CHAPTER 20 Induced Voltages and Inductance
... - Notice the B-field extends all the way around the inside of the iron. - A current in the secondary coil wire develops only momentarily when the switch is closed (indicated by the Galvanometer) and then returns to zero. - A current in the secondary coil also develops (in the opposite direction) mo ...
... - Notice the B-field extends all the way around the inside of the iron. - A current in the secondary coil wire develops only momentarily when the switch is closed (indicated by the Galvanometer) and then returns to zero. - A current in the secondary coil also develops (in the opposite direction) mo ...
Faraday`s Law.
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
PowerPoint
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
... cannot change a charged particle’s potential energy or electric potential. But electric fields can do work. This equation shows that a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field, which can change a charged particle’s potential energy. This induced electric field is responsible for induced emf. ...
B - college physics
... The flux through the left side is 1=-BA, A is outward and so is antiparallel to B. The flux through the right side is 2=+BA, A is parallel to B. The flux through the other sides is 0, A is perpendicular to B. The net flux is the sum of the flux through each side, net = 0. The magnetic flux throug ...
... The flux through the left side is 1=-BA, A is outward and so is antiparallel to B. The flux through the right side is 2=+BA, A is parallel to B. The flux through the other sides is 0, A is perpendicular to B. The net flux is the sum of the flux through each side, net = 0. The magnetic flux throug ...
Electromagnetism - GTU e
... presence of electric charges and currents, whether steady or rapidly fluctuating, in a vacuum or in matter. • The equations represent one of the most elegant and concise way to describe the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism. They pull together in a consistent way earlier results known from t ...
... presence of electric charges and currents, whether steady or rapidly fluctuating, in a vacuum or in matter. • The equations represent one of the most elegant and concise way to describe the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism. They pull together in a consistent way earlier results known from t ...
Essay 90-4cd DC motor
... perpendicular to a magnetic filed of uniform flux density B. The coil is then rotated at a uniform angular velocity about an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field and passing through the centre of the coil, as shown in Figure 2. Derive an expression for the e.m.f. induced in the coil at any sub ...
... perpendicular to a magnetic filed of uniform flux density B. The coil is then rotated at a uniform angular velocity about an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field and passing through the centre of the coil, as shown in Figure 2. Derive an expression for the e.m.f. induced in the coil at any sub ...
poster
... (Wassell et al. 2006). Thus, while the number of counts is small, this feature is compatible with what we expect from a real knot, which was 3 times brighter in 2011. ...
... (Wassell et al. 2006). Thus, while the number of counts is small, this feature is compatible with what we expect from a real knot, which was 3 times brighter in 2011. ...
Conserved quatities / Mirror / Tokamak
... increased forever. The tokamak is necessarily a pulsed machine That is not good for energy production Also thermal stresses are associated with the pulsed character One can either: live with it / drive current another way / use a different concept ...
... increased forever. The tokamak is necessarily a pulsed machine That is not good for energy production Also thermal stresses are associated with the pulsed character One can either: live with it / drive current another way / use a different concept ...
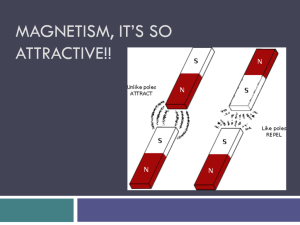
Magnetism
... uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.440 T. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (left or right) of the current required to remove the tension in the supporting leads? ...
... uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.440 T. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (left or right) of the current required to remove the tension in the supporting leads? ...
AC Circuits - Welcome | San Jose State University
... magnetic field induces an emf ! • How Faraday’s Law relates the induced emf in a loop to the change in magnetic flux through the loop. • How a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field that is very different from that produced by an arrangement of charges. • Four fundamental equations compl ...
... magnetic field induces an emf ! • How Faraday’s Law relates the induced emf in a loop to the change in magnetic flux through the loop. • How a changing magnetic flux generates an electric field that is very different from that produced by an arrangement of charges. • Four fundamental equations compl ...
Document
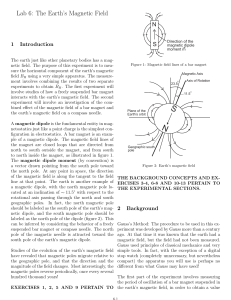
... Magnetic objects are surrounded a magnetic field. Moving electrical charges are also surrounded by a magnetic field (in addition to the electrical field). A vector quantity: magnitude and direction… The letter B is used to represent magnetic fields. ...
