ppt - Nils T. Basse
... First turbulence measurements from two new high frequency reflectometer channels have been made in Alcator C-Mod. We have studied two discharges where Li-pellets were injected: •Density perturbation decays in roughly 15 ms. •132 GHz signals almost identical for the two shots: Core fluctuations low f ...
... First turbulence measurements from two new high frequency reflectometer channels have been made in Alcator C-Mod. We have studied two discharges where Li-pellets were injected: •Density perturbation decays in roughly 15 ms. •132 GHz signals almost identical for the two shots: Core fluctuations low f ...
Maxwell`s Equations
... Yeah, I also had much more difficulty following the derivation in this section than those in the previous sections. Perhaps we can go over each step. Casey McGrath I'm with everyone else on this one. These derivations are the hardest and least straightforward thing in the chapter. At some point I lo ...
... Yeah, I also had much more difficulty following the derivation in this section than those in the previous sections. Perhaps we can go over each step. Casey McGrath I'm with everyone else on this one. These derivations are the hardest and least straightforward thing in the chapter. At some point I lo ...
Induced EMF - Edvantage Science
... Magnetism, EMF, and Electric Current An Englishman, Michael Faraday (1791-1867) and an American, Joseph Henry (17971878), working independently discovered that magnetism could produce or induce a current in a circuit. Inducing an EMF in a Straight Piece of Wire A current in circuit can be induced if ...
... Magnetism, EMF, and Electric Current An Englishman, Michael Faraday (1791-1867) and an American, Joseph Henry (17971878), working independently discovered that magnetism could produce or induce a current in a circuit. Inducing an EMF in a Straight Piece of Wire A current in circuit can be induced if ...
Contributions of Maxwell to Electromagnetism
... loadstone in the globular form had a peculiar property. He brought a small magnetic needle and marked the line along which the needle sets itself. He marked many such lines covering the entire surface of the globular loadstone. The lines drawn by Maricourt showed that these lines girdle the globular ...
... loadstone in the globular form had a peculiar property. He brought a small magnetic needle and marked the line along which the needle sets itself. He marked many such lines covering the entire surface of the globular loadstone. The lines drawn by Maricourt showed that these lines girdle the globular ...
Displacement Current 2.
... from the [top] plate to the [bottom] plate, charging the capacitor and increasing the electric field between its plates. The same current enters the [top] plate (say I ) as leaves the [bottom] plate. Although current is flowing through the capacitor, no actual charge is transported through the vacuu ...
... from the [top] plate to the [bottom] plate, charging the capacitor and increasing the electric field between its plates. The same current enters the [top] plate (say I ) as leaves the [bottom] plate. Although current is flowing through the capacitor, no actual charge is transported through the vacuu ...
M o
... But there’s a problem. If two researchers want to compare their data using magnets of different strengths, they have to adjust for that difference. That’s a pain, so, data is instead reported using the “chemical shift” scale as described on the next slide. ...
... But there’s a problem. If two researchers want to compare their data using magnets of different strengths, they have to adjust for that difference. That’s a pain, so, data is instead reported using the “chemical shift” scale as described on the next slide. ...
Basic law in Magnetostatics
... The magnetic dipole is analogous to the electric dipole. Just as the electric dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of dielectric materials, so the magnetic dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of magnetic materials. ...
... The magnetic dipole is analogous to the electric dipole. Just as the electric dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of dielectric materials, so the magnetic dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of magnetic materials. ...
Magnetic Flux Density (Cont`d)
... The magnetic dipole is analogous to the electric dipole. Just as the electric dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of dielectric materials, so the magnetic dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of magnetic materials. ...
... The magnetic dipole is analogous to the electric dipole. Just as the electric dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of dielectric materials, so the magnetic dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of magnetic materials. ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... • TV sets to provide HV to picture tubes, portable electronic device converters, transformers on the pole, etc ...
... • TV sets to provide HV to picture tubes, portable electronic device converters, transformers on the pole, etc ...
and magnetism - Ms. Athena Klock Science Teacher Pine Middle
... testing, they will discover that only some of the metals in Bag B are attracted. 3. Discuss the fact that only ferromagnetic materials (materials containing iron, cobalt nickel and/or rare earth elements) exhibit magnetic attraction. Most metals (aluminum, copper, lead, silver, gold, etc.) are NOT a ...
