Exemplar Assignment Brief - An Introduction to Electronics at Level 3
... Knowledge of magnetism and electromagnetism is essential in order to underpin futher learning in electrical subjects. In this assessment you will discover how magnetism is used to produce and distribute electricity throughout the country and how the same underlying principles are used in various dif ...
... Knowledge of magnetism and electromagnetism is essential in order to underpin futher learning in electrical subjects. In this assessment you will discover how magnetism is used to produce and distribute electricity throughout the country and how the same underlying principles are used in various dif ...
Lab I - Electromagnet
... We want to make a motor using a regular battery, a heart-shaped wire and a small magnet. • Take a 15 cm piece of tin wire and straighten it out, as shown in figure 5a. Make a small bump on the middle of the wire. • Bend the wire so that it is parallel to itself (Figure 5b). • Attach a pack of neodym ...
... We want to make a motor using a regular battery, a heart-shaped wire and a small magnet. • Take a 15 cm piece of tin wire and straighten it out, as shown in figure 5a. Make a small bump on the middle of the wire. • Bend the wire so that it is parallel to itself (Figure 5b). • Attach a pack of neodym ...
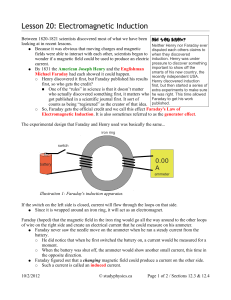
Faraday`s Law of Induction
... Faraday (hoped) that the magnetic field in the iron ring would go all the way around to the other loops of wire on the right side and create an electrical current that he could measure on his ammeter. ● Faraday never saw the needle move on the ammeter when he ran a steady current from the battery. ○ ...
... Faraday (hoped) that the magnetic field in the iron ring would go all the way around to the other loops of wire on the right side and create an electrical current that he could measure on his ammeter. ● Faraday never saw the needle move on the ammeter when he ran a steady current from the battery. ○ ...
Electromagnets
... domain consists of billions of aligned iron atoms. When a current is sent through the wire wrapped around the iron-containing metal, the domains align so their tiny magnetic fields add to the wire’s magnetic field. This creates a large magnetic field that extends into the space around the magnet. Th ...
... domain consists of billions of aligned iron atoms. When a current is sent through the wire wrapped around the iron-containing metal, the domains align so their tiny magnetic fields add to the wire’s magnetic field. This creates a large magnetic field that extends into the space around the magnet. Th ...
Processing Electroceramics - Universiti Sains Malaysia
... • Soft magnetic, or core products, do have the ability to store magnetic energy that has been converted from electrical energy; but it is normally short-term in nature because of the ease to demagnetize. • This is desirable in electronic and electrical circuits where cores are normally used because ...
... • Soft magnetic, or core products, do have the ability to store magnetic energy that has been converted from electrical energy; but it is normally short-term in nature because of the ease to demagnetize. • This is desirable in electronic and electrical circuits where cores are normally used because ...
Document
... When a wire with a current is places in a magnetic field, electrical energy is transformed into mechanical energy. ...
... When a wire with a current is places in a magnetic field, electrical energy is transformed into mechanical energy. ...
A Brief History of Electricity
... What are magnetic domains? Magnetic substances like iron, cobalt, and nickel are composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when ...
... What are magnetic domains? Magnetic substances like iron, cobalt, and nickel are composed of small areas where the groups of atoms are aligned like the poles of a magnet. These regions are called domains. All of the domains of a magnetic substance tend to align themselves in the same direction when ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... A loop of area 2.00 cm2 is in a constant magnetic field of 0.100 T. What is the magnetic flux through the loop in each of the following situations: When the loop is perpendicular to the field When the loop is parallel to the field When the normal to the loop and the field have an angle of 60 ...
... A loop of area 2.00 cm2 is in a constant magnetic field of 0.100 T. What is the magnetic flux through the loop in each of the following situations: When the loop is perpendicular to the field When the loop is parallel to the field When the normal to the loop and the field have an angle of 60 ...
Conceptual Physics - Southwest High School
... Force attracts N to S Magnets also strongly attract ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel and cobalt. ...
... Force attracts N to S Magnets also strongly attract ferromagnetic materials such as iron, nickel and cobalt. ...
Faraday`s Law
... into the page through the area enclosed by the loop increases in time. By Lenz’s law, the induced current must be counterclockwise so as to produce a counteracting magntic field directed out of the page. (b) When the bar moves to the left, the induced current must be clockwise. ...
... into the page through the area enclosed by the loop increases in time. By Lenz’s law, the induced current must be counterclockwise so as to produce a counteracting magntic field directed out of the page. (b) When the bar moves to the left, the induced current must be clockwise. ...
Ass. prof. Ali_ H. Ibrahim - The Six International Conference of ESES
... physical factors such as magnetic fields on plants (TANVIR et al., 2012; BILALIS et al., 2013). The literature survey reveals that most studies have been concerned with the interactive effect of magnetic field and salinity stress on plants during the ...
... physical factors such as magnetic fields on plants (TANVIR et al., 2012; BILALIS et al., 2013). The literature survey reveals that most studies have been concerned with the interactive effect of magnetic field and salinity stress on plants during the ...
19.- Modeling Electromagnetic Fields in Induction Heating
... Case 19 Modeling the Electromagnetic Fields in Induction Heating ...
... Case 19 Modeling the Electromagnetic Fields in Induction Heating ...
Probing Coronal and Chromospheric Magnetic Fields with Radio
... the corona and in the chromosphere observed by the Nobeyama Radioheliograph will be presented. There are other methods to estimate magnetic field strength using radio techniques in the solar atmosphere and also in the interplanetary space. These methods will also be reviewed. ...
... the corona and in the chromosphere observed by the Nobeyama Radioheliograph will be presented. There are other methods to estimate magnetic field strength using radio techniques in the solar atmosphere and also in the interplanetary space. These methods will also be reviewed. ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.