INTRODUCTION TO RADIO
... each other? • Radio communicators can operate without interfering by choosing different radio frequency • Each frequency generated by electromagnetic waves ...
... each other? • Radio communicators can operate without interfering by choosing different radio frequency • Each frequency generated by electromagnetic waves ...
Why not use near field probes
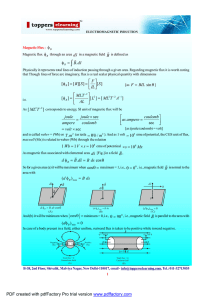
... we have seen, there are two types of near field, the electric (E) field and the magnetic (H) field. The magnetic probe takes the form of a small loop antenna which will respond to any magnetic flux coupling though the loop. The electric field probe is in essence a small monopole antenna. They are no ...
... we have seen, there are two types of near field, the electric (E) field and the magnetic (H) field. The magnetic probe takes the form of a small loop antenna which will respond to any magnetic flux coupling though the loop. The electric field probe is in essence a small monopole antenna. They are no ...
Topic XIII – Waves and Sound - Science - Miami
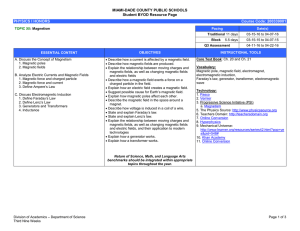
... Describe how a magnetic field exerts a force on a charged particle in the field. Explain how an electric field creates a magnetic field. Suggest possible cause for Earth’s magnetic field. Explain how magnetic poles affect each other. Describe the magnetic field in the space around a magnet ...
... Describe how a magnetic field exerts a force on a charged particle in the field. Explain how an electric field creates a magnetic field. Suggest possible cause for Earth’s magnetic field. Explain how magnetic poles affect each other. Describe the magnetic field in the space around a magnet ...
Lesson 12. Topic “Magnetic effect of an electric current”. Grammar
... A solenoid has two poles which attract and repel the poles of other magnets. While suspended, it takes up a north and a south direction exactly like the compass needle. A core of iron becomes strongly magnetized if placed within the solenoid, while the current is flowing. When winding a coil of wir ...
... A solenoid has two poles which attract and repel the poles of other magnets. While suspended, it takes up a north and a south direction exactly like the compass needle. A core of iron becomes strongly magnetized if placed within the solenoid, while the current is flowing. When winding a coil of wir ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
... induction and the generator effect. Pay particular attention to the technologies described on pages 614 and 615. In 1821, Michael Faraday invented the first electric motor. He publicly stated that if current had an effect on magnetism, then magnetism might have a corresponding effect on current. Far ...
... induction and the generator effect. Pay particular attention to the technologies described on pages 614 and 615. In 1821, Michael Faraday invented the first electric motor. He publicly stated that if current had an effect on magnetism, then magnetism might have a corresponding effect on current. Far ...
Electric Power Acquisition from the Vibration of an Electric Vehicle
... pilot generator. The linear power generators are then produced on the basis of the simulation and its performance will be tested by examinations. 2. LINEAR POWER GENERATOR AND MAGNETIC CHARACTERISTICS 2.1 Fundamental structure of linear power generator Figure 1 shows the fundamental structure of the ...
... pilot generator. The linear power generators are then produced on the basis of the simulation and its performance will be tested by examinations. 2. LINEAR POWER GENERATOR AND MAGNETIC CHARACTERISTICS 2.1 Fundamental structure of linear power generator Figure 1 shows the fundamental structure of the ...
Course Unit Title General Physics II Course Unit Code PHY 102
... A basic physics course which study electric and magnetic phenomenas. Topics include electricity, magnetism, and direct current circuits. Laboratory work is an important component of the course. Objectives of the Course: • Be able to know the basic laws of electricity and magnetism. • To apply those ...
... A basic physics course which study electric and magnetic phenomenas. Topics include electricity, magnetism, and direct current circuits. Laboratory work is an important component of the course. Objectives of the Course: • Be able to know the basic laws of electricity and magnetism. • To apply those ...