JA3116861689
... conservation equation for incompressible fluids is gives as, ∇. U = 0 The conservation of momentum gives rise to Navier-Stroke’s equation as follows, ∂ρU + ∇. ρUU = −∇p + ∇. ϑ∇U + J × B ∂t Where, J × B is the Lorentz force density. The generalise Ohm’s law is written as, J = σ(E + U × B) Maxwell’s e ...
... conservation equation for incompressible fluids is gives as, ∇. U = 0 The conservation of momentum gives rise to Navier-Stroke’s equation as follows, ∂ρU + ∇. ρUU = −∇p + ∇. ϑ∇U + J × B ∂t Where, J × B is the Lorentz force density. The generalise Ohm’s law is written as, J = σ(E + U × B) Maxwell’s e ...
Carolyn Tewksbury
... the dike, Delaney and Pollard (1981) modeled the subsurface structure of the northeast dike and concluded that the en echelon segments formed due to rotation of the maximum horizontal compressive stress direction as the dike propagated vertically. They proposed that a main dike was located at depth, ...
... the dike, Delaney and Pollard (1981) modeled the subsurface structure of the northeast dike and concluded that the en echelon segments formed due to rotation of the maximum horizontal compressive stress direction as the dike propagated vertically. They proposed that a main dike was located at depth, ...
Force Field Physics - 8.PS.1
... CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.8.2f Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented. ...
... CCSS.ELA-Literacy.W.8.2f Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented. ...
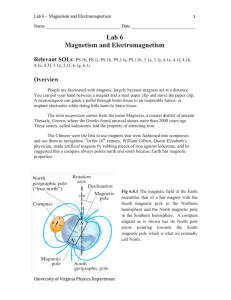
dA Chapter 3: Electricity and Magnetism Duration: 10 days Day 1
... An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. You have just made a mag ...
... An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. You have just made a mag ...
Electricity - Cobb Learning
... electricity as electric charges transfer from one object to another This means that when a negatively charged object and a positively charged object are brought together, electrons transfer until both objects have the same charge ...
... electricity as electric charges transfer from one object to another This means that when a negatively charged object and a positively charged object are brought together, electrons transfer until both objects have the same charge ...
Teaching Faraday`s law of electromagnetic induction in
... Although Eq. 共1兲 describes simple laboratory settings, it presents a conceptual challenge for students and teachers of introductory physics. We emphasize that the integral form of Faraday’s law in Eq. 共1兲 includes all cases, including transformer emf 共Ref. 1兲 and motional emf. In the latter case, Fa ...
... Although Eq. 共1兲 describes simple laboratory settings, it presents a conceptual challenge for students and teachers of introductory physics. We emphasize that the integral form of Faraday’s law in Eq. 共1兲 includes all cases, including transformer emf 共Ref. 1兲 and motional emf. In the latter case, Fa ...
Chapter 29 Slides - MSU Denver Sites
... • Follow the text discussion on the direction of the induced emf, using Figure 29.6 below. ...
... • Follow the text discussion on the direction of the induced emf, using Figure 29.6 below. ...
Chapter 7. Electrodynamics 7.1. Electromotive Force
... 0 J 0 B We thus conclude that Ampere's law does not hold for non-steady currents. The failure of Ampere's law can also be observed in a system in which a capacitor is being charged (see Figure 7.8). During the charging process a current I is flowing through the wire, and consequ ...
... 0 J 0 B We thus conclude that Ampere's law does not hold for non-steady currents. The failure of Ampere's law can also be observed in a system in which a capacitor is being charged (see Figure 7.8). During the charging process a current I is flowing through the wire, and consequ ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.