Understand Ohm`s law in both microscopic
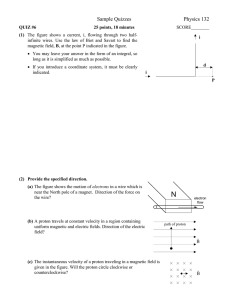
... sense of revolution of a charge in a given constant magnetic field given the field direction and the charge of the particle. F Idl B : be able to compute this direction, and understand the meaning of it, e.g. for a current loop above a magnet. ...
... sense of revolution of a charge in a given constant magnetic field given the field direction and the charge of the particle. F Idl B : be able to compute this direction, and understand the meaning of it, e.g. for a current loop above a magnet. ...
Chapter 8 Test Review – Electricity and Magnetism
... o Voltage = the potential energy difference needed to get current flowing (the push) o Resistance = opposition to the flow of current o Electrical power = the rate at work is done within an electrical device Know the units used to measure current, voltage, resistance, power o Current = amps (amperes ...
... o Voltage = the potential energy difference needed to get current flowing (the push) o Resistance = opposition to the flow of current o Electrical power = the rate at work is done within an electrical device Know the units used to measure current, voltage, resistance, power o Current = amps (amperes ...
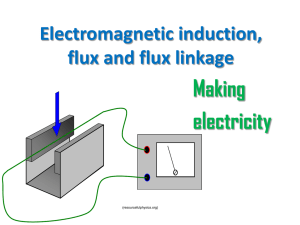
Electromagnetic induction, flux and flux linkage
... The same is true for other electrons in the rod, so the end P Q L will become negatively v P Flux charged, density (B) leaving Q with a positive charge. As a result, an electric field E builds up until the force on electrons in the rod due to this electric field (= Ee) balances the force due to the ...
... The same is true for other electrons in the rod, so the end P Q L will become negatively v P Flux charged, density (B) leaving Q with a positive charge. As a result, an electric field E builds up until the force on electrons in the rod due to this electric field (= Ee) balances the force due to the ...