Estimation of Magnetic Torquing and Momentum
... satellite's momentum storage facilities, the satellite must be capable of applying external torques to an object outside the satellite system, thus transferring some of the satellite's angular momentum to that external object. Applying such an external torque is referred to as momentum dumping. To d ...
... satellite's momentum storage facilities, the satellite must be capable of applying external torques to an object outside the satellite system, thus transferring some of the satellite's angular momentum to that external object. Applying such an external torque is referred to as momentum dumping. To d ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Maxwell’s Amazing Leap of Faith • According to Maxwell, a magnetic field will be produced even in empty space if there is a changing electric field – He then took this concept one step further and concluded that • If a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, the electric field is also c ...
... Maxwell’s Amazing Leap of Faith • According to Maxwell, a magnetic field will be produced even in empty space if there is a changing electric field – He then took this concept one step further and concluded that • If a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, the electric field is also c ...
PHYS 1442-004, Dr. Brandt
... Maxwell’s Amazing Leap of Faith • According to Maxwell, a magnetic field will be produced even in empty space if there is a changing electric field – He then took this concept one step further and concluded that • If a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, the electric field is also c ...
... Maxwell’s Amazing Leap of Faith • According to Maxwell, a magnetic field will be produced even in empty space if there is a changing electric field – He then took this concept one step further and concluded that • If a changing magnetic field produces an electric field, the electric field is also c ...
Magnetism
... Slide 10 / 49 Electric Currents Produce Magnetic Fields The direction of the field is given by a right-hand ...
... Slide 10 / 49 Electric Currents Produce Magnetic Fields The direction of the field is given by a right-hand ...
Ch.20
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
Self-Assembly of Colloidal Pyramids in Magnetic Fields
... be pointed out that in some cases we also observed pyramids with tails (i.e., with linear chains attached to the apex), but a physical explanation for this phenomenon has not yet been revealed. That is, we do not yet understand why these tails do not conform to increase the size of the pyramid in or ...
... be pointed out that in some cases we also observed pyramids with tails (i.e., with linear chains attached to the apex), but a physical explanation for this phenomenon has not yet been revealed. That is, we do not yet understand why these tails do not conform to increase the size of the pyramid in or ...
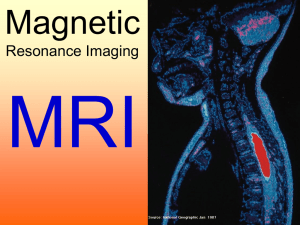
MRI
... strong resonance signal, and so MRI can be used to compare the blood content of different tissues. This is often greater in cancerous tissue, because of the high growth rates, and so MRI is an effective diagnostic tool for ...
... strong resonance signal, and so MRI can be used to compare the blood content of different tissues. This is often greater in cancerous tissue, because of the high growth rates, and so MRI is an effective diagnostic tool for ...
Inv 14
... have around your home, including the other magnet, interact with your reference magnet. Class 1 will be objects that are attracted to and repelled from your reference magnet. Class 2 will be objects that are only attracted to the reference magnet. Class 3 will be objects that are only repelled from ...
... have around your home, including the other magnet, interact with your reference magnet. Class 1 will be objects that are attracted to and repelled from your reference magnet. Class 2 will be objects that are only attracted to the reference magnet. Class 3 will be objects that are only repelled from ...
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 20 Physics: Principles with
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
... the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students exc ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.