College Physics, PHYS 104, Behavioral Objectives, Unit III (b)
... magnetic flux thru a coil of known magnetic field and area, potential difference for a coil (wire): (i) or one of the other variables for a given no. of turns, cross-sectional area, and a magnetic field changing at a given rate, and vice versa (ii) given speed and length in a given magnetic field, ( ...
... magnetic flux thru a coil of known magnetic field and area, potential difference for a coil (wire): (i) or one of the other variables for a given no. of turns, cross-sectional area, and a magnetic field changing at a given rate, and vice versa (ii) given speed and length in a given magnetic field, ( ...
yuval9
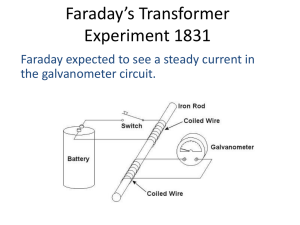
... In 1831, Michael Faraday (in England) and Joseph Henry (in the U.S.) independently discovered that a changing magnetic flux ΦB through a conducting circuit induces a current! ...
... In 1831, Michael Faraday (in England) and Joseph Henry (in the U.S.) independently discovered that a changing magnetic flux ΦB through a conducting circuit induces a current! ...
End of chapter exercises
... current changes with every half turn of the coil. As one side of the loop moves to the other pole of the magnetic field, the current in the loop changes direction. The two slip rings of the AC generator allow the coil to turn without breaking the connections to the load circuit. This type of current ...
... current changes with every half turn of the coil. As one side of the loop moves to the other pole of the magnetic field, the current in the loop changes direction. The two slip rings of the AC generator allow the coil to turn without breaking the connections to the load circuit. This type of current ...
Pretest 13 (EMF) - University of Colorado Boulder
... On which part of the wing will the positive charge accumulate? Please select ALL that apply. a) Top b) Bottom c) Front d) Rear e) Other f) Not enough information Please explain your answers to the previous 2 questions briefly but clearly: ...
... On which part of the wing will the positive charge accumulate? Please select ALL that apply. a) Top b) Bottom c) Front d) Rear e) Other f) Not enough information Please explain your answers to the previous 2 questions briefly but clearly: ...
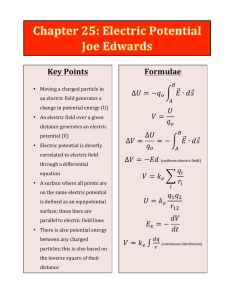
2-27 Potential Energy, Potential, and Work
... Two identical point charges of mass of 0.01g are placed 1m apart. The right-hand charge is released. Find its velocity when it is 10cm farther away. E Field and Force are not the same ...
... Two identical point charges of mass of 0.01g are placed 1m apart. The right-hand charge is released. Find its velocity when it is 10cm farther away. E Field and Force are not the same ...
EM Induction 2
... Faraday’s Law of EM induction states that an emf is induced when flux changes and is equal to the rate of change of flux. Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced emf is such that it opposes the change of flux. According to the laws of energy conservation, the emf must try to oppose or r ...
... Faraday’s Law of EM induction states that an emf is induced when flux changes and is equal to the rate of change of flux. Lenz’s law states that the direction of the induced emf is such that it opposes the change of flux. According to the laws of energy conservation, the emf must try to oppose or r ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... • If two electrons are spinning the same way, they make a stronger magnet • If two electrons are spinning in opposite directions, their magnetic field cancels out (why most substances are not magnets) ...
... • If two electrons are spinning the same way, they make a stronger magnet • If two electrons are spinning in opposite directions, their magnetic field cancels out (why most substances are not magnets) ...
Physics 122 â Class #28 (4/28/15) â Announcements Torque on an
... Copper wire in a rectangle 10 cm on a side. It is placed in a 10 milliTesla magnetic field. What is the maximum torque with a 100 amp current? ...
... Copper wire in a rectangle 10 cm on a side. It is placed in a 10 milliTesla magnetic field. What is the maximum torque with a 100 amp current? ...
buds public school, dubai physics worksheet
... I Very Short Answer Type Questions 1. What is the frequency of an alternating current if its direction changes after 0.01S? 2. How can it be shown that a magnetic field at a point near a wire related to the strength of the electric current flowing in a wire? 3. Name the physical quantity whose SI un ...
... I Very Short Answer Type Questions 1. What is the frequency of an alternating current if its direction changes after 0.01S? 2. How can it be shown that a magnetic field at a point near a wire related to the strength of the electric current flowing in a wire? 3. Name the physical quantity whose SI un ...
Chapter 5 Electrostatics
... Electronic Terms, con’t • Electric Potential = Volt (V) • Resistance = Increasing electric resistance (Ohm’s) = LESS current flow in amps (A) • Ohm’s Law = voltage across the circuit is equal to the CURRENT X RESISTANCE (V + IR) where I= current (amps), R= resistance in ohm’s, V= POTENTIAL in volts ...
... Electronic Terms, con’t • Electric Potential = Volt (V) • Resistance = Increasing electric resistance (Ohm’s) = LESS current flow in amps (A) • Ohm’s Law = voltage across the circuit is equal to the CURRENT X RESISTANCE (V + IR) where I= current (amps), R= resistance in ohm’s, V= POTENTIAL in volts ...