Tesla_04 - StealthSkater
... student who helped with Soljacic's theoretical model and computer simulations. Instead, "the electric field is at its maximum when the magnetic field is zero and vice versa," which is the opposite of being in phase, Karalis says. This arrangement means that the fields' energy stays mostly in the vic ...
... student who helped with Soljacic's theoretical model and computer simulations. Instead, "the electric field is at its maximum when the magnetic field is zero and vice versa," which is the opposite of being in phase, Karalis says. This arrangement means that the fields' energy stays mostly in the vic ...
AC Circuits - Welcome | San Jose State University
... • The experimental evidence that a changing magnetic field induces an emf ! • How Faraday’s Law relates the induced emf in a loop to the change in magnetic flux through the loop. • How a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field that is very different from that produced by an arrangement of ...
... • The experimental evidence that a changing magnetic field induces an emf ! • How Faraday’s Law relates the induced emf in a loop to the change in magnetic flux through the loop. • How a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field that is very different from that produced by an arrangement of ...
MAGNETIC FORCE ON A MOVING CHARGE – 1302Lab5Prob8
... the currents flows in the two Helmholtz coils? Should it be in the same direction or opposite directions? Ensure to send currents in the coils accordingly. Set up your Hall probe as explained in the Equipment and Software appendices. Before you push any buttons on the computer, locate the magnetic f ...
... the currents flows in the two Helmholtz coils? Should it be in the same direction or opposite directions? Ensure to send currents in the coils accordingly. Set up your Hall probe as explained in the Equipment and Software appendices. Before you push any buttons on the computer, locate the magnetic f ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... They are confined on the object surface and related with its nanostructure. For their non propagating nature nature, it’s not possible to detect them far away from the sample (i.e. far field region). It’s necessary to put very near to the object’s surface (i.e.near field region) a small scattering e ...
... They are confined on the object surface and related with its nanostructure. For their non propagating nature nature, it’s not possible to detect them far away from the sample (i.e. far field region). It’s necessary to put very near to the object’s surface (i.e.near field region) a small scattering e ...
Lesson 2 Worksheet - OG
... 13. What does the crust record as it cools? Direction of Earth’s magnetic field 14. What does basalt contain that makes this possible? Iron-rich minerals 15. What forms when Earth’s magnetic field changes direction? Magnetic stripes on ocean floor 16. What do magnetic stripes confirm? Ocean crust i ...
... 13. What does the crust record as it cools? Direction of Earth’s magnetic field 14. What does basalt contain that makes this possible? Iron-rich minerals 15. What forms when Earth’s magnetic field changes direction? Magnetic stripes on ocean floor 16. What do magnetic stripes confirm? Ocean crust i ...
Electricity and Magnetism Power Point Presentation
... Magnets and Electricity 4. One light in a strand of Christmas lights goes out and the rest of the lights also go out – what kind of circuit is formed? ...
... Magnets and Electricity 4. One light in a strand of Christmas lights goes out and the rest of the lights also go out – what kind of circuit is formed? ...
A rotating coil - Collins.co.uk.
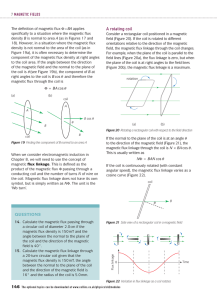
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
L10_EM_Induction
... If there are N turns of wire in the loop, each sees the same changing flux. Then: A circuit will respond to this emf the same way it would to a battery (with no internal resistance). In the loop at right, if the magnetic flux inside the loop is changing, then: emfloop = DV = RI. Discuss “where”. ...
... If there are N turns of wire in the loop, each sees the same changing flux. Then: A circuit will respond to this emf the same way it would to a battery (with no internal resistance). In the loop at right, if the magnetic flux inside the loop is changing, then: emfloop = DV = RI. Discuss “where”. ...
magnetic effects of electric current
... direction of current and the direction of the magnetic field. Experiments have shown that the displacement of the rod is largest (or the magnitude of the force is the highest) when the direction of current is at right angles to the direction of the magnetic field. In such a condition we can use a si ...
... direction of current and the direction of the magnetic field. Experiments have shown that the displacement of the rod is largest (or the magnitude of the force is the highest) when the direction of current is at right angles to the direction of the magnetic field. In such a condition we can use a si ...
Lab 12: Faraday`s Effect
... b) Connect the PASport voltage sensor cables to the coil. c) Click “START” to start recording, and move the magnet back and forth a few times to see what happens. d) Move the magnet slowly. e) Describe qualitatively what you observe. f) Move the magnet rapidly. g) Describe qualitatively what is diff ...
... b) Connect the PASport voltage sensor cables to the coil. c) Click “START” to start recording, and move the magnet back and forth a few times to see what happens. d) Move the magnet slowly. e) Describe qualitatively what you observe. f) Move the magnet rapidly. g) Describe qualitatively what is diff ...
