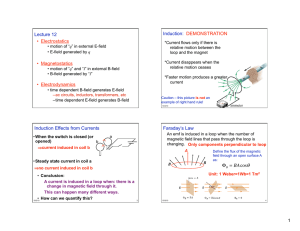
... b) When the magnet is pushed toward the coil or pulled away from it an induced current appears in the coil. c) The induced current only appears when the magnet is being moved ...
... b) When the magnet is pushed toward the coil or pulled away from it an induced current appears in the coil. c) The induced current only appears when the magnet is being moved ...
3 Electric Currents from Magnetism
... the current is zero. At 270°, the loop is parallel to the magnetic field. The current is at its maximum. However, because the sides of the loop are in opposite locations, the current in the loop is in the opposite direction. As the loop continues to rotate, the current continues to change direction. ...
... the current is zero. At 270°, the loop is parallel to the magnetic field. The current is at its maximum. However, because the sides of the loop are in opposite locations, the current in the loop is in the opposite direction. As the loop continues to rotate, the current continues to change direction. ...
Faraday`s Law - Rutgers Physics
... Notice the negative sign. Lenz's Law states that the induced emf (and current) will be in a direction such that the induced magnetic field opposes the original magnetic flux change. Keep in mind that the induced current will now produce an induced magnetic field. The direction of that magnetic field ...
... Notice the negative sign. Lenz's Law states that the induced emf (and current) will be in a direction such that the induced magnetic field opposes the original magnetic flux change. Keep in mind that the induced current will now produce an induced magnetic field. The direction of that magnetic field ...
Grade-Level Domain MAP
... The unit of electrical resistance is the ohm. B. Magnetism and Electricity • Earth’s magnetism Earth’s magnetism is believed to be caused by movements of charged atoms in the molten interior of the planet. Navigation by magnetic compass is made possible because the earth is a magnet with north and s ...
... The unit of electrical resistance is the ohm. B. Magnetism and Electricity • Earth’s magnetism Earth’s magnetism is believed to be caused by movements of charged atoms in the molten interior of the planet. Navigation by magnetic compass is made possible because the earth is a magnet with north and s ...
ΦB = BAcosθ - Purdue Physics
... magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current. Binduced always opposes the change in Opposition to Flux: the flux of B, but does not always point opposite it!!! ...
... magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current. Binduced always opposes the change in Opposition to Flux: the flux of B, but does not always point opposite it!!! ...
Maxwell`s equation
... point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also i ...
... point in space by currents J flowing along other curves in space. It has its experimental roots in Oersted’s great discovery that an electric current produces a magnetic field in the space around it. If another term is added to this equation, it follows that the magnetic field can be produced also i ...