... Magnetic objects are surrounded a magnetic field. Moving electrical charges are also surrounded by a magnetic field (in addition to the electrical field). A vector quantity: magnitude and direction… The letter B is used to represent magnetic fields. ...
Magnetic Field
... • Lorentz force on an electron = - evd x B (normal to wire) Motor effect: wire is pushed or pulled by the charges ...
... • Lorentz force on an electron = - evd x B (normal to wire) Motor effect: wire is pushed or pulled by the charges ...
Simulation of the Trajectory of a Charged Particle in Two
... escape velocity at a point and leaves the dipole field. There is also a tendency to this in Fig. 5b. Moreover it can be seen that small changes in the initial conditions cause rather big changes in the trajectory. See Fig. 5c and Fig. 5d, where although the difference in the strength of the magnetic ...
... escape velocity at a point and leaves the dipole field. There is also a tendency to this in Fig. 5b. Moreover it can be seen that small changes in the initial conditions cause rather big changes in the trajectory. See Fig. 5c and Fig. 5d, where although the difference in the strength of the magnetic ...
Make it into a magnet
... Make it into a magnet nce a magnet, always a magnet? Not necessarily. Some magnets keep their magnetic effect for years. Others lose their magnetic effect in just minutes. There are also magnets that can be turned on and off at the flick of a switch. No matter what type of magnet, the materials that ...
... Make it into a magnet nce a magnet, always a magnet? Not necessarily. Some magnets keep their magnetic effect for years. Others lose their magnetic effect in just minutes. There are also magnets that can be turned on and off at the flick of a switch. No matter what type of magnet, the materials that ...
Chapter 1 Magnetic properties of heavy lanthanide metals
... of the involved electronic states n. Because of the energy denominator, large contributions to this sum come from pairs of electronic states with energies close to the Fermi energy, one of which is occupied and the other one empty, separated by a defined momentum transfer q 0 . The maximum in the su ...
... of the involved electronic states n. Because of the energy denominator, large contributions to this sum come from pairs of electronic states with energies close to the Fermi energy, one of which is occupied and the other one empty, separated by a defined momentum transfer q 0 . The maximum in the su ...
A fast, high-tech, low cost electric motor construction
... magnet and a short wire and set in rotation. The magnet, through its attractive power, attaches to the screw to make a rotor, and the screw, which has itself become magnetised, is suspended from the battery pole. Two constructive exercises are illustrated: on the one hand the magnet holds essential ...
... magnet and a short wire and set in rotation. The magnet, through its attractive power, attaches to the screw to make a rotor, and the screw, which has itself become magnetised, is suspended from the battery pole. Two constructive exercises are illustrated: on the one hand the magnet holds essential ...
Ferrofluid

A ferrofluid (portmanteau of ferromagnetic and fluid) is a liquid that becomes strongly magnetized in the presence of a magnetic field.Ferrofluid was invented in 1963 by NASA's Steve Papell as a liquid rocket fuel that could be drawn toward a pump inlet in a weightless environment by applying a magnetic field.Ferrofluids are colloidal liquids made of nanoscale ferromagnetic, or ferrimagnetic, particles suspended in a carrier fluid (usually an organic solvent or water). Each tiny particle is thoroughly coated with a surfactant to inhibit clumping. Large ferromagnetic particles can be ripped out of the homogeneous colloidal mixture, forming a separate clump of magnetic dust when exposed to strong magnetic fields. The magnetic attraction of nanoparticles is weak enough that the surfactant's Van der Waals force is sufficient to prevent magnetic clumping or agglomeration. Ferrofluids usually do not retain magnetization in the absence of an externally applied field and thus are often classified as ""superparamagnets"" rather than ferromagnets.The difference between ferrofluids and magnetorheological fluids (MR fluids) is the size of the particles. The particles in a ferrofluid primarily consist of nanoparticles which are suspended by Brownian motion and generally will not settle under normal conditions. MR fluid particles primarily consist of micrometre-scale particles which are too heavy for Brownian motion to keep them suspended, and thus will settle over time because of the inherent density difference between the particle and its carrier fluid. These two fluids have very different applications as a result.