... testing, they will discover that only some of the metals in Bag B are attracted. 3. Discuss the fact that only ferromagnetic materials (materials containing iron, cobalt nickel and/or rare earth elements) exhibit magnetic attraction. Most metals (aluminum, copper, lead, silver, gold, etc.) are NOT a ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields - Hydro
... technical characteristics of the lines (for example, pole height). Even underground distribution lines produce EMFs, since the magnetic field passes through matter and is not diminished by earth, rock or concrete. ...
... technical characteristics of the lines (for example, pole height). Even underground distribution lines produce EMFs, since the magnetic field passes through matter and is not diminished by earth, rock or concrete. ...
Estimation of Magnetic Torquing and Momentum
... through momentum storage knowledge and angular velocity measurements. may be measured via a 3-axis magnetometer on board the satellite or through knowledge of the spacecraft’s position in combination with a model of Earth’s magnetic field. In the case of the magnetometer, the satellite’s magnetic mo ...
... through momentum storage knowledge and angular velocity measurements. may be measured via a 3-axis magnetometer on board the satellite or through knowledge of the spacecraft’s position in combination with a model of Earth’s magnetic field. In the case of the magnetometer, the satellite’s magnetic mo ...
Fundamentals of magnetic field
... The main point of induction is that the change of magnetic field causes electrical field. Using the term of induced voltage a phenomenon in magnetic field may be replaced with a phenomenon in electrical circuit. In real equipment the two types of inductance (transformer and motional) often appear si ...
... The main point of induction is that the change of magnetic field causes electrical field. Using the term of induced voltage a phenomenon in magnetic field may be replaced with a phenomenon in electrical circuit. In real equipment the two types of inductance (transformer and motional) often appear si ...
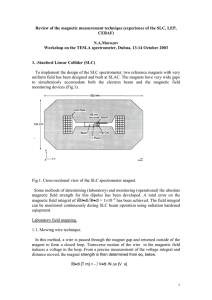
Review of the magnetic measurement technique (experience
... Fig.5. Principle of the measurement. 2.2. The experimental apparatus. A. The search coils. To avoid second oder effects and to provide a consistency check in the comparison between forward and backward data, the two coils must be indentical in terms of magnetic area within a relative accuracy of fe ...
... Fig.5. Principle of the measurement. 2.2. The experimental apparatus. A. The search coils. To avoid second oder effects and to provide a consistency check in the comparison between forward and backward data, the two coils must be indentical in terms of magnetic area within a relative accuracy of fe ...
Document
... The magnetic dipole is analogous to the electric dipole. Just as the electric dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of dielectric materials, so the magnetic dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of magnetic materials. ...
... The magnetic dipole is analogous to the electric dipole. Just as the electric dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of dielectric materials, so the magnetic dipole is useful in helping us to understand the behavior of magnetic materials. ...
FARADAY’S LAW
... Thus a magnetic field which changes in time produces a non-conservative electric field. This has profound consequences, as we shall see. Note that there are now two sources of EMF – a time varying magnetic field, and a loop which changes shape or orientation. The first is new, the second is not. Ul ...
... Thus a magnetic field which changes in time produces a non-conservative electric field. This has profound consequences, as we shall see. Note that there are now two sources of EMF – a time varying magnetic field, and a loop which changes shape or orientation. The first is new, the second is not. Ul ...
Hyperfine Splitting and Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism of Ni at Multimegabar Pressure
... Depending on the band structure, the balance between these effects may result in fractional spin polarization of the electrons at each lattice site, and hence, a net magnetization. Application of pressure broadens the band, thus increasing the kinetic energy. At sufficiently high pressure, kinetic e ...
... Depending on the band structure, the balance between these effects may result in fractional spin polarization of the electrons at each lattice site, and hence, a net magnetization. Application of pressure broadens the band, thus increasing the kinetic energy. At sufficiently high pressure, kinetic e ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.