Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
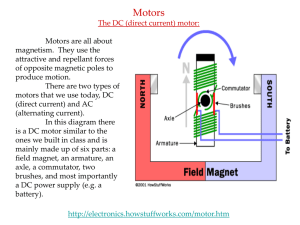
... 27. How does an electromagnet differ from a solenoid? A solenoid is a coil of wire with a current; an electromagnet is a solenoid with a ferromagnetic (iron) core. ...
... 27. How does an electromagnet differ from a solenoid? A solenoid is a coil of wire with a current; an electromagnet is a solenoid with a ferromagnetic (iron) core. ...
1. Two electromagnetic waves travel through empty space
... The loop remains in the plane of the page and never exits the magnetic field. Experiment III: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is shrunk to one half its initial radius, always remaining within the plane of the page. Experiment IV: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is rot ...
... The loop remains in the plane of the page and never exits the magnetic field. Experiment III: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is shrunk to one half its initial radius, always remaining within the plane of the page. Experiment IV: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is rot ...
Document
... Direct Current the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by sources such as batteries. ...
... Direct Current the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by sources such as batteries. ...
PHYS 241-1
... Know the definition of magnetic flux, Equation 30-1. Know Faraday's law of induction, Equations 30-4 and 30-5. Be able to state Lenz's law: An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current. The induced ...
... Know the definition of magnetic flux, Equation 30-1. Know Faraday's law of induction, Equations 30-4 and 30-5. Be able to state Lenz's law: An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic flux that induces the current. The induced ...
Electromagnetism - Physical Science
... the wire increases from 4 A to 9 A? A. Remains the same B. Increases C. Decreases ...
... the wire increases from 4 A to 9 A? A. Remains the same B. Increases C. Decreases ...
Unit IIA Electricity and Magnetism
... even when it is not close to other magnets—always a magnet! ...
... even when it is not close to other magnets—always a magnet! ...
magnetic field induced by overhead power transmission lines in
... Fig.9.Magnetic induction with conductor section S = 2x288mm² for 220kV-50Hz vertical single circuit line Table 2. Magnetic induction for different conductors sections and various load current ...
... Fig.9.Magnetic induction with conductor section S = 2x288mm² for 220kV-50Hz vertical single circuit line Table 2. Magnetic induction for different conductors sections and various load current ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
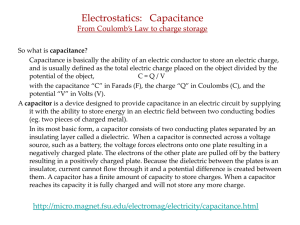
... (1) Friction---transfer of electrons by rubbing 2 uncharged objects together. Electrons transfer from one of the objects to the other. Objects become oppositely charged. (Socks rubbing across carpet as you walk) (2) Conduction—transfer of electrons from one object to another by direct contact. (Sock ...
... (1) Friction---transfer of electrons by rubbing 2 uncharged objects together. Electrons transfer from one of the objects to the other. Objects become oppositely charged. (Socks rubbing across carpet as you walk) (2) Conduction—transfer of electrons from one object to another by direct contact. (Sock ...