PPT
... current were to flow clockwise, hence creating a magnetic flux “upwards.” • So, the induced EMF is in a direction that makes a current flow clockwise. • If the N pole moves AWAY, the flux “downwards” DECREASES, so the loop has a counter clockwise current! ...
... current were to flow clockwise, hence creating a magnetic flux “upwards.” • So, the induced EMF is in a direction that makes a current flow clockwise. • If the N pole moves AWAY, the flux “downwards” DECREASES, so the loop has a counter clockwise current! ...
Brief History of Electromagnetics
... • Self-taught English chemist and physicist discovered electromagnetic induction in 1831 by which a changing magnetic field induces an electric field • “Distinct conversion of magnetism into electricity” (Faraday) ...
... • Self-taught English chemist and physicist discovered electromagnetic induction in 1831 by which a changing magnetic field induces an electric field • “Distinct conversion of magnetism into electricity” (Faraday) ...
26.2 Magnetic field
... A simple motor is composed of a coil of 100 turns, two magnets with opposite poles facing each other and a cell. The length and width of the coil are 3 cm and 2 cm respectively. The magnitude of the magnetic field between the magnets is 3 T. The current flowing in the coil is 1.5 A. ...
... A simple motor is composed of a coil of 100 turns, two magnets with opposite poles facing each other and a cell. The length and width of the coil are 3 cm and 2 cm respectively. The magnitude of the magnetic field between the magnets is 3 T. The current flowing in the coil is 1.5 A. ...
magnetic field - bba-npreiser
... metal target, like tungsten or copper. When electrons hit this material, some of the electrons will approach the nucleus of the metal atoms where they are deflected because of their opposite charges (electrons are negative and the nucleus is positive, so the electrons are attracted to the nucleus). ...
... metal target, like tungsten or copper. When electrons hit this material, some of the electrons will approach the nucleus of the metal atoms where they are deflected because of their opposite charges (electrons are negative and the nucleus is positive, so the electrons are attracted to the nucleus). ...
Chapter 8: Magnetic and Electrical Properties 1
... order in small clusters, but no order between the clusters (similar to a spin glass). • Metamagnet – There is a field-induced magnetic transition from a state of low magnetization to one of relatively high magnetization. Typically the external field causes a transition from an antiferromagnetic stat ...
... order in small clusters, but no order between the clusters (similar to a spin glass). • Metamagnet – There is a field-induced magnetic transition from a state of low magnetization to one of relatively high magnetization. Typically the external field causes a transition from an antiferromagnetic stat ...
physics - 3rd chapter- solution - e
... 1Sol. Flux meter is used to measure magnetic field. 2Sol. A magnet is broken into three pieces in length. The strength of the new poles is the same as the strength of the poles of original magnet 3Sol. Magnetic fields do not interact with stationary electric charge 4Sol. Magnetic field produced by e ...
... 1Sol. Flux meter is used to measure magnetic field. 2Sol. A magnet is broken into three pieces in length. The strength of the new poles is the same as the strength of the poles of original magnet 3Sol. Magnetic fields do not interact with stationary electric charge 4Sol. Magnetic field produced by e ...
EC6403
... Course Outcome 1:Apply vector calculus to static electric-magnetic fields in different engineering situations. Course Outcome 2:An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems Course Outcome 3:Analyze Maxwell’s equation in different forms (differential and integral) and apply them ...
... Course Outcome 1:Apply vector calculus to static electric-magnetic fields in different engineering situations. Course Outcome 2:An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems Course Outcome 3:Analyze Maxwell’s equation in different forms (differential and integral) and apply them ...
Charges, currents & reference frames
... currents- a puzzle Choice of inertial frame can affect interpretation of a physical situation ...
... currents- a puzzle Choice of inertial frame can affect interpretation of a physical situation ...
CITRUS COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CREDIT COURSE
... Students will be graded, at minimum, in at least one of the following categories. If "essay" is not checked, it must be explained why essays are an inappropriate basis for at least part of the grade in the course. ESSAY OR SUBSTANTIAL WRITING ASSIGNMENT Includes not only "blue book" examinations but ...
... Students will be graded, at minimum, in at least one of the following categories. If "essay" is not checked, it must be explained why essays are an inappropriate basis for at least part of the grade in the course. ESSAY OR SUBSTANTIAL WRITING ASSIGNMENT Includes not only "blue book" examinations but ...
Electrical Energy and Magnetism
... The strong magnetic field causes the magnetic domains in the material to line up The magnetic fields of these aligned domains add together and create a strong magnetic field inside the material This field prevents the constant motion of the atoms from bumping the domains out of alignment. The materi ...
... The strong magnetic field causes the magnetic domains in the material to line up The magnetic fields of these aligned domains add together and create a strong magnetic field inside the material This field prevents the constant motion of the atoms from bumping the domains out of alignment. The materi ...
unit 4 physics index book 1 — electric power
... Discuss and show with a diagram, how a strong magnetic field could be used to separate these three particles. Have the particles project from left to right, and the magnetic field directed into the page. Solution ...
... Discuss and show with a diagram, how a strong magnetic field could be used to separate these three particles. Have the particles project from left to right, and the magnetic field directed into the page. Solution ...
スライド 1 - Nanjing University
... Aim of this study: •What about heat conduction? •Can we find observational signature of asymmetric heat conduction? ...
... Aim of this study: •What about heat conduction? •Can we find observational signature of asymmetric heat conduction? ...
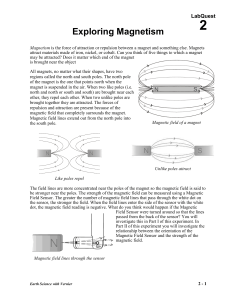
PHET Magnetism
... and record the value of B. Repeat until you’ve completed the table below. NOTE: Be sure to take all of your values along the axis of the coil. You’ll know you’re on the axis because the y component of the magnetic field is zero along the axis. ...
... and record the value of B. Repeat until you’ve completed the table below. NOTE: Be sure to take all of your values along the axis of the coil. You’ll know you’re on the axis because the y component of the magnetic field is zero along the axis. ...
Faraday`s Law
... When an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it. The induced magnetic field inside any loop of wire always acts to keep the magnetic flux in ...
... When an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it. The induced magnetic field inside any loop of wire always acts to keep the magnetic flux in ...
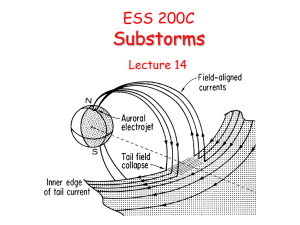
expansion phase
... • At the same time a density gradient on the boundary of the plasma sheet drives the lower-hybrid-drift instability. The two types of waves cause the plasma sheet to act resistively thereby disrupting the cross tail current. • This gives the “current wedge” which launches a rarefaction wave that pro ...
... • At the same time a density gradient on the boundary of the plasma sheet drives the lower-hybrid-drift instability. The two types of waves cause the plasma sheet to act resistively thereby disrupting the cross tail current. • This gives the “current wedge” which launches a rarefaction wave that pro ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.








![L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001482032_1-b69d1eb7a0f8c001e0e2a09bf26d62d2-300x300.png)