Magnetism - Springer
... tremendous net magnetization even though there is no external applied field. Therefore, these materials have two main traits: (1) spontaneous magnetization, which is the net magnetization that can be presented inside of an even magnetized microscopic volume, and (2) the presence of magnetic ordering ...
... tremendous net magnetization even though there is no external applied field. Therefore, these materials have two main traits: (1) spontaneous magnetization, which is the net magnetization that can be presented inside of an even magnetized microscopic volume, and (2) the presence of magnetic ordering ...
Magnetism Demonstrations: Magnetic Signatures of Some Common
... Figure 5. Moment vs. field for Ti foil at 300 K showing paramagnetic behavior, with a low field kink that may be due to sample impurities. Note that this sample of Ti foil has a small moment, especially when compared to the Dy2O3. For such samples, the choice of mounting medium becomes extremely im ...
... Figure 5. Moment vs. field for Ti foil at 300 K showing paramagnetic behavior, with a low field kink that may be due to sample impurities. Note that this sample of Ti foil has a small moment, especially when compared to the Dy2O3. For such samples, the choice of mounting medium becomes extremely im ...
ESS 7 Lecture 14 October 31, 2008 Magnetic Storms
... Energetic Neutral Atom Imaging • The new neutral atoms are very energetic. • They fly from the charge exchange region in straight lines. ...
... Energetic Neutral Atom Imaging • The new neutral atoms are very energetic. • They fly from the charge exchange region in straight lines. ...
magnetic field
... A proton is released from rest at point A, which is located next to the positive plate of a parallel plate capacitor (see Figure 21.13). The proton then accelerates toward the negative plate, leaving the capacitor at point B through a small hole in the plate. The electric potential of the positive p ...
... A proton is released from rest at point A, which is located next to the positive plate of a parallel plate capacitor (see Figure 21.13). The proton then accelerates toward the negative plate, leaving the capacitor at point B through a small hole in the plate. The electric potential of the positive p ...
unit 7 magnetic circuit, electromagnetism and electromagnetic
... The principles of magnetism and its characteristic ...
... The principles of magnetism and its characteristic ...
Feasability of Increasing Oxygen Density Through the Applicaiton of
... The most prevalent oxygen configuration found in Earth’s atmosphere is the O2 molecule. The significance of this configuration lies in the valence electrons found in the molecule. Two of these electrons are unpaired and are in the degenerate orbital, allowing them to have the same spin without viola ...
... The most prevalent oxygen configuration found in Earth’s atmosphere is the O2 molecule. The significance of this configuration lies in the valence electrons found in the molecule. Two of these electrons are unpaired and are in the degenerate orbital, allowing them to have the same spin without viola ...
Earth Science
... Earth has a magnetic field generated by the flow of molten iron in the outer core. This field is what causes a compass needle to point to the North. A magnetic reversal happens when the flow in the outer core changes, and Earth’s magnetic field changes direction. ...
... Earth has a magnetic field generated by the flow of molten iron in the outer core. This field is what causes a compass needle to point to the North. A magnetic reversal happens when the flow in the outer core changes, and Earth’s magnetic field changes direction. ...
Electromagnetic - NUS Physics Department
... When a current flows in a conductor placed in the neighbourhood of another conductor also carrying a current, a force is found to be exerted between them. Similarly a charge moving in the vicinity of another moving charge is found to experience a force (over and above the electrostatic force). A mag ...
... When a current flows in a conductor placed in the neighbourhood of another conductor also carrying a current, a force is found to be exerted between them. Similarly a charge moving in the vicinity of another moving charge is found to experience a force (over and above the electrostatic force). A mag ...
Spin
... all possible spin orientations. Pass them through a magnetic gradient..they get pushed by the field gradient, with a force proportional to the spin orientation. ==> Expected smeared out distribution of positions transverse to beam What they actually found: But there are only two spots...it is as if ...
... all possible spin orientations. Pass them through a magnetic gradient..they get pushed by the field gradient, with a force proportional to the spin orientation. ==> Expected smeared out distribution of positions transverse to beam What they actually found: But there are only two spots...it is as if ...
Determination of synchronous motor vibrations due to
... evolution of forces in the time domain these calculations are done for each state selected for the electromagnetic field computation. The modeling approach described here, and given in details in [5] , is applied to compare vibrations produced by two permanent magnet synchronous motors [7]. These mo ...
... evolution of forces in the time domain these calculations are done for each state selected for the electromagnetic field computation. The modeling approach described here, and given in details in [5] , is applied to compare vibrations produced by two permanent magnet synchronous motors [7]. These mo ...
x a a = 3.0 cm B = 0.04 T I = 5 A y I 60° 30° C B A
... (d) What is the torque on the loop? Since is a vector, remember to specify its direction. Is it the same as what you found in part (b)? I hope so … and I hope you’ll agree that using magnetic moments to analyze the loop is a lot easier than working with forces directly! ...
... (d) What is the torque on the loop? Since is a vector, remember to specify its direction. Is it the same as what you found in part (b)? I hope so … and I hope you’ll agree that using magnetic moments to analyze the loop is a lot easier than working with forces directly! ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.